| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
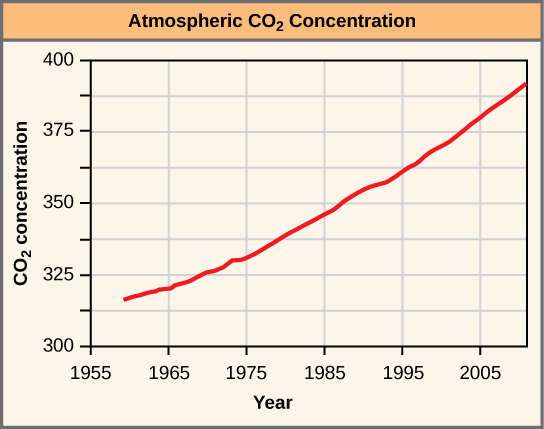
The Industrial Revolution, which began around 1750, was characterized by changes in much of human society. Advances in agriculture increased the food supply, which improved the standard of living for people in Europe and the United States. New technologies were invented and provided jobs and cheaper goods. These new technologies were powered using fossil fuels, especially coal. The Industrial Revolution starting in the early nineteenth century ushered in the beginning of the Industrial Era. When a fossil fuel is burned, carbon dioxide is released. With the beginning of the Industrial Era, atmospheric carbon dioxide began to rise ( [link] ).
Since it is not possible to go back in time to directly observe and measure climate, scientists use indirect evidence to determine the drivers, or factors, that may be responsible for climate change. The indirect evidence includes data collected using ice cores, boreholes (a narrow shaft bored into the ground), tree rings, glacier lengths, pollen remains, and ocean sediments. The data shows a correlation between the timing of temperature changes and drivers of climate change: before the Industrial Era (pre-1780), there were three drivers of climate change that were not related to human activity or atmospheric gases. The first of these is the Milankovitch cycles. The Milankovitch cycles describe the effects of slight changes in the Earth’s orbit on Earth’s climate. The length of the Milankovitch cycles ranges between 19,000 and 100,000 years. In other words, one could expect to see some predictable changes in the Earth’s climate associated with changes in the Earth’s orbit at a minimum of every 19,000 years.
The variation in the sun’s intensity is the second natural factor responsible for climate change. Solar intensity is the amount of solar power or energy the sun emits in a given amount of time. There is a direct relationship between solar intensity and temperature. As solar intensity increases (or decreases), the Earth’s temperature correspondingly increases (or decreases). Changes in solar intensity have been proposed as one of several possible explanations for the Little Ice Age.
Finally, volcanic eruptions are a third natural driver of climate change. Volcanic eruptions can last a few days, but the solids and gases released during an eruption can influence the climate over a period of a few years, causing short-term climate changes. The gases and solids released by volcanic eruptions can include carbon dioxide, water vapor, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide. Generally, volcanic eruptions cool the climate. This occurred in 1783 when volcanos in Iceland erupted and caused the release of large volumes of sulfuric oxide. This led to haze-effect cooling , a global phenomenon that occurs when dust, ash, or other suspended particles block out sunlight and trigger lower global temperatures as a result; haze-effect cooling usually extends for one or more years. In Europe and North America, haze-effect cooling produced some of the lowest average winter temperatures on record in 1783 and 1784.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 105: adventures in physics' conversation and receive update notifications?