| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The pure rolling is a combination of pure rotation and translation. Obviously, it can not be termed as pure rotation as far as the actual motion is concerned. We can, however, exploit the fact that the disk in rolling is actually rotating at any given instant - not over a period but for an instant. This enables us with a very powerful alternative technique to analyze rolling motion.
The alternative consideration assumes rotation about an axis passing through the point of contact and perpendicular to the plane of rotating disk. Each particle can be considered to rotate about the axis instantaneously i.e. at a particular instant. Clearly, this is an equivalent analysis paradigm that gives the same result as when rolling motion is considered as combination of rotation and translation.
Rolling motion as pure rotation
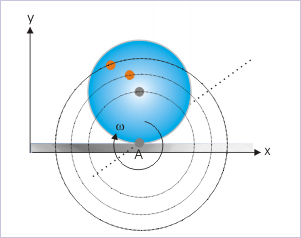
Under this alternative analysis framework, the angular velocities of all particles about this instantaneously stationary axis are considered same. Importantly, this unique angular velocity is equal to angular velocity of rolling (ω). Depending on the linear distance of the particles from the contact point, their linear velocity vary. This alternative framework is consistent with the fact that linear velocities of the particles away from the point of contact are indeed greater as worked out in previous module titled " Rolling motion ".
Rolling motion as pure rotation
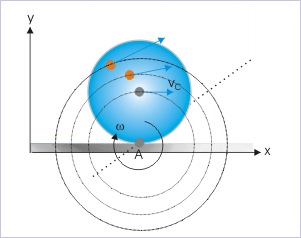
The most important aspect of the equivalence of analysis frameworks, as described earlier, is that rolling motion, which is a combination of pure translation and rotation in physical sense, is described in terms of pure rotation only for the analysis of the motion. In this analysis, we do not need to consider translation at all, as if the rolling body were stationary.
In the nutshell, the equivalent description of rolling in terms of pure rolling has following important considerations :
1. The axis of rotation through contact point is parallel to central axis. This axis is instantaneously at rest and is also referred as "Instantaneous axis of rotation (IAOR)"
2. Each particle of the body is rotating about IAOR with an angular velocity given by :
where " " is the linear velocity of center of mass and "R" is the radius of the disk.
3. The linear velocity of any of the position within the rotating disk is obtained by using the relation,
The vector notation of the relation above is important. It emphasizes that the linear velocity is directed such that it is perpendicular to both angular velocity vector ( ω ) and position vector ( r ). In the figure below, the vector ω is into the plane of figure i.e. angular velocity vector is perpendicular to xy-plane. The velocity vector being perpendicular to angular velocity vector, therefore, lies in xy-plane. Further, the velocity vector is perpendicular to the positions vector drawn from the point of contact. Note that this is the requirement of pure rotation. The linear velocity should be tangential to the circular path of the particle about the axis in pure rotation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?