| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The Group 2 metals have a particular name: the alkaline earth metals. The name is derived from the observation that they have such high melting points ( [link] ) that they remain solids (“earths”) in a fire. [link] lists the derivation of the names of the alkali metals.
| Alkali metal | Melting point (°C) | Alkaline earth metal | Melting point (°C) |
| Li | 180.54 | Be | 1287 |
| Na | 97.72 | Mg | 650 |
| K | 63.38 | Ca | 842 |
| Rb | 39.31 | Sr | 777 |
| Cs | 28.44 | Ba | 727 |
| Fr | 27 (estimated) | Ra | 700 |
| Element | Symbol | Name |
| Beryllium | Be | From the Greek bērullos meaning to become pale , in reference to the pale semiprecious gemstone beryl |
| Magnesium | Mg | From the Magnesia district in Greece |
| Calcium | Ca | From the Latin calcis meaning lime |
| Strontium | Sr | From the mineral strontianite named after the Scottish village of Strontian |
| Barium | Ba | From the Greek bary , meaning heavy |
| Radium | Ra | From the Latin radius meaning ray |
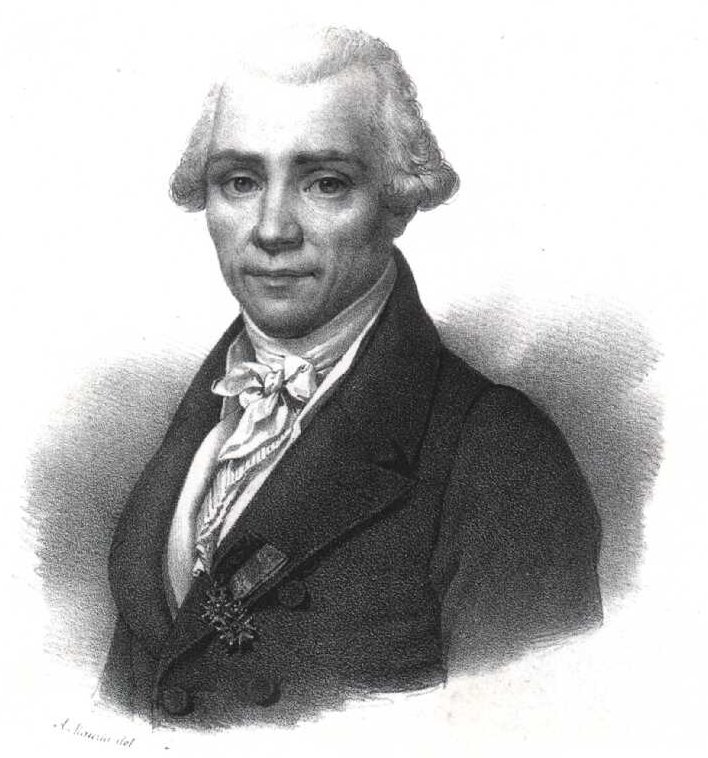
