| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Surely the mitochondrion that first entered another cell was not thinking about the future benefits of cooperation and integration; it was merely trying to make its own living in a tough Darwinian world.Stephen Jay Gould, in Wonderful Life: the Burgess Shale and the Nature of History , (1990)
All living organisms require energy, and for all organisms this energy comes from the chemical energy found in compounds that they acquire from their environment. The mitochondrion, a descendent of an aerobically-respiring bacteria, is the site of energy generation in eukaryotes. As we learned previously, the process of photosynthesis uses solar energy (sunlight) and converts this energy into chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates. In order for the chemical energy in the carbohydrates to be made available to do cellular work, the energy must be converted into a useable form known as ATP. Adenosine Triphosphate is the energy currency of the cell, and everything you do from walking down the street to reading this book requires energy in the form of ATP. Organisms need a constant supply of ATP, and the potential energy stored in food is the source of energy to meet this need. By connecting all this together, you should realize that your daily activities are fueled by the energy from the sun and that even on the cellular level nutrients cycle and energy flows (
[link] ).
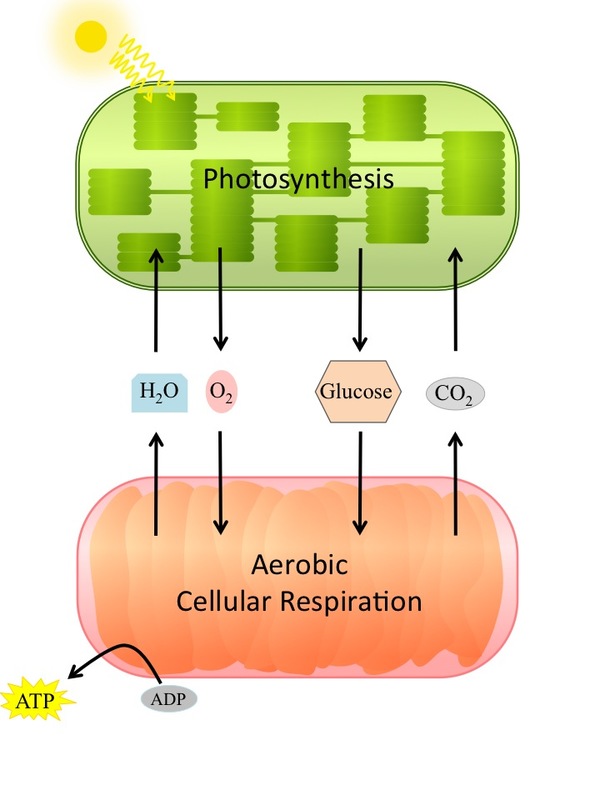
All organisms need ATP, but not all organisms use the same pathways to generate ATP from the food that is consumed.
Aerobic cellular respiration , the main subject of this chapter, uses oxygen (O
2 ) and glucose to generate ATP. Organisms (plants, animals, fungi and microbes) that live in an oxygen (O
2 ) rich environment use this process to generate ATP. The overall equation for aerobic cellular respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis, is an exergonic reaction, and supplies the ATP for cellular functions (
[link] ).

As the aerobic cellular respiration equation shows ( [link] ), an organism needs to acquire the O 2 from its surroundings and to get rid of the CO 2 that is produced. The acquisition of O 2 and the release of CO 2 is accomplished in a variety of ways. In single celled organisms, the movement of O 2 and CO 2 (gas exchange) is done by simple diffusion. However, in complex organisms there are specialized organs that allow for gas exchange; for example, gills in aquatic organisms and lungs in terrestrial animals.
A common misconception is that plants do not undergo cellular respiration because they make their own energy by photosynthesis. Plants do perform cellular respiration using the carbohydrates produced via photosynthesis; this occurs in tissues that are not photosynthetically active (e.g., roots), as well as in leaves and stems. Approximately half of the glucose produced by photosynthesis is consumed by the plant, mostly to generate ATP during aerobic cellular respiration. Other uses of glucose in the plant include synthesis of cell walls, starch, and other plant carbohydrates. So, plants harvest light energy via photosynthesis, making carbohydrates, and then they use the energy stored in those carbohydrates to perform various cellular functions. This is the reason why they are called autotrophs , or self feeders.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?