| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nervous systems throughout the animal kingdom vary in structure and complexity, as illustrated by the variety of animals shown in [link] . Some organisms, like sea sponges, lack a true nervous system. Others, like jellyfish, lack a true brain and instead have a system of separate but connected nerve cells (neurons) called a “nerve net.” Echinoderms such as sea stars have nerve cells that are bundled into fibers called nerves. Flatworms of the phylum Platyhelminthes have both a central nervous system (CNS), made up of a small “brain” and two nerve cords, and a peripheral nervous system (PNS) containing a system of nerves that extend throughout the body. The insect nervous system is more complex but also fairly decentralized. It contains a brain, ventral nerve cord, and ganglia (clusters of connected neurons). These ganglia can control movements and behaviors without input from the brain. Octopi may have the most complicated of invertebrate nervous systems—they have neurons that are organized in specialized lobes and eyes that are structurally similar to vertebrate species.
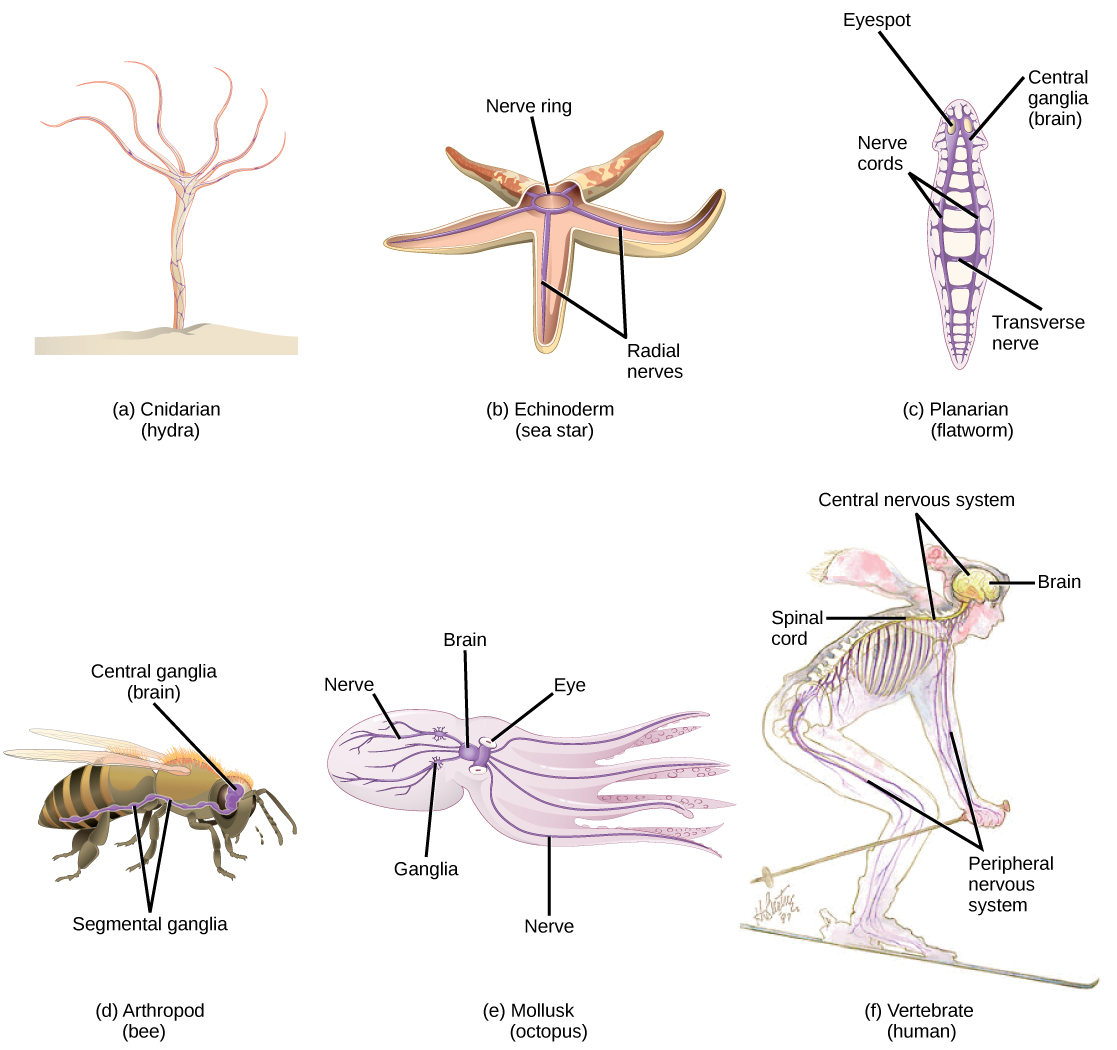
Compared to invertebrates, vertebrate nervous systems are more complex, centralized, and specialized. While there is great diversity among different vertebrate nervous systems, they all share a basic structure: a CNS that contains a brain and spinal cord and a PNS made up of peripheral sensory and motor nerves. One interesting difference between the nervous systems of invertebrates and vertebrates is that the nerve cords of many invertebrates are located ventrally whereas the vertebrate spinal cords are located dorsally. There is debate among evolutionary biologists as to whether these different nervous system plans evolved separately or whether the invertebrate body plan arrangement somehow “flipped” during the evolution of vertebrates.
Watch this video of biologist Mark Kirschner discussing the “flipping” phenomenon of vertebrate evolution.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bmcc 103 - concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?