| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The questions have been selected to enhance understanding of the topics covered in the module titled " Angular momentum ". All questions are multiple choice questions with one or more correct answers. There are two sets of the questions. The “understanding level” questions seek to unravel the fundamental concepts involved, whereas “application level” are relatively difficult, which may interlink concepts from other topics.
Each of the questions is provided with solution. However, it is recommended that solutions may be seen only when your answers do not match with the ones given at the end of this module.
Two particles of same mass, move with same speed along two parallel lines in opposite directions as shown in the figure. Then, magnitude of net angular moment of two particles about the origin of coordinate system :
Two moving particles
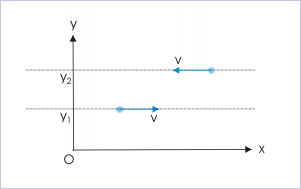
Here, moment arms of the particles are and . Let the mass of each particle be “m” and speed of each particle is “v”. Then, the angular momentum of the individual particles about the origin of coordinate system are :
Since angular momentum are along the same direction, we can find the net angular momentum by arithmetic sum as :
We see that the magnitude of net angular momentum is directly proportional to the perpendicular distance between the parallel lines. Further, the perpendicular distance is fixed for a given pair of parallel paths. Hence, net angular momentum is constant for a given pair.
Hence, options (a) and (c) are correct.
A particle of mass “m” is moving with linear velocity v = (2 i – j + k ) m/s. At an instant, the particle is situated at a position (in meters) given by the coordinates 0,1,1. What is the angular momentum of the particle about the origin of coordinate system at that instant?
This question can be evaluated using cross product in component form as :
ℓ = |
i
j
k |
| 0 1 1 || 2 -1 1 |
Hence, option (b) is correct.
A projectile of mass “m” is projected with a velocity “v”, making and angle “θ” with the horizontal. The angular momentum of the projectile about the point of projection, when it reaches the highest point is :
Projectile
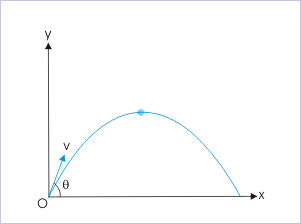
The velocity of the projectile at the highest point is equal to the horizontal component of velocity as vertical component of velocity is zero. Further, there is no acceleration in the horizontal direction. Therefore, horizontal component of velocity is same as the horizontal component of the velocity at projection. It means that velocity of projection at the highest point is :
Projectile motion
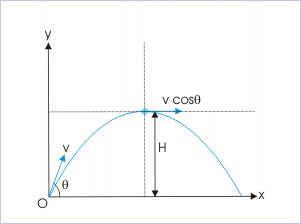
Here, the moment arm i.e. the perpendicular drawn from the point of projection on the extended line of velocity is equal to the height attained by the projectile. Thus,
The angular momentum as required is :
Hence, option (a) is correct.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?