| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

For mobile organisms, such as mammals, birds, or fish, a technique called mark and recapture is often used. This method involves marking a sample of captured animals in some way (such as tags, bands, paint, or other body markings), and then releasing them back into the environment to allow them to mix with the rest of the population; later, a new sample is collected, including some individuals that are marked (recaptures) and some individuals that are unmarked ( [link] ).
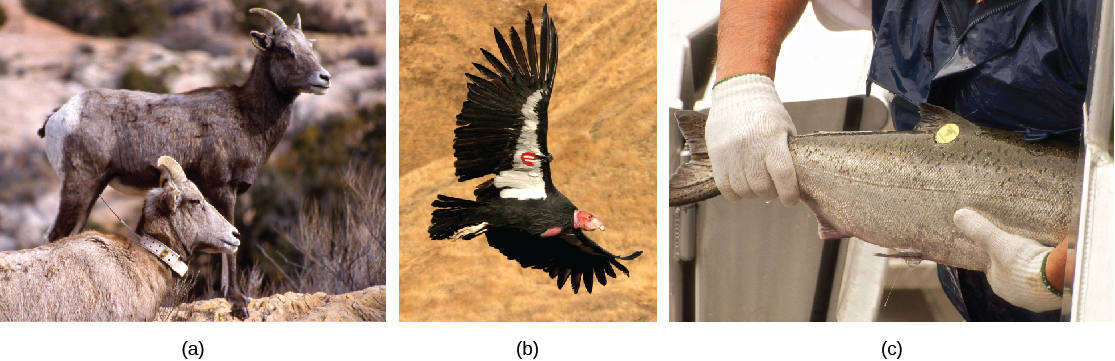
Using the ratio of marked and unmarked individuals, scientists determine how many individuals are in the sample. From this, calculations are used to estimate the total population size. This method assumes that the larger the population, the lower the percentage of tagged organisms that will be recaptured since they will have mixed with more untagged individuals. For example, if 80 deer are captured, tagged, and released into the forest, and later 100 deer are captured and 20 of them are already marked, we can determine the population size ( N ) using the following equation:
Using our example, the population size would be estimated at 400.
Therefore, there are an estimated 400 total individuals in the original population.
There are some limitations to the mark and recapture method. Some animals from the first catch may learn to avoid capture in the second round, thus inflating population estimates. Alternatively, animals may preferentially be retrapped (especially if a food reward is offered), resulting in an underestimate of population size. Also, some species may be harmed by the marking technique, reducing their survival. A variety of other techniques have been developed, including the electronic tracking of animals tagged with radio transmitters and the use of data from commercial fishing and trapping operations to estimate the size and health of populations and communities.
In addition to measuring simple density, further information about a population can be obtained by looking at the distribution of the individuals. Species dispersion patterns (or distribution patterns) show the spatial relationship between members of a population within a habitat at a particular point in time. In other words, they show whether members of the species live close together or far apart, and what patterns are evident when they are spaced apart.
Individuals in a population can be more or less equally spaced apart, dispersed randomly with no predictable pattern, or clustered in groups. These are known as uniform, random, and clumped dispersion patterns, respectively ( [link] ). Uniform dispersion is observed in plants that secrete substances inhibiting the growth of nearby individuals (such as the release of toxic chemicals by the sage plant Salvia leucophylla, a phenomenon called allelopathy or plants in arid habitats that compete intensely for limited soil water and nutrients.) and in animals like the penguin that maintain a defined territory. An example of random dispersion occurs with dandelion and other plants that have wind-dispersed seeds that germinate wherever they happen to fall in a favorable environment. A clumped dispersion may be seen in plants that drop their seeds straight to the ground, such as oak trees, or animals that live in groups (schools of fish or herds of elephants). Clumped dispersions may also be a function of habitat heterogeneity. Thus, the dispersion of the individuals within a population provides more information about how they interact with each other than does a simple density measurement. Just as lower density species might have more difficulty finding a mate, solitary species with a random distribution might have a similar difficulty when compared to social species clumped together in groups.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?