| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Learners frequently exchange hands because they are unable to cross over the middleline of the body. Problems around such middleline crossing results in continuous repositioning of the body, which has a negative effect on concentration and work speed and leads to tiredness.

Examples of activities:
Examples of activities:

Learners show that they are able to apply what they have learnt in different situations in the community. Help them with the challenges that life offers so that they can play an active and productive role in the community. Discussing situations can help to develop problem solving skills, logical thinking and reasoning, as well as creative and critical thinking.
Examples of activities:
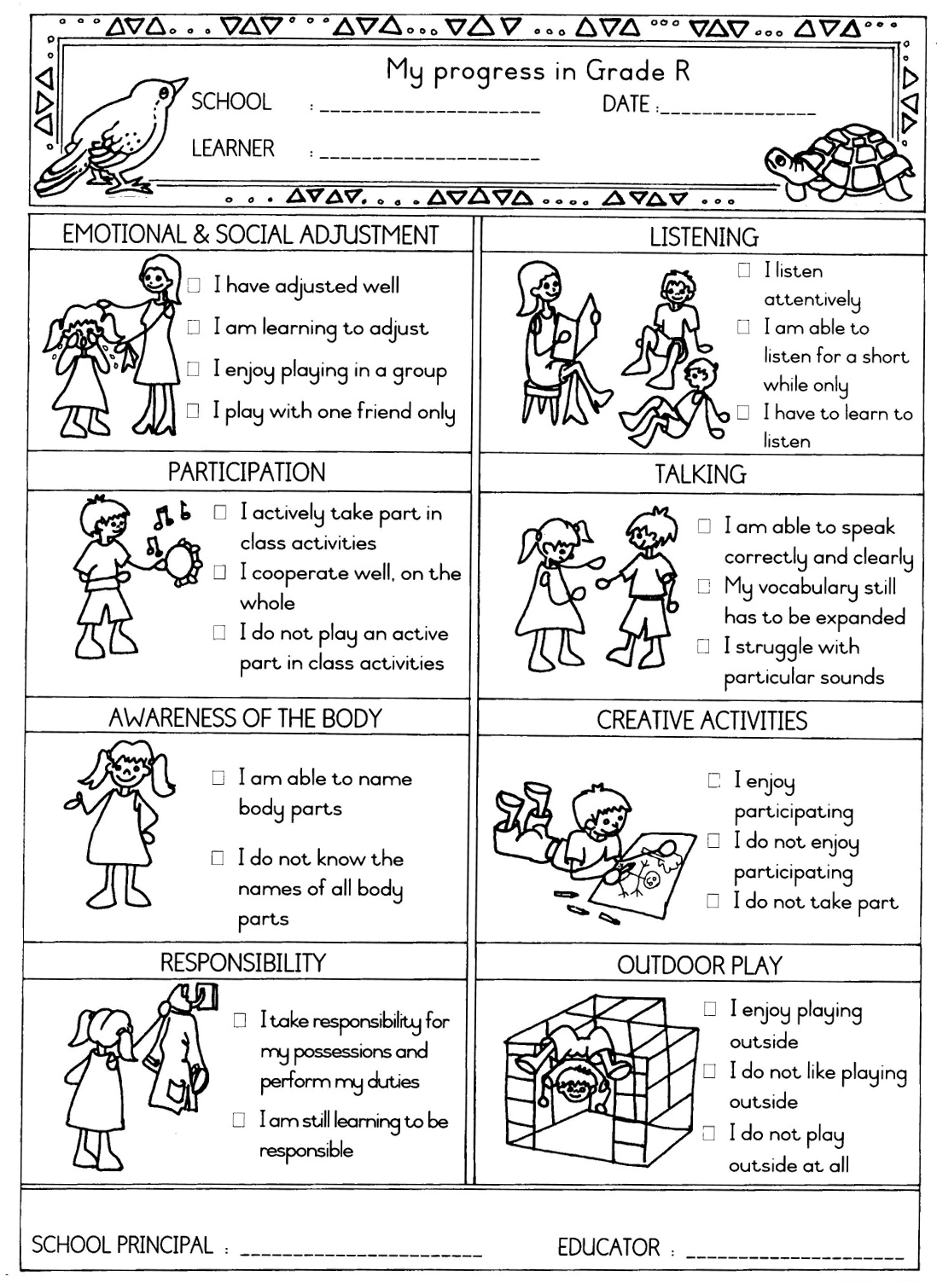
An example of an (optional) elementary report on the learner’s progress during the first quarter is included for educators who regard it as desirable to report to parents.
| MODULE FRAMEWORK | |
| LEARNING OUTCOMES | ASSESSMENT STANDARDS |
| NUMERACY(LO 1)NUMBERS, OPERATIONS AND RELATIONSHIPSThe learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent numbers and their relationships, and to count, estimate, calculate and check with competence and confidence in solving problems.(LO 2)PATTERNS, FUNCTIONS AND ALGEBRAThe learner will be able to recognise, describe and represent patterns and relationships, as well as to solve problems using algebraic language and skills.(LO 5)DATA HANDLINGThe learner will be able to collect, summarise, display and critically analyse data in order to draw conclusions and make predictions, and to interpret and determine chance variation.LITERACY(LO 1)LISTENINGThe learner will be able to listen for information and enjoyment, and respond appropriately and critically in a wide range of situations(LO 2)SPEAKINGThe learner will be able to communicate confidently and effectively in spoken language in a wide range of situations.(LO 3)READING AND VIEWINGThe learner will be able to read and view for information and enjoyment, and respond critically to the aesthetic, cultural and emotional values in texts.(LO4)WRITINGThe learner will be able to write different kinds of factual and imaginative texts for a wide range of purposes.(LO 5)THINKING AND REASONINGThe learner will be able to use language to think and reason, as well as to access, process and use information for learning. | We know this when the learner:1.2 counts to at least 10 everyday objects reliably;1.3 says and uses number names in familiar contexts;1.4 knows the number names and symbols for 1 to 10.We know this when the learner:2.1 copies and extends simple patterns using physical objects and drawings (e.g. using colours and shapes);We know this when the learner:5.2 sorts physical objects according to one attribute (property), e.g. red shapes.We know this when the learner:1.1 listens attentively to questions, instructions and announcements, and responds appropriately;1.4 develops phonic awareness:
|
| LIFE ORIENTATION(LO 1)HEALTH PROMOTIONThe learner will be able to make informed decisions regarding personal, community and environmental health.(LO 3)PERSONAL DEVELOPMENTThe learner will be able to use acquired life skills to achieve and extend personal potential to respond effectively to challenges in his or her world. | We know this when the learner:1.2 describes steps that can be taken to ensure personal hygiene;1.4 demonstrates precautions against the spread of communicable diseases.We know this when the learner:3.1 says own name and address. |
Auditory discrimination
Fine coordination

