| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
So far in this text, we have mainly studied translational motion, including the variables that describe it: displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Now we expand our description of motion to rotation—specifically, rotational motion about a fixed axis. We will find that rotational motion is described by a set of related variables similar to those we used in translational motion.
Uniform circular motion (discussed previously in Motion in Two and Three Dimensions ) is motion in a circle at constant speed. Although this is the simplest case of rotational motion, it is very useful for many situations, and we use it here to introduce rotational variables.
In [link] , we show a particle moving in a circle. The coordinate system is fixed and serves as a frame of reference to define the particle’s position. Its position vector from the origin of the circle to the particle sweeps out the angle , which increases in the counterclockwise direction as the particle moves along its circular path. The angle is called the angular position of the particle. As the particle moves in its circular path, it also traces an arc length s .
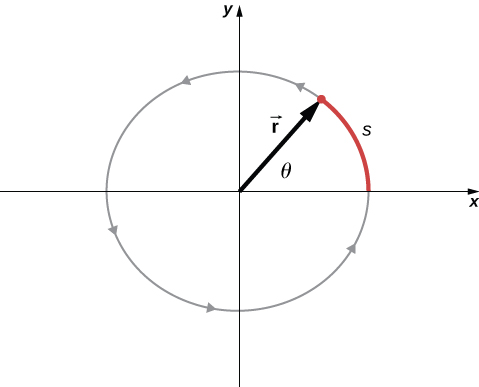
The angle is related to the radius of the circle and the arc length by
The angle , the angular position of the particle along its path, has units of radians (rad). There are radians in Note that the radian measure is a ratio of length measurements, and therefore is a dimensionless quantity. As the particle moves along its circular path, its angular position changes and it undergoes angular displacements
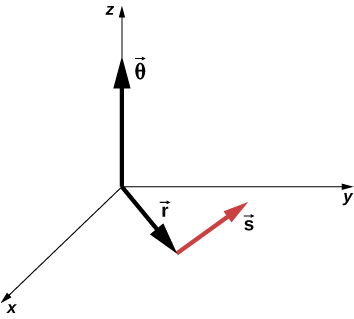
We can assign vectors to the quantities in [link] . The angle is a vector out of the page in [link] . The angular position vector and the arc length both lie in the plane of the page. These three vectors are related to each other by
That is, the arc length is the cross product of the angle vector and the position vector, as shown in [link] .
The magnitude of the angular velocity , denoted by , is the time rate of change of the angle as the particle moves in its circular path. The instantaneous angular velocity is defined as the limit in which in the average angular velocity :

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?