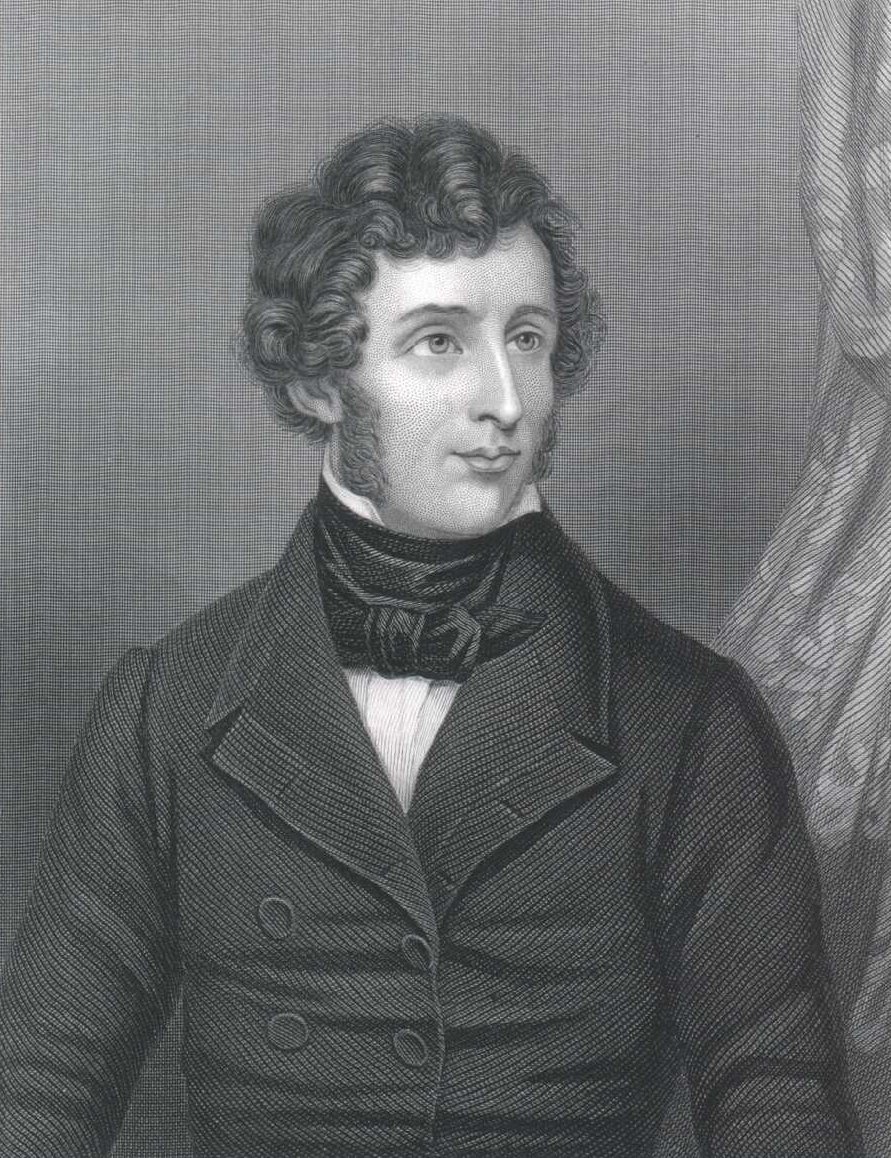
Beryllium was discovered by Louis-Nicolas Vauquelin ( [link] ) in 1798 as a component in beryls and emeralds; however, Fredrich Wöhler ( [link] ) and Antoine Bussy ( [link] ) independently isolated the metal in 1828 by reacting potassium with beryllium chloride, [link] .


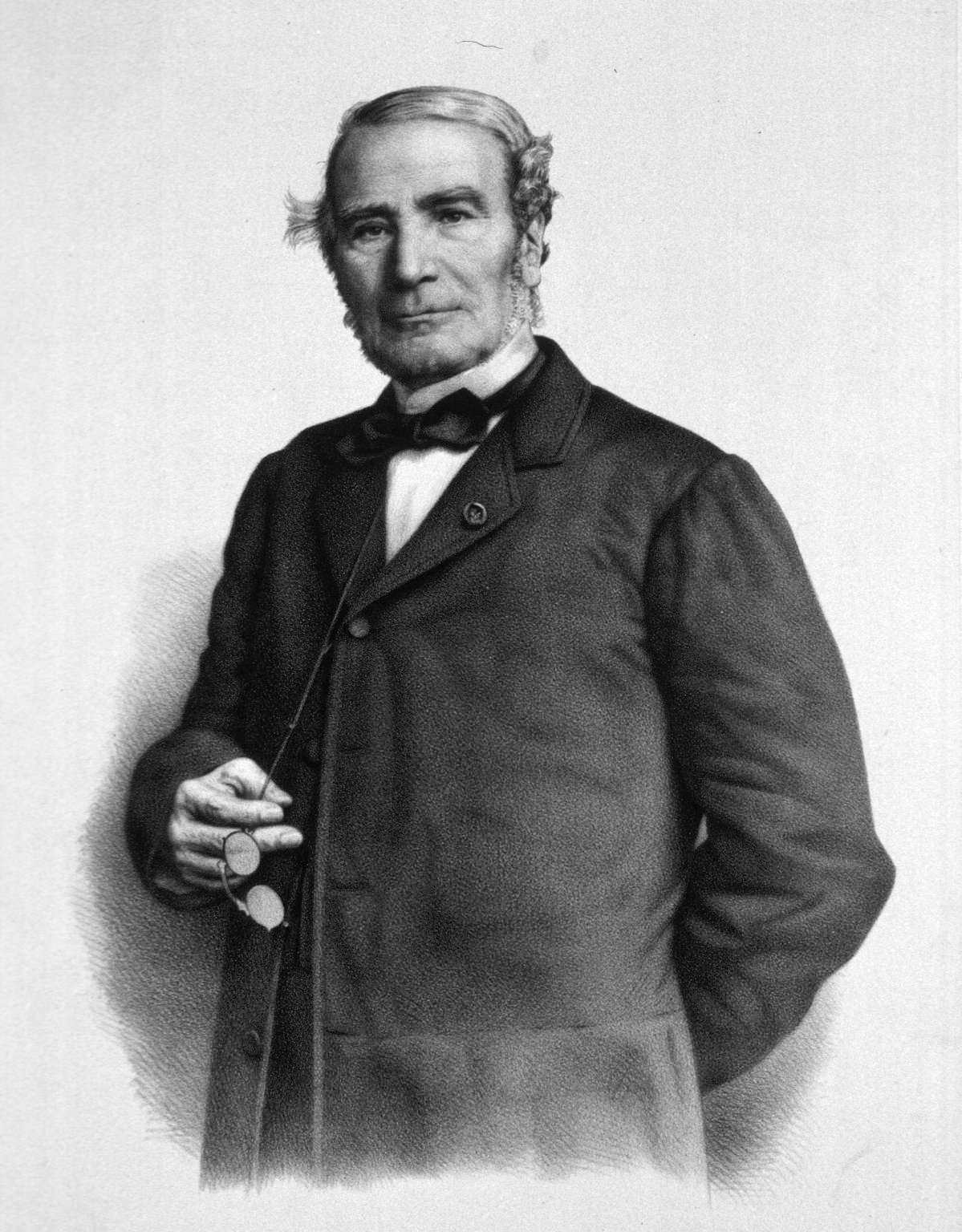
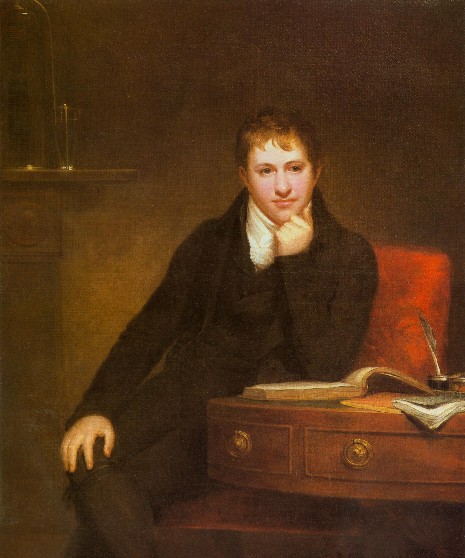
Magnesium is found in large deposits of magnesite and dolomite, and in mineral waters where the Mg 2+ ion is soluble. In 1618 a farmer at Epsom in England attempted to give his cows water from a well. The farmer noticed that the water seemed to heal scratches and rashes. These Epsom salts were recognized to be hydrated magnesium sulfate, MgSO 4 . The metal was first isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy ( [link] ) via the electrolysis of a mixture of magnesia and mercury oxide.

Antoine Bussy ( [link] ) subsequently prepared magnesium by heating magnesium chloride and potassium in a glass tube, [link] . When the potassium chloride was washed out, small globules of magnesium remained.