Activity: Look for more examples in the classroom, that begin with a .
| Literacy LO : 1.4 |
Fine coordination
Letter Formation
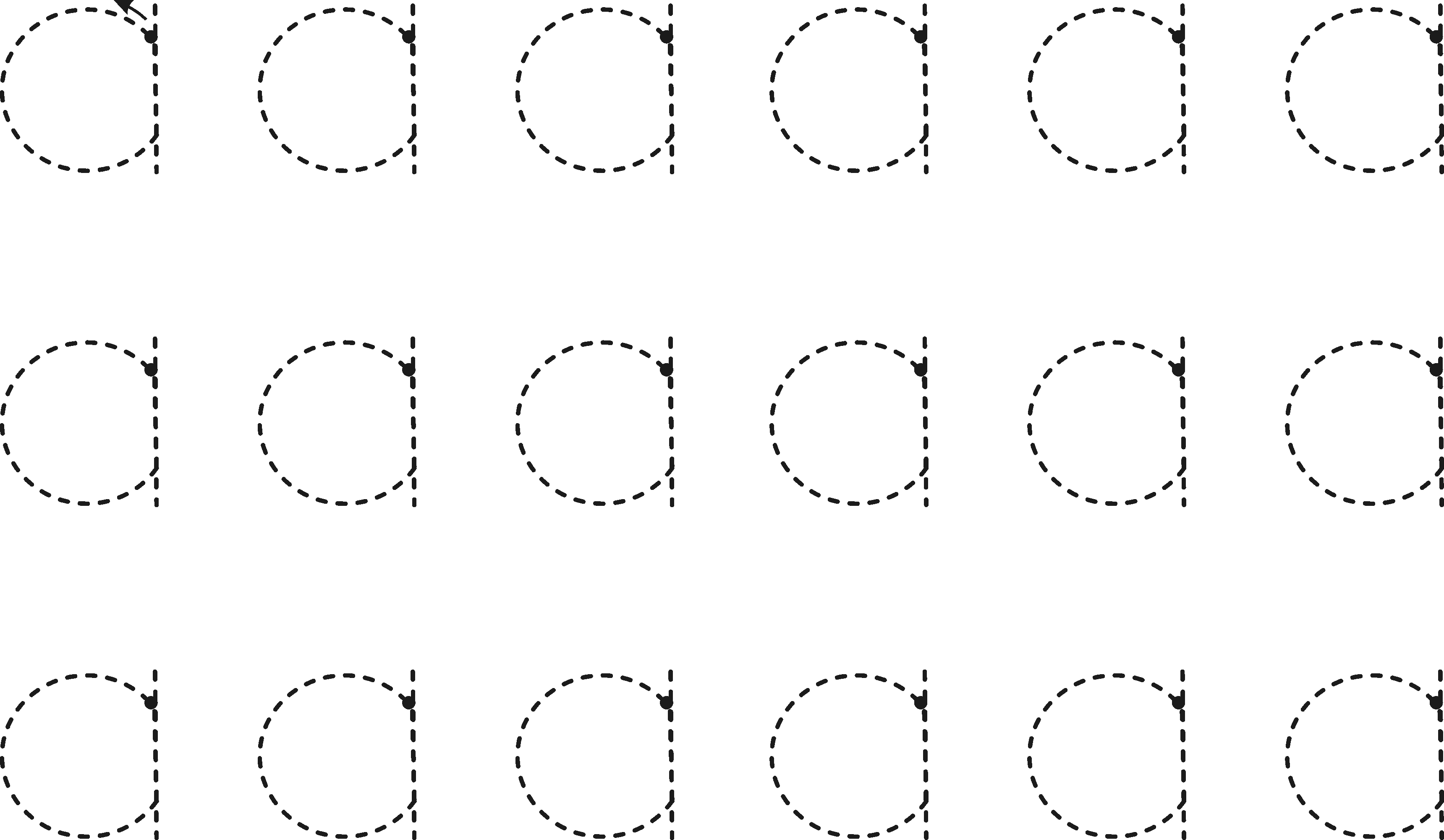
