| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Throughout this chapter, we have been studying traveling waves, or waves that transport energy from one place to another. Under certain conditions, waves can bounce back and forth through a particular region, effectively becoming stationary. These are called standing wave s .
Another related effect is known as resonance . In Oscillations , we defined resonance as a phenomenon in which a small-amplitude driving force could produce large-amplitude motion. Think of a child on a swing, which can be modeled as a physical pendulum. Relatively small-amplitude pushes by a parent can produce large-amplitude swings. Sometimes this resonance is good—for example, when producing music with a stringed instrument. At other times, the effects can be devastating, such as the collapse of a building during an earthquake. In the case of standing waves, the relatively large amplitude standing waves are produced by the superposition of smaller amplitude component waves.
Sometimes waves do not seem to move; rather, they just vibrate in place. You can see unmoving waves on the surface of a glass of milk in a refrigerator, for example. Vibrations from the refrigerator motor create waves on the milk that oscillate up and down but do not seem to move across the surface. [link] shows an experiment you can try at home. Take a bowl of milk and place it on a common box fan. Vibrations from the fan will produce circular standing waves in the milk. The waves are visible in the photo due to the reflection from a lamp. These waves are formed by the superposition of two or more traveling waves, such as illustrated in [link] for two identical waves moving in opposite directions. The waves move through each other with their disturbances adding as they go by. If the two waves have the same amplitude and wavelength, then they alternate between constructive and destructive interference. The resultant looks like a wave standing in place and, thus, is called a standing wave.

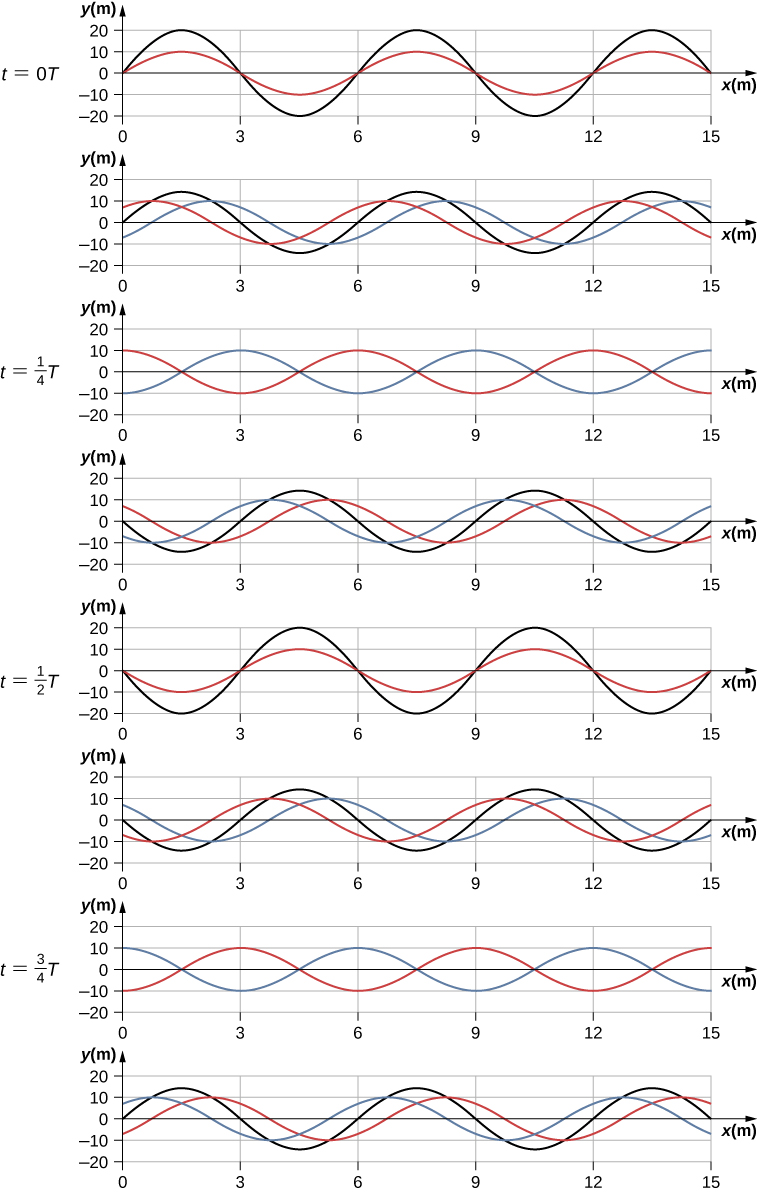
Consider two identical waves that move in opposite directions. The first wave has a wave function of and the second wave has a wave function . The waves interfere and form a resultant wave

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?