| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Grade 10, we studied how light is reflected and refracted. This chapter builds on what you have learnt in Grade 10. You will learn about lenses, how the human eye works as well as how telescopes and microscopes work.
In this section we will discuss properties of thin lenses . In Grade 10, you learnt about two kinds of mirrors: concave mirrors which were also known as converging mirrors and convex mirrors which were also known as diverging mirrors. Similarly, there are two types of lenses: converging and diverging lenses.
We have learnt how light travels in different materials, and we are now ready to learn how we can control the direction of light rays. We use lenses to control the direction of light. When light enters a lens, the light rays bend or change direction as shown in [link] .
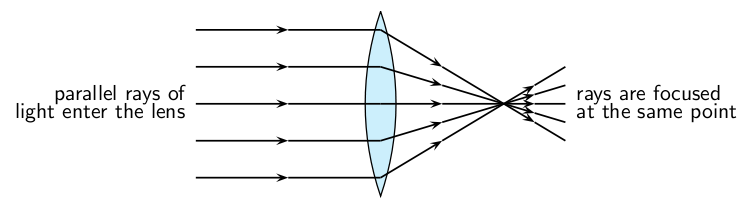
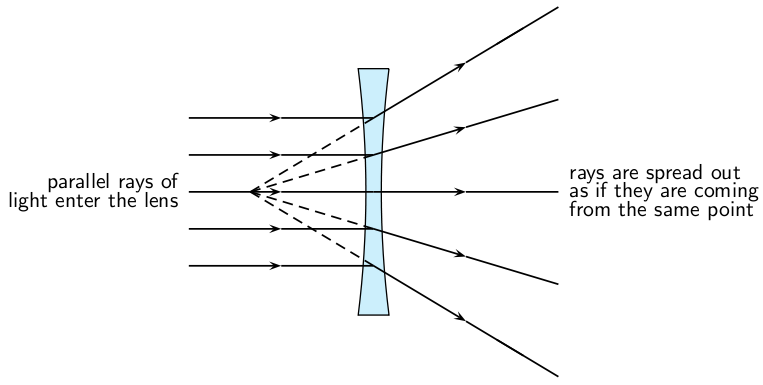
A lens is any transparent material (e.g. glass) of an appropriate shape that can take parallel rays of incident light and either converge the rays to a point or diverge the rays from a point.
Some lenses will focus light rays to a single point. These lenses are called converging or convex lenses. Other lenses spread out the light rays so that it looks like they all come from the same point. These lenses are called diverging or concave lenses. Lenses change the direction of light rays by refraction . They are designed so that the image appears in a certain place or as a certain size. Lenses are used in eyeglasses, cameras, microscopes, and telescopes. You also have lenses in your eyes!
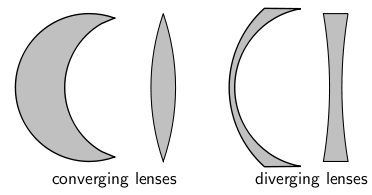
Converging lenses converge parallel rays of light and are thicker in the middle than at the edges.
Diverging lenses diverge parallel rays of light and are thicker at the edges than in the middle.
Examples of converging and diverging lenses are shown in [link] .
Before we study lenses in detail, there are a few important terms that must be defined. [link] shows important lens properties:
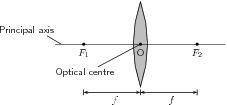
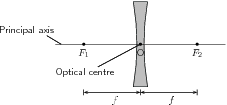
We will only discuss double convex converging lenses as shown in [link] . Converging lenses are thinner on the outside and thicker on the inside.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?