| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We analyzed the biceps muscle example with the angle between forearm and upper arm set at . Using the same numbers as in [link] , find the force exerted by the biceps muscle when the angle is and the forearm is in a downward position.
Even when the head is held erect, as in [link] , its center of mass is not directly over the principal point of support (the atlanto-occipital joint). The muscles at the back of the neck should therefore exert a force to keep the head erect. That is why your head falls forward when you fall asleep in the class. (a) Calculate the force exerted by these muscles using the information in the figure. (b) What is the force exerted by the pivot on the head?
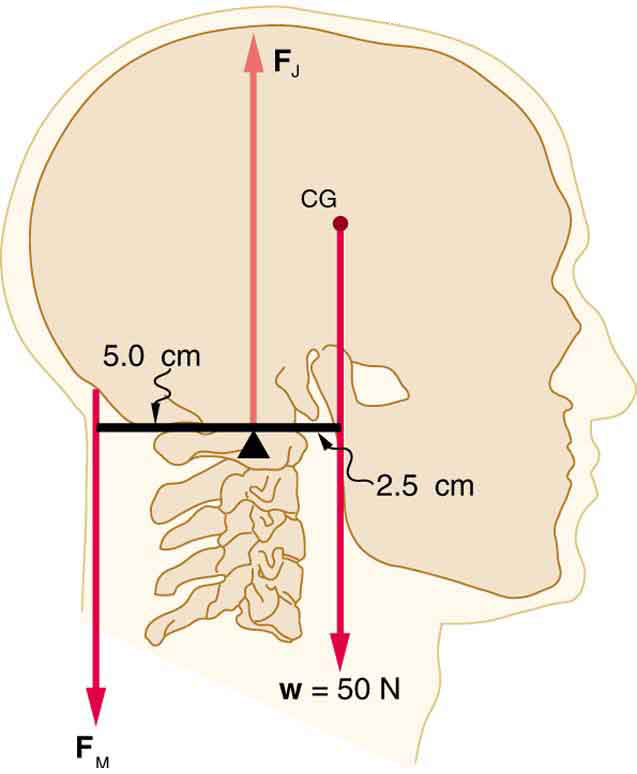
(a) 25 N downward
(b) 75 N upward
A 75-kg man stands on his toes by exerting an upward force through the Achilles tendon, as in [link] . (a) What is the force in the Achilles tendon if he stands on one foot? (b) Calculate the force at the pivot of the simplified lever system shown—that force is representative of forces in the ankle joint.
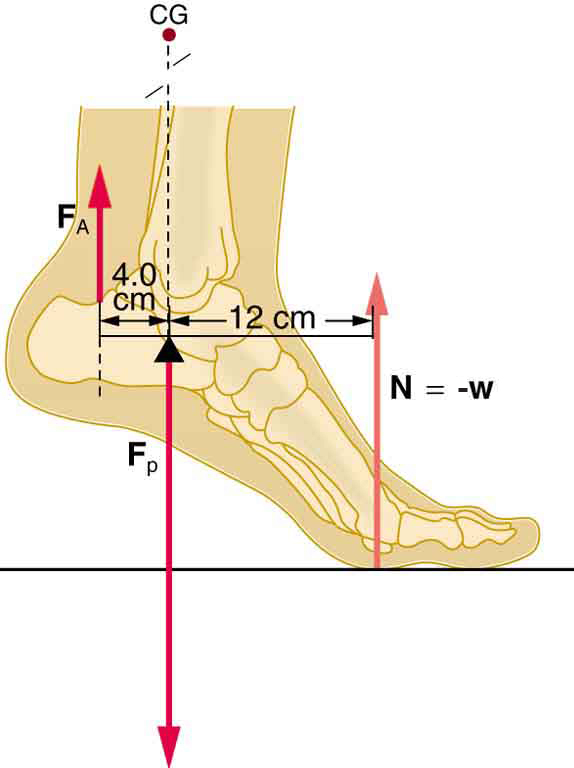
