| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When the force acting on an object is parallel to the direction of the motion of the center of mass, the mechanical energy ____. When the force acting on an object is antiparallel to the direction of the center of mass, the mechanical energy ____.
Describe a system in which the main forces acting are parallel or antiparallel to the center of mass, and justify your answer.
The potato cannon (and many other projectile launchers) above is an option, with a force launching the projectile, friction, potentially gravity depending on the direction it is pointed, etc. A drag (or other) car accelerating is another possibility.
A child is pulling two red wagons, with the second one tied to the first by a (non-stretching) rope. Each wagon has a mass of 10 kg. If the child exerts a force of 30 N for 5.0 m, how much has the kinetic energy of the two-wagon system changed?
A child has two red wagons, with the rear one tied to the front by a (non-stretching) rope. If the child pushes on the rear wagon, what happens to the kinetic energy of each of the wagons, and the two-wagon system?
The kinetic energy of the rear wagon increases. The front wagon does not, until the rear wagon collides with it. The total system may be treated by its center of mass, halfway between the wagons, and its energy increases by the same amount as the sum of the two individual wagons.
Draw a graph of the force parallel to displacement exerted on a stunt motorcycle going through a loop-the-loop versus the distance traveled around the loop. Explain the net change in energy.
The person in [link] does work on the lawn mower. Under what conditions would the mower gain energy? Under what conditions would it lose energy?
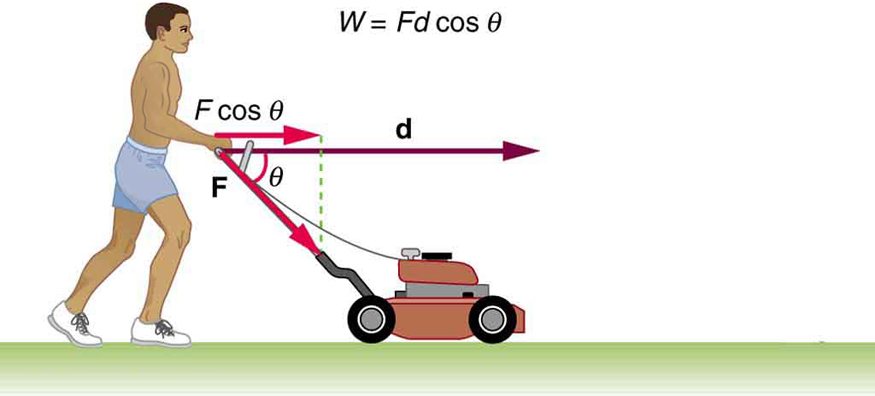
Work done on a system puts energy into it. Work done by a system removes energy from it. Give an example for each statement.
When solving for speed in [link] , we kept only the positive root. Why?
Compare the kinetic energy of a 20,000-kg truck moving at 110 km/h with that of an 80.0-kg astronaut in orbit moving at 27,500 km/h.
(a) How fast must a 3000-kg elephant move to have the same kinetic energy as a 65.0-kg sprinter running at 10.0 m/s? (b) Discuss how the larger energies needed for the movement of larger animals would relate to metabolic rates.
Confirm the value given for the kinetic energy of an aircraft carrier in [link] . You will need to look up the definition of a nautical mile (1 knot = 1 nautical mile/h).
(a) Calculate the force needed to bring a 950-kg car to rest from a speed of 90.0 km/h in a distance of 120 m (a fairly typical distance for a non-panic stop). (b) Suppose instead the car hits a concrete abutment at full speed and is brought to a stop in 2.00 m. Calculate the force exerted on the car and compare it with the force found in part (a).
A car’s bumper is designed to withstand a 4.0-km/h (1.1-m/s) collision with an immovable object without damage to the body of the car. The bumper cushions the shock by absorbing the force over a distance. Calculate the magnitude of the average force on a bumper that collapses 0.200 m while bringing a 900-kg car to rest from an initial speed of 1.1 m/s.
Boxing gloves are padded to lessen the force of a blow. (a) Calculate the force exerted by a boxing glove on an opponent’s face, if the glove and face compress 7.50 cm during a blow in which the 7.00-kg arm and glove are brought to rest from an initial speed of 10.0 m/s. (b) Calculate the force exerted by an identical blow in the gory old days when no gloves were used and the knuckles and face would compress only 2.00 cm. (c) Discuss the magnitude of the force with glove on. Does it seem high enough to cause damage even though it is lower than the force with no glove?
Using energy considerations, calculate the average force a 60.0-kg sprinter exerts backward on the track to accelerate from 2.00 to 8.00 m/s in a distance of 25.0 m, if he encounters a headwind that exerts an average force of 30.0 N against him.
102 N

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?