| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Tension is the magnitude of the force that exists in objects like ropes, chains and struts that are providing support. For example, there are tension forces in the ropes supporting a child's swing hanging from a tree.
In this chapter we have come across a number of different types of forces, for example a push or a pull, tension in a string, frictional forces and the normal force. These are all examples of contact forces where there is a physical point of contact between applying the force and the object. Non-contact forces are forces that act over a distance, for example magnetic forces, electrostatic forces and gravitational forces.
When an object is placed on a surface, two types of surface forces can be identified. Friction is a force that acts between the surface and the object and is parallel to the surface. The normal force is a force that acts between the object and the surface and is perpendicular to the surface.
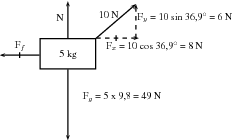
A 5 kg box is placed on a rough surface and a 10 N force is applied at an angle of 36,9 to the horizontal. The box does not move. The normal force (N or F ) is the force between the box and the surface acting in the vertical direction. If this force is not present the box would fall through the surface because the force of gravity pulls it downwards. The normal force therefore acts upwards. We can calculate the normal force by considering all the forces in the vertical direction. All the forces in the vertical direction must add up to zero because there is no movement in the vertical direction.
The most interesting and illustrative normal force question, that is often asked, has to do with a scale in a lift. Using Newton's third law we can solve these problems quite easily.
When you stand on a scale to measure your weight you are pulled down by gravity. There is no acceleration downwards because there is a reaction force we call the normal force acting upwards on you. This is the force that the scale would measure. If the gravitational force were less then the reading on the scale would be less.
A man with a mass of 100 kg stands on a scale (measuring newtons). What is the reading on the scale?
We are given the mass of the man. We know the gravitational acceleration that acts on him is 9,8 = m s .
The scale measures the normal force on the man. This is the force that balances gravity. We can use Newton's laws to solve the problem:
where is the resultant force on the man.
We now know the gravitational force downwards. We know that the sum of all the forces must equal the resultant acceleration times the mass. The overall resultant acceleration of the man on the scale is 0 - so .
The normal force is 980 N upwards. It exactly balances the gravitational force downwards so there is no net force and no acceleration on the man. The reading on the scale is 980 N.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?