| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As we mentioned earlier, the distance of the earth from the sun is not the only reason that temperatures on earth are within a range that is suitable to support life. The composition of the atmosphere is also critically important.
The earth receives electromagnetic energy from the sun in the visible spectrum . There are also small amounts of infrared and ultraviolet radiation in this incoming solar energy. Most of the radiation is shortwave radiation, and it passes easily through the atmosphere towards the earth's surface, with some being reflected before reaching the surface. At the surface, some of the energy is absorbed, and this heats up the earth's surface. But the situation is a little more complex than this.
A large amount of the sun's energy is re-radiated from the surface back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation, which is invisible. As this radiation passes through the atmosphere, some of it is absorbed by greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapour and methane. These gases are very important because they re-emit the energy back towards the surface. By doing this, they help to warm the lower layers of the atmosphere even further. It is this 're-emission' of heat by greenhouse gases, combined with surface heating and other processes (e.g. conduction and convection) that maintain temperatures at exactly the right level to support life. Without the presence of greenhouse gases, most of the sun's energy would be lost and the Earth would be a lot colder than it is! A simplified diagram of the heating of the atmosphere is shown in [link] .
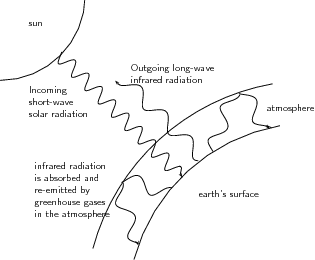
Many of the greenhouse gases occur naturally in small quantities in the atmosphere. However, human activities have greatly increased their concentration, and this has led to a lot of concern about the impact that this could have in increasing global temperatures. This phenomenon is known as global warming . Because the natural concentrations of these gases are low, even a small increase in their concentration as a result of human emissions, could have a big effect on temperature. But before we go on, let's look at where some of these human gas emissions come from.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?