| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Work is itself energy, but plays a specific role with respect to other forms for energy. Its relationship with different energy forms will automatically come to the fore as we investigate them. In this module, we shall investigate the relationship between work and kinetic energy.
To appreciate the connection between work and kinetic energy, let us consider a block, which is moving with a speed "v" in a straight line on a rough horizontal plane. The kinetic friction opposes the motion and eventually brings the block to rest after a displacement say "r".
A block is brought to rest by friction
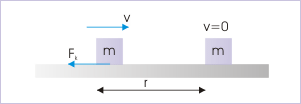
Here, kinetic friction is equal to the product of coefficient of kinetic friction and normal force applied by the horizontal surface on the block,
Kinetic friction opposes the motion of the block with deceleration, a, :
Considering motion in x-direction and using equation of motion for deacceleration, , we have :
Thus, kinetic energy of the block in the beginning of motion is :
A close inspection of the expression of initial kinetic energy as calculated above reveals that the expression is equal to the magnitude of work done by the kinetic friction to bring the block to rest from its initial sate of motion. The magnitude of work done by the kinetic friction is :
This brings up to a new definition of kinetic energy :
Work - kinetic energy theorem is a generalized description of motion - not specific to any force type like gravity or friction. We shall, here, formally write work - kinetic energy theorem considering an external force. The application of a constant external force results in the change in kinetic energy of the particle. For the time being, we consider a "constant" external force. At the end of this module, we shall extend the concept to variable force as well.
Let be the initial speed of the particle, when we start observing motion. Now, the acceleration of the particle is :
A force moves the block on a horizontal surface
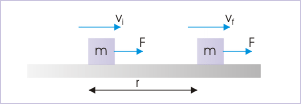
Let the final velocity of the particle be . Then using equation of motion, ,
Multiplying each term by 1/2 m, we have :
This is the equation, which is known as work - kinetic energy theorem. In words, change in kinetic energy resulting from application of external force(s) is equal to the work done by the force(s). Equivalently, work done by the force(s) in displacing a particle is equal to change in the kinetic energy of the particle. The above work - kinetic energy equation can be rearranged as :
In this form, work - kinetic energy theorem states that kinetic energy changes by the amount of work done on the particle. We know that work can be either positive or negative. Hence, positive work results in an increase of the kinetic energy and negative work results in a decrease of the kinetic energy by the amount of work done on the particle. It is emphasized here for clarity that "work" in the theorem refers to work by "net" force - not individual force.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics for k-12' conversation and receive update notifications?