| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
In the previous section, we explained how to add and subtract fractions with a common denominator. But how can we add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators?
Let’s think about coins again. Can you add one quarter and one dime? You could say there are two coins, but that’s not very useful. To find the total value of one quarter plus one dime, you change them to the same kind of unit—cents. One quarter equals cents and one dime equals cents, so the sum is cents. See [link] .

Similarly, when we add fractions with different denominators we have to convert them to equivalent fractions with a common denominator. With the coins, when we convert to cents, the denominator is Since there are cents in one dollar, cents is and cents is So we add to get which is cents.
You have practiced adding and subtracting fractions with common denominators. Now let’s see what you need to do with fractions that have different denominators.
First, we will use fraction tiles to model finding the common denominator of and
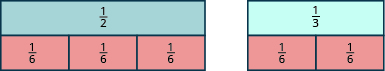
We’ll start with one tile and tile. We want to find a common fraction tile that we can use to match both and exactly.
If we try the pieces, of them exactly match the piece, but they do not exactly match the piece.

If we try the pieces, they do not exactly cover the piece or the piece.

If we try the pieces, we see that exactly of them cover the piece, and exactly of them cover the piece.
If we were to try the pieces, they would also work.
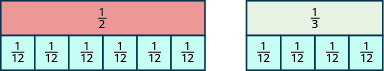
Even smaller tiles, such as and would also exactly cover the piece and the piece.
The denominator of the largest piece that covers both fractions is the least common denominator (LCD) of the two fractions. So, the least common denominator of and is
Notice that all of the tiles that cover and have something in common: Their denominators are common multiples of and the denominators of and The least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators is and so we say that is the least common denominator (LCD) of the fractions and
To find the LCD of two fractions, we will find the LCM of their denominators. We follow the procedure we used earlier to find the LCM of two numbers. We only use the denominators of the fractions, not the numerators, when finding the LCD.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Prealgebra' conversation and receive update notifications?