| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown or projected into the air, subject to only the acceleration of gravity. The object is called a projectile , and its path is called its trajectory . The motion of falling objects, as covered in Problem-Solving Basics for One-Dimensional Kinematics , is a simple one-dimensional type of projectile motion in which there is no horizontal movement. In this section, we consider two-dimensional projectile motion, such as that of a football or other object for which air resistance is negligible .
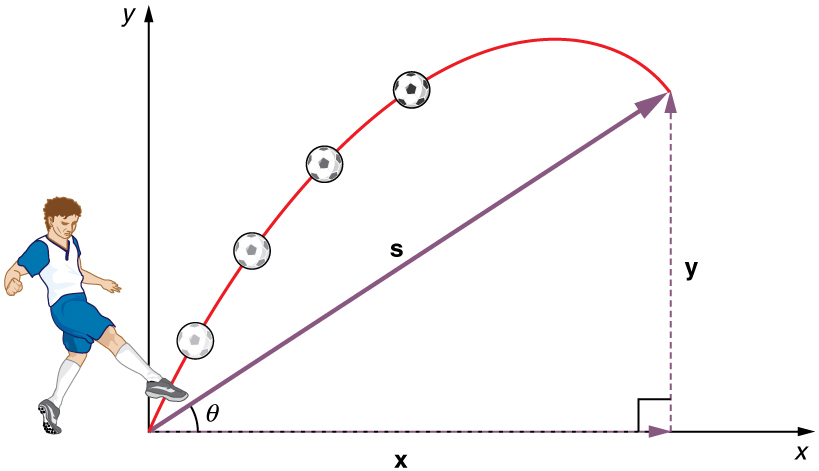
The most important fact to remember here is that motions along perpendicular axes are independent and thus can be analyzed separately. This fact was discussed in Kinematics in Two Dimensions: An Introduction , where vertical and horizontal motions were seen to be independent. The key to analyzing two-dimensional projectile motion is to break it into two motions, one along the horizontal axis and the other along the vertical. (This choice of axes is the most sensible, because acceleration due to gravity is vertical—thus, there will be no acceleration along the horizontal axis when air resistance is negligible.) As is customary, we call the horizontal axis the x -axis and the vertical axis the y -axis. [link] illustrates the notation for displacement, where is defined to be the total displacement and and are its components along the horizontal and vertical axes, respectively. The magnitudes of these vectors are s , x , and y . (Note that in the last section we used the notation to represent a vector with components and . If we continued this format, we would call displacement with components and . However, to simplify the notation, we will simply represent the component vectors as and .)
Of course, to describe motion we must deal with velocity and acceleration, as well as with displacement. We must find their components along the x - and y -axes, too. We will assume all forces except gravity (such as air resistance and friction, for example) are negligible. The components of acceleration are then very simple: . (Note that this definition assumes that the upwards direction is defined as the positive direction. If you arrange the coordinate system instead such that the downwards direction is positive, then acceleration due to gravity takes a positive value.) Because gravity is vertical, . Both accelerations are constant, so the kinematic equations can be used.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 110 at une' conversation and receive update notifications?