| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

No one knows exactly when viruses emerged or from where they came, since viruses do not leave historical footprints such as fossils. Modern viruses are thought to be a mosaic of bits and pieces of nucleic acids picked up from various sources along their respective evolutionary paths. Viruses are acellular , parasitic entities that are not classified within any domain because they are not considered alive. They have no plasma membrane, internal organelles, or metabolic processes, and they do not divide. Instead, they infect a host cell and use the host’s replication processes to produce progeny virus particles. Viruses infect all forms of organisms including bacteria, archaea, fungi, plants, and animals. Living things grow, metabolize, and reproduce. Viruses replicate, but to do so, they are entirely dependent on their host cells. They do not metabolize or grow, but are assembled in their mature form.
Viruses are diverse. They vary in their structure, their replication methods, and in their target hosts or even host cells. While most biological diversity can be understood through evolutionary history, such as how species have adapted to conditions and environments, much about virus origins and evolution remains unknown.
Viruses were first discovered after the development of a porcelain filter, called the Chamberland-Pasteur filter, which could remove all bacteria visible under the microscope from any liquid sample. In 1886, Adolph Meyer demonstrated that a disease of tobacco plants, tobacco mosaic disease, could be transferred from a diseased plant to a healthy one through liquid plant extracts. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanowski showed that this disease could be transmitted in this way even after the Chamberland-Pasteur filter had removed all viable bacteria from the extract. Still, it was many years before it was proven that these “filterable” infectious agents were not simply very small bacteria but were a new type of tiny, disease-causing particle.
Virions, single virus particles, are very small, about 20–250 nanometers (1 nanometer = 1/1,000,000 mm). These individual virus particles are the infectious form of a virus outside the host cell. Unlike bacteria (which are about 100 times larger), we cannot see viruses with a light microscope, with the exception of some large virions of the poxvirus family ( [link] ).
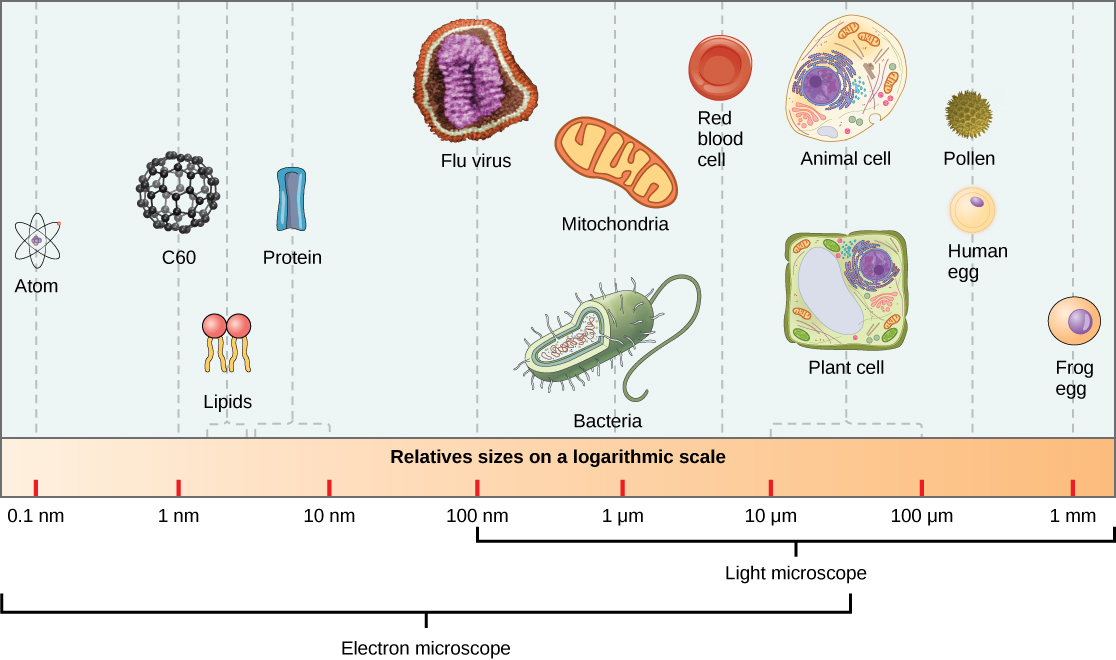
It was not until the development of the electron microscope in the 1940s that scientists got their first good view of the structure of the tobacco mosaic virus ( [link] ) and others. The surface structure of virions can be observed by both scanning and transmission electron microscopy, whereas the internal structures of the virus can only be observed in images from a transmission electron microscope ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology for the university of georgia' conversation and receive update notifications?