| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A mass of 250.0 g is suspended from a spring hanging vertically. The spring stretches 6.00 cm. How much will the spring stretch if the suspended mass is 530.0 g?
As shown below, two identical springs, each with the spring constant 20 N/m, support a 15.0-N weight. (a) What is the tension in spring A? (b) What is the amount of stretch of spring A from the rest position?
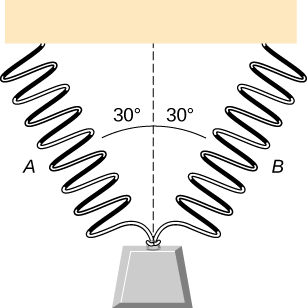
a. 8.66 N; b. 0.433 m
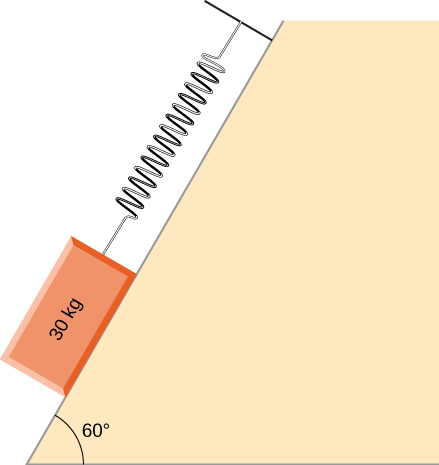
Shown below is a 30.0-kg block resting on a frictionless ramp inclined at to the horizontal. The block is held by a spring that is stretched 5.0 cm. What is the force constant of the spring?
In building a house, carpenters use nails from a large box. The box is suspended from a spring twice during the day to measure the usage of nails. At the beginning of the day, the spring stretches 50 cm. At the end of the day, the spring stretches 30 cm. What fraction or percentage of the nails have been used?
0.40 or 40%
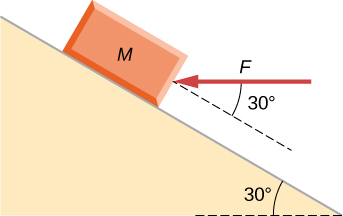
A force is applied to a block to move it up a incline. The incline is frictionless. If and , what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block?
Two forces are applied to a 5.0-kg object, and it accelerates at a rate of in the positive y -direction. If one of the forces acts in the positive x -direction with magnitude 12.0 N, find the magnitude of the other force.
16 N
The block on the right shown below has more mass than the block on the left ( ). Draw free-body diagrams for each block.
If two tugboats pull on a disabled vessel, as shown here in an overhead view, the disabled vessel will be pulled along the direction indicated by the result of the exerted forces. (a) Draw a free-body diagram for the vessel. Assume no friction or drag forces affect the vessel. (b) Did you include all forces in the overhead view in your free-body diagram? Why or why not?
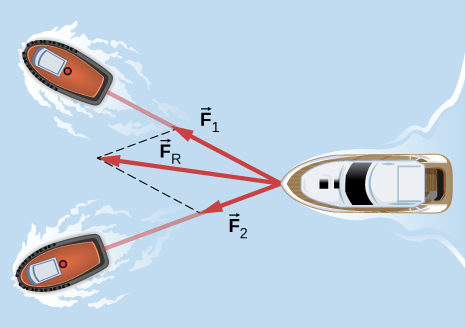
a.
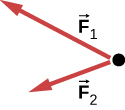 ; b. No;
is not shown, because it would replace
and
. (If we want to show it, we could draw it and then place squiggly lines on
and
to show that they are no longer considered.
; b. No;
is not shown, because it would replace
and
. (If we want to show it, we could draw it and then place squiggly lines on
and
to show that they are no longer considered.
A 10.0-kg object is initially moving east at 15.0 m/s. Then a force acts on it for 2.00 s, after which it moves northwest, also at 15.0 m/s. What are the magnitude and direction of the average force that acted on the object over the 2.00-s interval?
On June 25, 1983, shot-putter Udo Beyer of East Germany threw the 7.26-kg shot 22.22 m, which at that time was a world record. (a) If the shot was released at a height of 2.20 m with a projection angle of , what was its initial velocity? (b) If while in Beyer’s hand the shot was accelerated uniformly over a distance of 1.20 m, what was the net force on it?
a. 14.1 m/s; b. 601 N
A body of mass m moves in a horizontal direction such that at time t its position is given by where a , b , and c are constants. (a) What is the acceleration of the body? (b) What is the time-dependent force acting on the body?
A body of mass m has initial velocity in the positive x -direction. It is acted on by a constant force F for time t until the velocity becomes zero; the force continues to act on the body until its velocity becomes in the same amount of time. Write an expression for the total distance the body travels in terms of the variables indicated.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?