Activity: Practise writing the a in sand or on the board.
| Literacy LO : 4.1 |
Sequencing of events
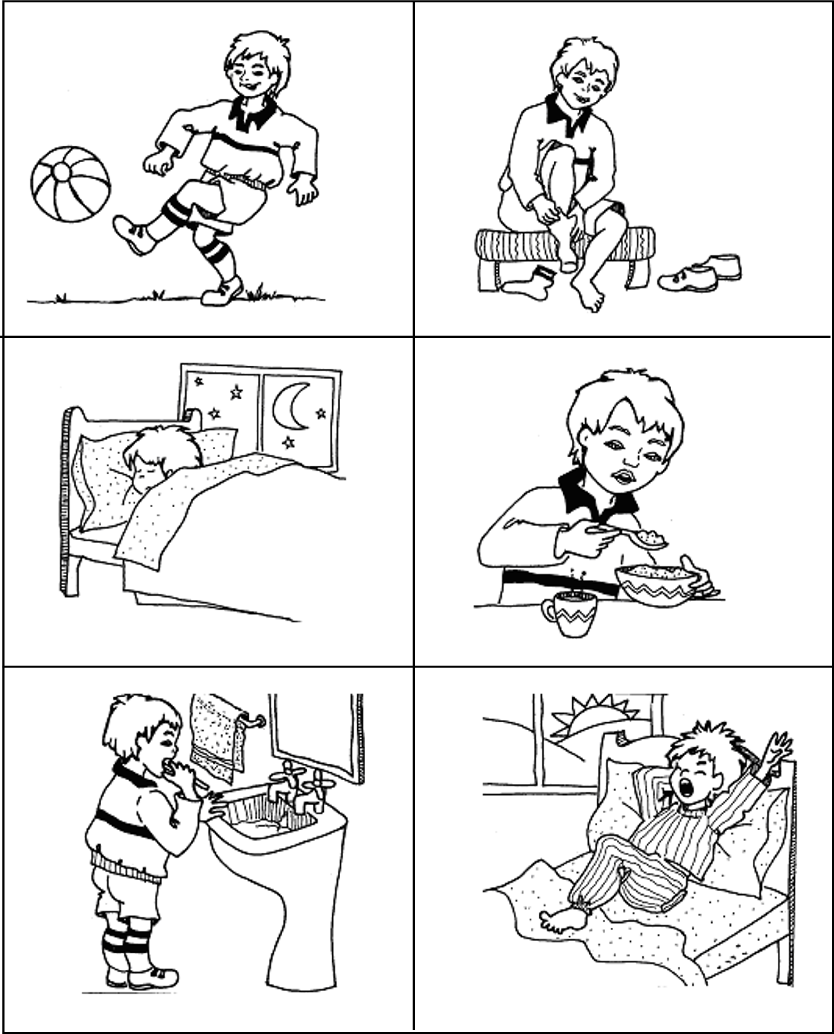