Calcium oxide or lime was known in ancient Rome, while even in 975 AD, Plaster of Paris (calcium sulphate) was reported to be useful for setting broken bones. The element itself was not isolated until 1808 when Sir Humphry Davy ( [link] ) electrolyzed a mixture of lime and mercuric oxide (HgO). His work was based upon prior work by Jöns Berzelius ( [link] ) who had prepared calcium amalgam (an alloy of calcium and mercury) by electrolyzing lime in mercury.
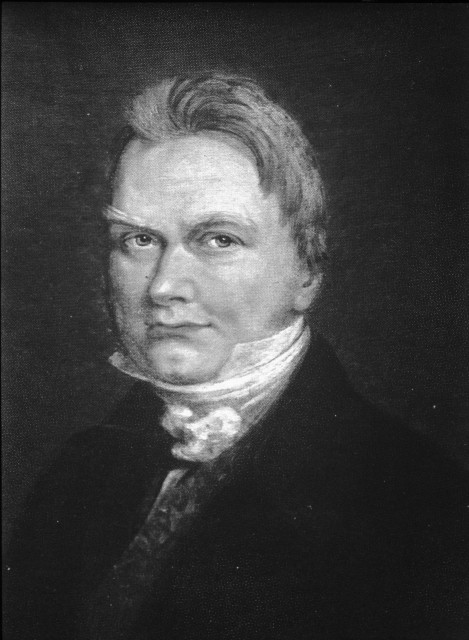

Discovered in lead mines in 1787 the mineral strontianite was named after the Scottish village of Strontian. Although it was realized that this mineral was different from others that contained barium, it wasn’t until 1798 that Thomas Hope ( [link] ) suggested the presence of a new element. As with calcium, metallic strontium was first isolated by Sir Humphry Davy ( [link] ) in 1808 using electrolysis of a mixture containing strontium chloride and mercuric oxide.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry of the main group elements' conversation and receive update notifications?