| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Why study ecology? Perhaps you are interested in learning about the natural world and how living things have adapted to the physical conditions of their environment. Or, perhaps you’re a future physician seeking to understand the connection between human health and ecology.
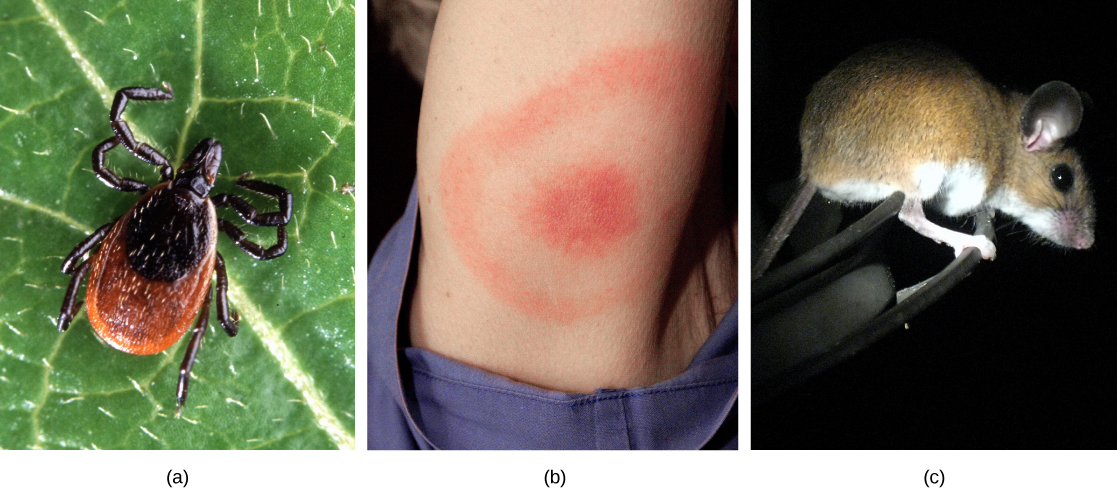
Humans are a part of the ecological landscape, and human health is one important part of human interaction with our physical and living environment. Lyme disease, for instance, serves as one modern-day example of the connection between our health and the natural world ( [link] ). More formally known as Lyme borreliosis, Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that can be transmitted to humans when they are bitten by the deer tick ( Ixodes scapularis ), which is the primary vector for this disease. However, not all deer ticks carry the bacteria that will cause Lyme disease in humans, and I. scapularis can have other hosts besides deer. In fact, it turns out that the probability of infection depends on the type of host upon which the tick develops: a higher proportion of ticks that live on white-footed mice carry the bacterium than do ticks that live on deer. Knowledge about the environments and population densities in which the host species is abundant would help a physician or an epidemiologist better understand how Lyme disease is transmitted and how its incidence could be reduced.
Ecology is the study of the interactions of living organisms with their environment. One core goal of ecology is to understand the distribution and abundance of living things in the physical environment. Attainment of this goal requires the integration of scientific disciplines inside and outside of biology, such as biochemistry, physiology, evolution, biodiversity, molecular biology, geology, and climatology. Some ecological research also applies aspects of chemistry and physics, and it frequently uses mathematical models.
Climate change can alter where organisms live, which can sometimes directly affect human health. Watch the PBS video “Feeling the Effects of Climate Change” in which researchers discover a pathogenic organism living far outside of its normal range.
When a discipline such as biology is studied, it is often helpful to subdivide it into smaller, related areas. For instance, cell biologists interested in cell signaling need to understand the chemistry of the signal molecules (which are usually proteins) as well as the result of cell signaling. Ecologists interested in the factors that influence the survival of an endangered species might use mathematical models to predict how current conservation efforts affect endangered organisms. To produce a sound set of management options, a conservation biologist needs to collect accurate data, including current population size, factors affecting reproduction (like physiology and behavior), habitat requirements (such as plants and soils), and potential human influences on the endangered population and its habitat (which might be derived through studies in sociology and urban ecology). Within the discipline of ecology, researchers work at four specific levels, sometimes discretely and sometimes with overlap: organism, population, community, and ecosystem ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bi 101 for lbcc ilearn campus' conversation and receive update notifications?