| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When discussing the Doppler effect of a moving source and a stationary observer, the only cases we considered were cases where the source was moving at speeds that were less than the speed of sound. Recall that the observed frequency for a moving source approaching a stationary observer is As the source approaches the speed of sound, the observed frequency increases. According to the equation, if the source moves at the speed of sound, the denominator is equal to zero, implying the observed frequency is infinite. If the source moves at speeds greater than the speed of sound, the observed frequency is negative.
What could this mean? What happens when a source approaches the speed of sound? It was once argued by some scientists that such a large pressure wave would result from the constructive interference of the sound waves, that it would be impossible for a plane to exceed the speed of sound because the pressures would be great enough to destroy the airplane. But now planes routinely fly faster than the speed of sound. On July 28, 1976, Captain Eldon W. Joersz and Major George T. Morgan flew a Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird #61-7958 at 3529.60 km/h (2193.20 mi/h), which is Mach 2.85. The Mach number is the speed of the source divided by the speed of sound:
You will see that interesting phenomena occur when a source approaches and exceeds the speed of sound.
What happens to the sound produced by a moving source, such as a jet airplane, that approaches or even exceeds the speed of sound? The answer to this question applies not only to sound but to all other waves as well. Suppose a jet plane is coming nearly straight at you, emitting a sound of frequency The greater the plane’s speed the greater the Doppler shift and the greater the value observed for ( [link] ).
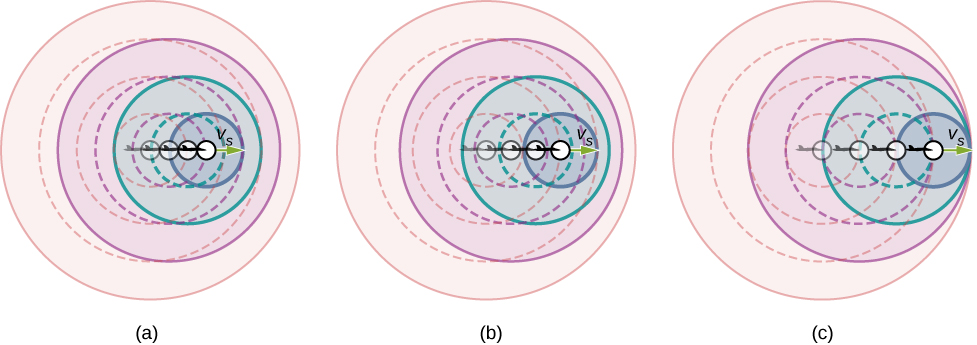
Now, as approaches the speed of sound, approaches infinity, because the denominator in approaches zero. At the speed of sound, this result means that in front of the source, each successive wave interferes with the previous one because the source moves forward at the speed of sound. The observer gets them all at the same instant, so the frequency is infinite [part (c) of the figure].
If the source exceeds the speed of sound, no sound is received by the observer until the source has passed, so that the sounds from the approaching source are mixed with those from it when receding. This mixing appears messy, but something interesting happens—a shock wave is created ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?