(a) upward
(b) downward
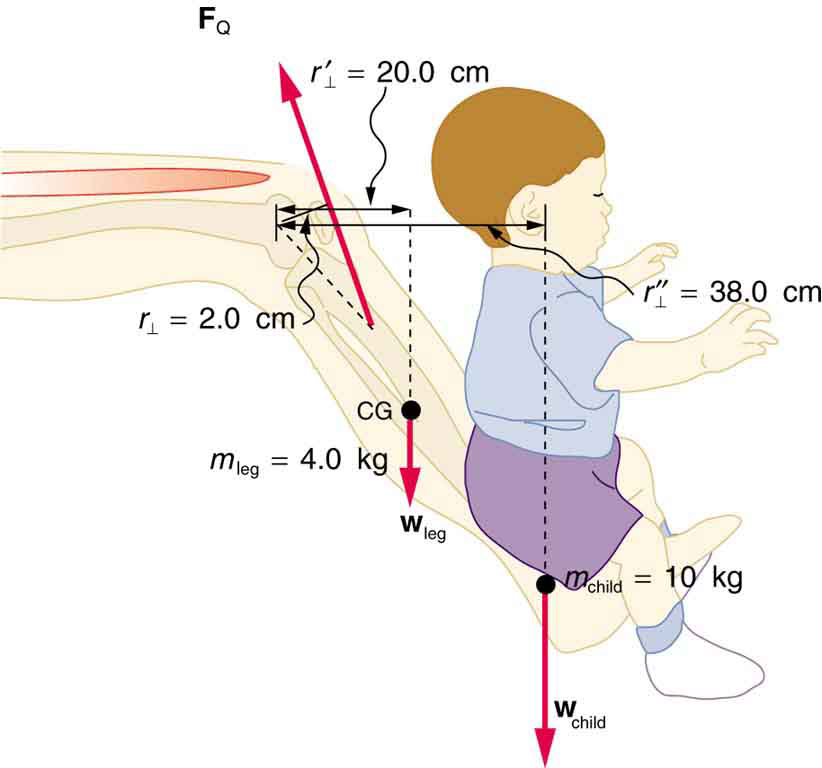
A father lifts his child as shown in [link] . What force should the upper leg muscle exert to lift the child at a constant speed?
Unlike most of the other muscles in our bodies, the masseter muscle in the jaw, as illustrated in [link] , is attached relatively far from the joint, enabling large forces to be exerted by the back teeth. (a) Using the information in the figure, calculate the force exerted by the lower teeth on the bullet. (b) Calculate the force on the joint.
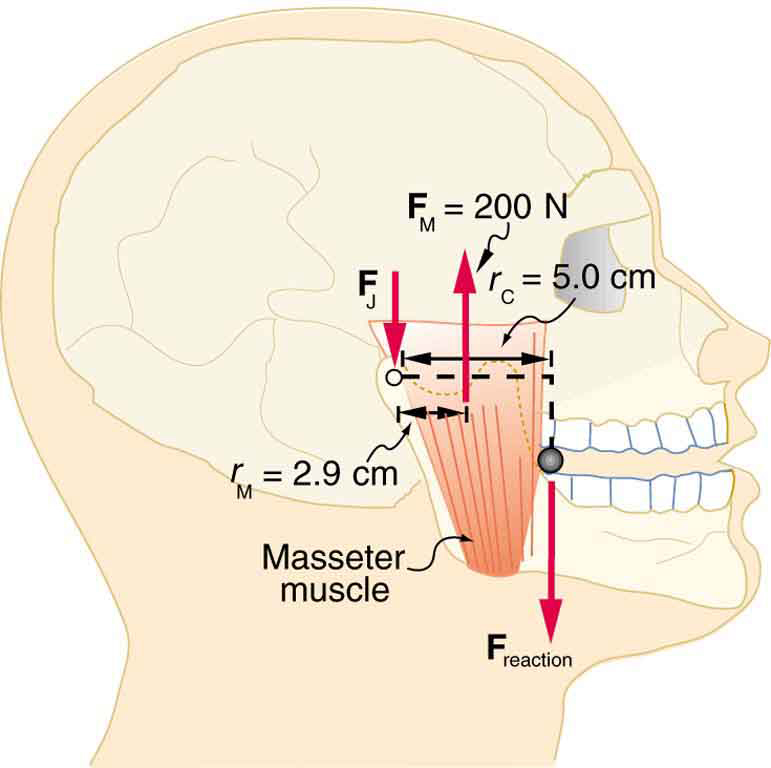
(a) upward
(b) downward
Integrated Concepts
Suppose we replace the 4.0-kg book in [link] of the biceps muscle with an elastic exercise rope that obeys Hooke’s Law. Assume its force constant . (a) How much is the rope stretched (past equilibrium) to provide the same force as in this example? Assume the rope is held in the hand at the same location as the book. (b) What force is on the biceps muscle if the exercise rope is pulled straight up so that the forearm makes an angle of with the horizontal? Assume the biceps muscle is still perpendicular to the forearm.