Tell your own story about what you do when you wake up until you go to bed.
| Literacy LO : 1.3 |
Logical Reasoning
Midline Crossing
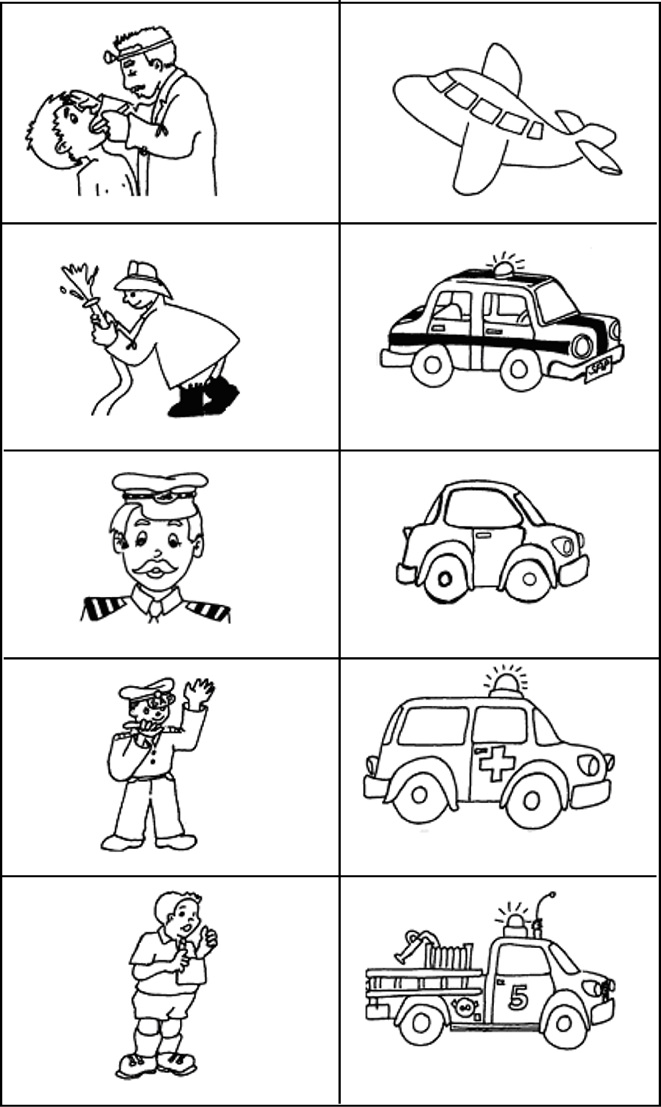

