| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Drawings using lines to represent electric fields around charged objects are very useful in visualizing field strength and direction. Since the electric field has both magnitude and direction, it is a vector. Like all vectors , the electric field can be represented by an arrow that has length proportional to its magnitude and that points in the correct direction. (We have used arrows extensively to represent force vectors, for example.)
[link] shows two pictorial representations of the same electric field created by a positive point charge . [link] (b) shows the standard representation using continuous lines. [link] (b) shows numerous individual arrows with each arrow representing the force on a test charge . Field lines are essentially a map of infinitesimal force vectors.
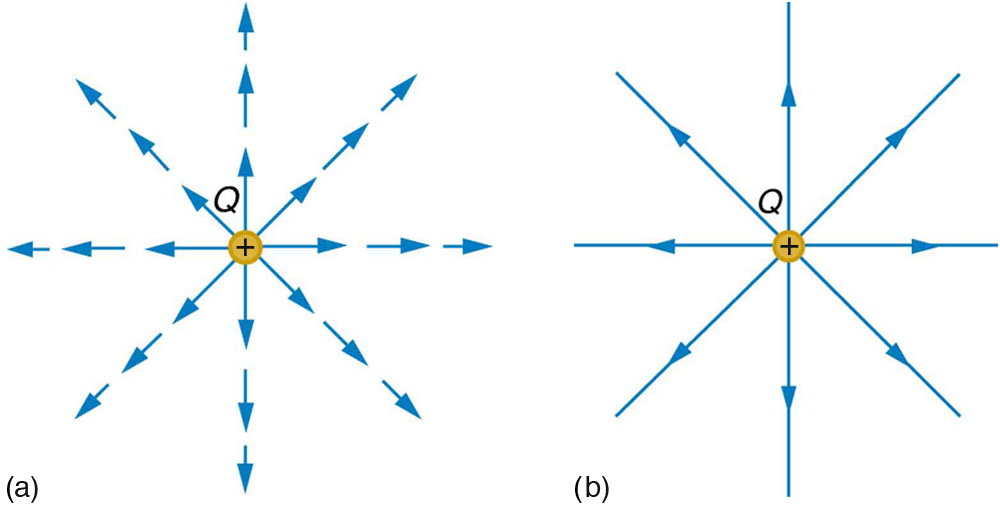
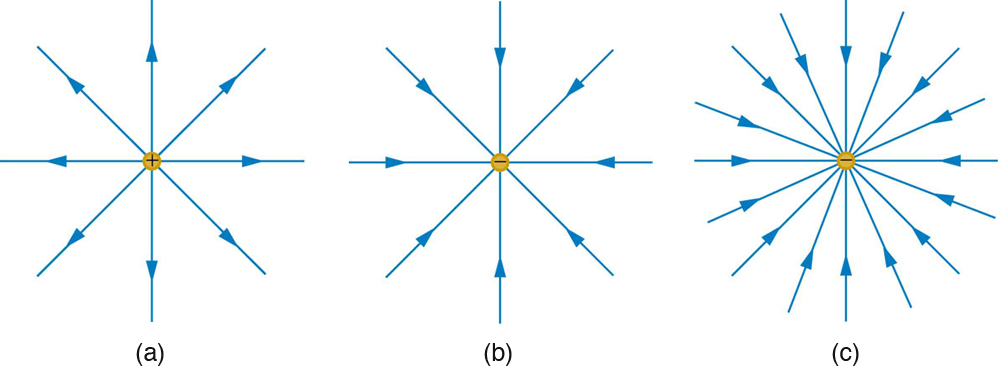
Note that the electric field is defined for a positive test charge , so that the field lines point away from a positive charge and toward a negative charge. (See [link] .) The electric field strength is exactly proportional to the number of field lines per unit area, since the magnitude of the electric field for a point charge is and area is proportional to . This pictorial representation, in which field lines represent the direction and their closeness (that is, their areal density or the number of lines crossing a unit area) represents strength, is used for all fields: electrostatic, gravitational, magnetic, and others.
In many situations, there are multiple charges. The total electric field created by multiple charges is the vector sum of the individual fields created by each charge. The following example shows how to add electric field vectors.
Find the magnitude and direction of the total electric field due to the two point charges, and , at the origin of the coordinate system as shown in [link] .
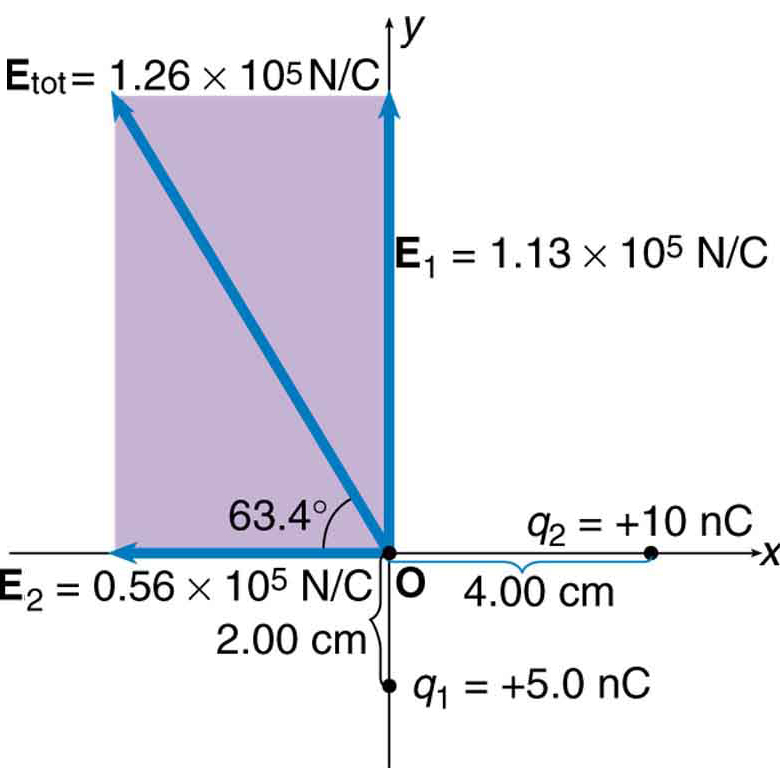
Strategy
Since the electric field is a vector (having magnitude and direction), we add electric fields with the same vector techniques used for other types of vectors. We first must find the electric field due to each charge at the point of interest, which is the origin of the coordinate system (O) in this instance. We pretend that there is a positive test charge, , at point O, which allows us to determine the direction of the fields and . Once those fields are found, the total field can be determined using vector addition .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?