| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nature has put itself the problem how to catch in flight light streaming to the earth and to store the most elusive of all powers in rigid form. To achieve this aim, it has covered the crust of earth with organisms which in their life processes absorb the light of the sun and use this power to produce a continuously accumulating chemical difference. ... The plants take in one form of power, light; and produce another power, chemical difference.Robert Mayer, German physicist who developed the concept of the conservation of heat, 1845
The sun not only provides the energy for the plants themselves, but for all other creatures on the planet. Indeed, ancient photosynthesis provided the fossil fuel energy that we use to generate electricity or power our cars. Each cell in every organism runs on the chemical energy found mainly in carbohydrate molecules (food), and the majority of these molecules are produced by one process: photosynthesis. Through photosynthesis, certain organisms convert solar energy (sunlight) into chemical energy, which is then used to build carbohydrate molecules. The energy used to hold these molecules together is released when an organism breaks down food during cellular respiration. Cells then use this energy to perform work, such as movement.
The energy that is harnessed from photosynthesis enters the ecosystems of our planet continuously and is transferred from one organism to another until almost all of the harvested energy is transferred and released as heat energy. Therefore, directly or indirectly, the process of photosynthesis provides most of the energy required by living things on earth ( [link] ).
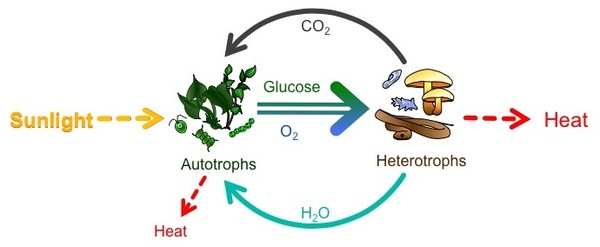
Photosynthesis also results in the release of oxygen into the atmosphere. In short, to eat and breathe, humans depend almost entirely on the organisms that carry out photosynthesis.
Some organisms can carry out photosynthesis, whereas others cannot. An autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food. The Greek roots of the word autotroph mean “self” ( auto ) “feeder” ( troph ). Plants are the best-known autotrophs, but others exist, including certain types of bacteria and algae ( [link] ). Oceanic algae contribute enormous quantities of food and oxygen to global food chains. Plants are also photoautotrophs , a type of autotroph that uses sunlight and carbon from carbon dioxide to synthesize chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. All organisms carrying out photosynthesis require sunlight.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?