| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Show that the acceleration of any object down a frictionless incline that makes an angle with the horizontal is . (Note that this acceleration is independent of mass.)
Show that the acceleration of any object down an incline where friction behaves simply (that is, where ) is Note that the acceleration is independent of mass and reduces to the expression found in the previous problem when friction becomes negligibly small
Calculate the deceleration of a snow boarder going up a , slope assuming the coefficient of friction for waxed wood on wet snow. The result of [link] may be useful, but be careful to consider the fact that the snow boarder is going uphill. Explicitly show how you follow the steps in Problem-Solving Strategies .
(a) Calculate the acceleration of a skier heading down a slope, assuming the coefficient of friction for waxed wood on wet snow. (b) Find the angle of the slope down which this skier could coast at a constant velocity. You can neglect air resistance in both parts, and you will find the result of [link] to be useful. Explicitly show how you follow the steps in the Problem-Solving Strategies .
If an object is to rest on an incline without slipping, then friction must equal the component of the weight of the object parallel to the incline. This requires greater and greater friction for steeper slopes. Show that the maximum angle of an incline above the horizontal for which an object will not slide down is . You may use the result of the previous problem. Assume that and that static friction has reached its maximum value.
Calculate the maximum deceleration of a car that is heading down a slope (one that makes an angle of with the horizontal) under the following road conditions. You may assume that the weight of the car is evenly distributed on all four tires and that the coefficient of static friction is involved—that is, the tires are not allowed to slip during the deceleration. (Ignore rolling.) Calculate for a car: (a) On dry concrete. (b) On wet concrete. (c) On ice, assuming that , the same as for shoes on ice.
Calculate the maximum acceleration of a car that is heading up a slope (one that makes an angle of with the horizontal) under the following road conditions. Assume that only half the weight of the car is supported by the two drive wheels and that the coefficient of static friction is involved—that is, the tires are not allowed to slip during the acceleration. (Ignore rolling.) (a) On dry concrete. (b) On wet concrete. (c) On ice, assuming that , the same as for shoes on ice.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Repeat [link] for a car with four-wheel drive.
A freight train consists of two engines and 45 cars with average masses of . (a) What force must each engine exert backward on the track to accelerate the train at a rate of if the force of friction is , assuming the engines exert identical forces? This is not a large frictional force for such a massive system. Rolling friction for trains is small, and consequently trains are very energy-efficient transportation systems. (b) What is the magnitude of the force in the coupling between the 37th and 38th cars (this is the force each exerts on the other), assuming all cars have the same mass and that friction is evenly distributed among all of the cars and engines?
(a)
(b)
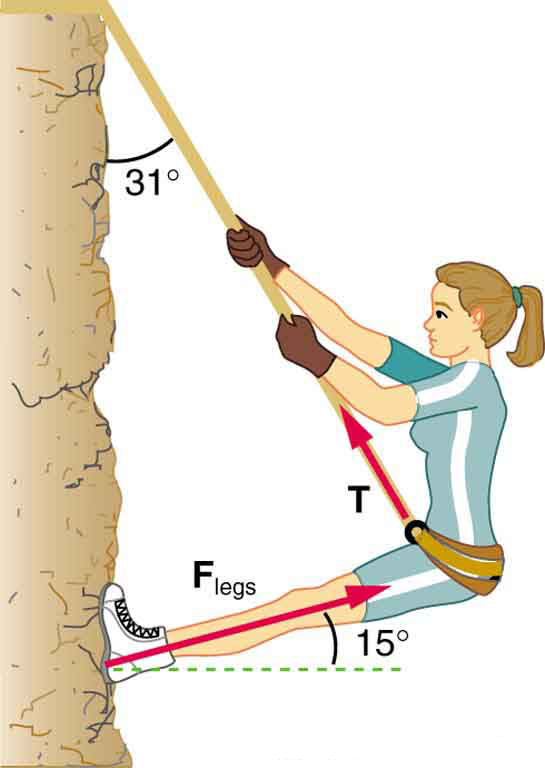
Consider the 52.0-kg mountain climber in [link] . (a) Find the tension in the rope and the force that the mountain climber must exert with her feet on the vertical rock face to remain stationary. Assume that the force is exerted parallel to her legs. Also, assume negligible force exerted by her arms. (b) What is the minimum coefficient of friction between her shoes and the cliff?
A contestant in a winter sporting event pushes a 45.0-kg block of ice across a frozen lake as shown in [link] (a). (a) Calculate the minimum force he must exert to get the block moving. (b) What is the magnitude of its acceleration once it starts to move, if that force is maintained?
(a)
(b)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics arranged for cpslo phys141' conversation and receive update notifications?