| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Vertebrates are among the most recognizable organisms of the animal kingdom. More than 62,000 vertebrate species have been identified. The vertebrate species now living represent only a small portion of the vertebrates that have existed. The best-known extinct vertebrates are the dinosaurs, a unique group of reptiles, which reached sizes not seen before or after in terrestrial animals. They were the dominant terrestrial animals for 150 million years, until they died out in a mass extinction near the end of the Cretaceous period. Although it is not known with certainty what caused their extinction, a great deal is known about the anatomy of the dinosaurs, given the preservation of skeletal elements in the fossil record.
Currently, a number of vertebrate species face extinction primarily due to habitat loss and pollution. According to the International Union for the Conservation of Nature, more than 6,000 vertebrate species are classified as threatened. Amphibians and mammals are the classes with the greatest percentage of threatened species, with 29 percent of all amphibians and 21 percent of all mammals classified as threatened. Attempts are being made around the world to prevent the extinction of threatened species. For example, the Biodiversity Action Plan is an international program, ratified by 188 countries, which is designed to protect species and habitats.
Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ( [link] ). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups—protostomes and deuterostomes—based on their patterns of embryonic development. The deuterostomes, whose name translates as “second mouth,” consist of two phyla: Chordata and Echinodermata. Echinoderms are invertebrate marine animals that have radial symmetry and a spiny body covering, a group that includes sea stars, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers. The most conspicuous and familiar members of Chordata are vertebrates, but this phylum also includes two groups of invertebrate chordates.
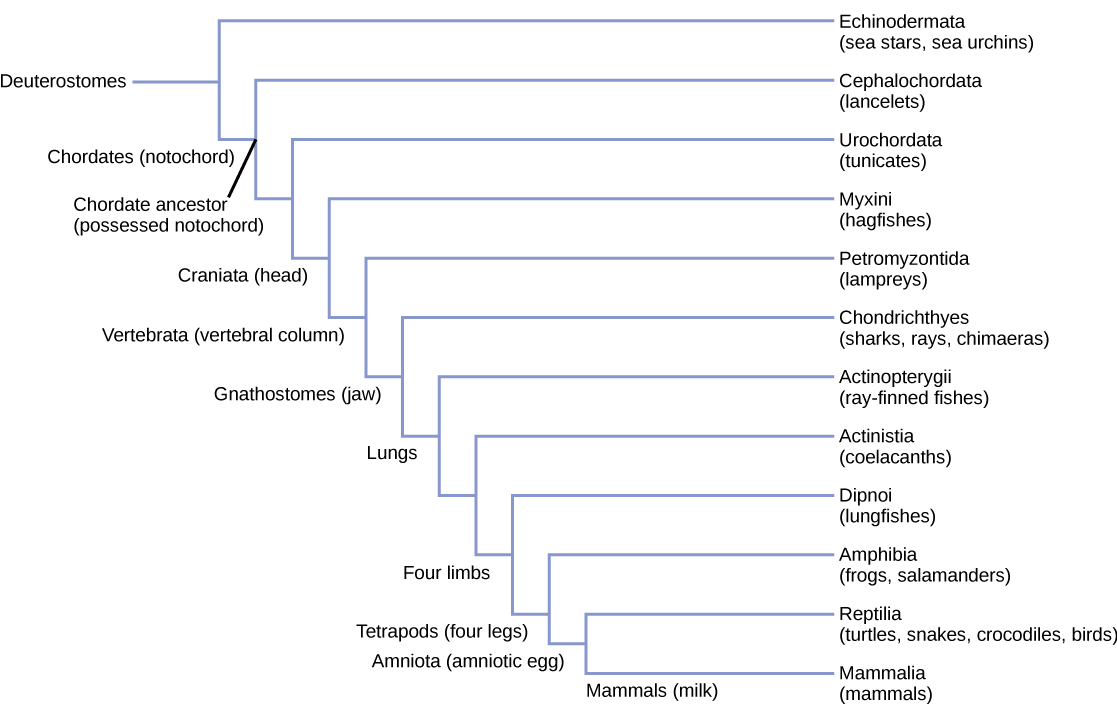
Animals in the phylum Chordata share four key features that appear at some stage during their development: a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail ( [link] ). In some groups, some of these are present only during embryonic development.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bi 101 for lbcc ilearn campus' conversation and receive update notifications?