(a) What force should the woman in [link] exert on the floor with each hand to do a push-up? Assume that she moves up at a constant speed. (b) The triceps muscle at the back of her upper arm has an effective lever arm of 1.75 cm, and she exerts force on the floor at a horizontal distance of 20.0 cm from the elbow joint. Calculate the magnitude of the force in each triceps muscle, and compare it to her weight. (c) How much work does she do if her center of mass rises 0.240 m? (d) What is her useful power output if she does 25 pushups in one minute?
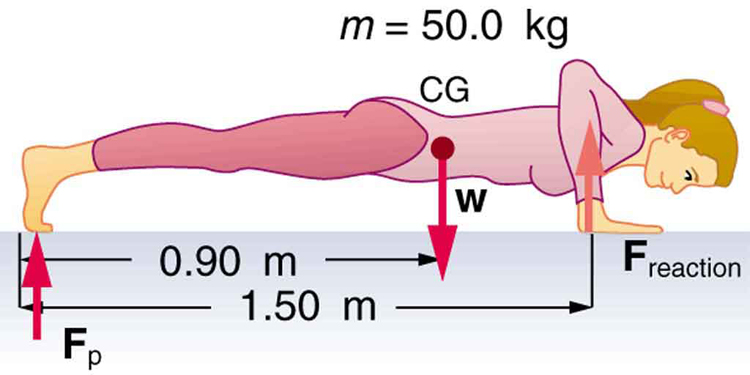
(a) 147 N downward
(b) 1680 N, 3.4 times her weight
(c) 118 J
(d) 49.0 W
You have just planted a sturdy 2-m-tall palm tree in your front lawn for your mother’s birthday. Your brother kicks a 500 g ball, which hits the top of the tree at a speed of 5 m/s and stays in contact with it for 10 ms. The ball falls to the ground near the base of the tree and the recoil of the tree is minimal. (a) What is the force on the tree? (b) The length of the sturdy section of the root is only 20 cm. Furthermore, the soil around the roots is loose and we can assume that an effective force is applied at the tip of the 20 cm length. What is the effective force exerted by the end of the tip of the root to keep the tree from toppling? Assume the tree will be uprooted rather than bend. (c) What could you have done to ensure that the tree does not uproot easily?
Unreasonable Results
Suppose two children are using a uniform seesaw that is 3.00 m long and has its center of mass over the pivot. The first child has a mass of 30.0 kg and sits 1.40 m from the pivot. (a) Calculate where the second 18.0 kg child must sit to balance the seesaw. (b) What is unreasonable about the result? (c) Which premise is unreasonable, or which premises are inconsistent?
a)
b) The seesaw is 3.0 m long, and hence, there is only 1.50 m of board on the other side of the pivot. The second child is off the board.
c) The position of the first child must be shortened, i.e. brought closer to the pivot.
Construct Your Own Problem
Consider a method for measuring the mass of a person’s arm in anatomical studies. The subject lies on her back, extends her relaxed arm to the side and two scales are placed below the arm. One is placed under the elbow and the other under the back of her hand. Construct a problem in which you calculate the mass of the arm and find its center of mass based on the scale readings and the distances of the scales from the shoulder joint. You must include a free body diagram of the arm to direct the analysis. Consider changing the position of the scale under the hand to provide more information, if needed. You may wish to consult references to obtain reasonable mass values.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics 101' conversation and receive update notifications?