Discussion:
Who has been a doctor, dentist or in the hospital?
Tell your own story.
| Literacy LO : 5.2 |
Auditory discrimination
Fine coordination
Activity: Look for more examples in the classroom, that begin with e .
| Literacy LO : 1.4 |
Fine coordination
Letter Formation
Activity: Practise writing the ee in sand or on the board.
| Literacy LO : 4.1 |
Logical Reasoning

| Literacy LO : 5.2 |
Auditory Discrimination
Fine coordination

Activity : Look for more examples in the classroom that begin
| Literacy LO : 1.4 |
Fine coordination
Letter Formation
| Literacy LO : 4.1 |
| Literacy LO : 4.1 |
Left / Right Discrimination
Activity : Play games that are based on left / right concepts – for example, touch your right eye / left ear or kick with your right foot.
| Literacy LO : 5.1 |
Make your own telephone
You need two carton mugs and 6 metres of strong string. Make a hole in each mug’s bottom. Push the two ends of the string through the two holes and tie a match to it so that it cannot be pulled back through the holes again. Pull the string tight so that you and your friend stand away from each other, each holding a mug. Hold the mug to your ear while your friend talks into the other one.
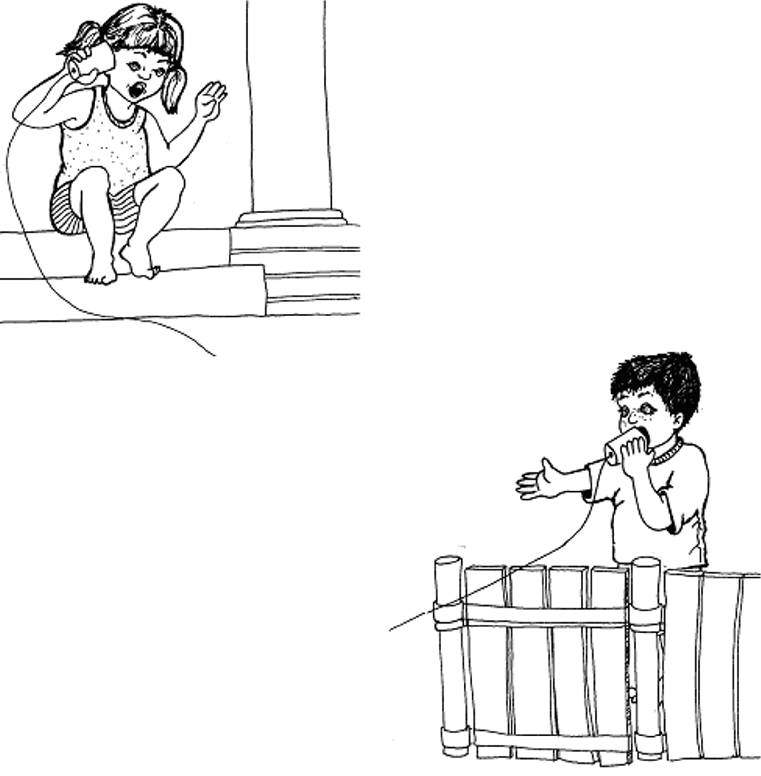
Auditory Discrimination

| Literacy LO : 1.4 |
Auditory Discrimination

| Literacy LO : 4.1 |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Grade r - a learning programme' conversation and receive update notifications?