| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Solution for (a)
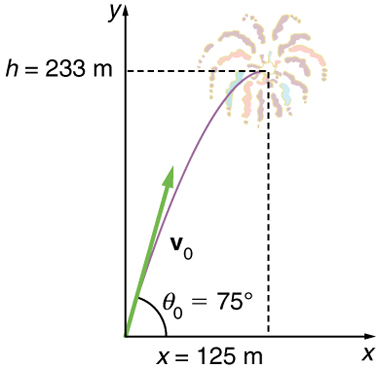
By “height” we mean the altitude or vertical position above the starting point. The highest point in any trajectory, called the apex, is reached when . Since we know the initial and final velocities as well as the initial position, we use the following equation to find :
Because and are both zero, the equation simplifies to
Solving for gives
Now we must find , the component of the initial velocity in the y -direction. It is given by , where is the initial velocity of 70.0 m/s, and is the initial angle. Thus,
and is
so that
Discussion for (a)
Note that because up is positive, the initial velocity is positive, as is the maximum height, but the acceleration due to gravity is negative. Note also that the maximum height depends only on the vertical component of the initial velocity, so that any projectile with a 67.6 m/s initial vertical component of velocity will reach a maximum height of 233 m (neglecting air resistance). The numbers in this example are reasonable for large fireworks displays, the shells of which do reach such heights before exploding. In practice, air resistance is not completely negligible, and so the initial velocity would have to be somewhat larger than that given to reach the same height.
Solution for (b)
As in many physics problems, there is more than one way to solve for the time to the highest point. In this case, the easiest method is to use . Because is zero, this equation reduces to simply
Note that the final vertical velocity, , at the highest point is zero. Thus,
Discussion for (b)
This time is also reasonable for large fireworks. When you are able to see the launch of fireworks, you will notice several seconds pass before the shell explodes. (Another way of finding the time is by using , and solving the quadratic equation for .)
Solution for (c)
Because air resistance is negligible, and the horizontal velocity is constant, as discussed above. The horizontal displacement is horizontal velocity multiplied by time as given by , where is equal to zero:
where is the x -component of the velocity, which is given by Now,
The time for both motions is the same, and so is
Discussion for (c)
The horizontal motion is a constant velocity in the absence of air resistance. The horizontal displacement found here could be useful in keeping the fireworks fragments from falling on spectators. Once the shell explodes, air resistance has a major effect, and many fragments will land directly below.
In solving part (a) of the preceding example, the expression we found for is valid for any projectile motion where air resistance is negligible. Call the maximum height ; then,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?