| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
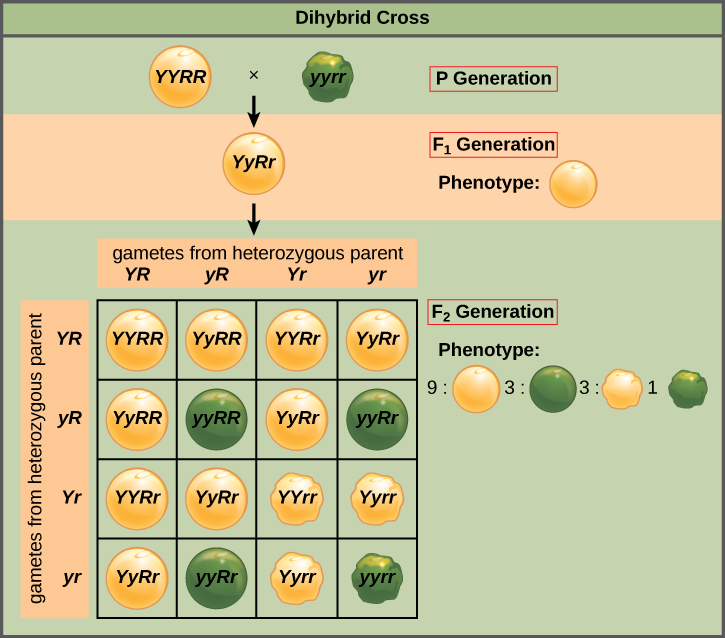
Mendel’s law of independent assortment states that genes do not influence each other with regard to the sorting of alleles into gametes, and every possible combination of alleles for every gene is equally likely to occur. Independent assortment of genes can be illustrated by the dihybrid cross, a cross between two true-breeding parents that express different traits for two characteristics. Consider the characteristics of seed color and seed texture for two pea plants, one that has wrinkled, green seeds ( rryy ) and another that has round, yellow seeds ( RRYY ). Because each parent is homozygous, the law of segregation indicates that the gametes for the wrinkled–green plant all are ry , and the gametes for the round–yellow plant are all RY . Therefore, the F 1 generation of offspring all are RrYy ( [link] ).
In pea plants, purple flowers ( P ) are dominant to white ( p ), and yellow peas ( Y ) are dominant to green ( y ). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a cross between PpYY and ppYy pea plants? How many squares would you need to complete a Punnett square analysis of this cross?
The gametes produced by the F 1 individuals must have one allele from each of the two genes. For example, a gamete could get an R allele for the seed shape gene and either a Y or a y allele for the seed color gene. It cannot get both an R and an r allele; each gamete can have only one allele per gene. The law of independent assortment states that a gamete into which an r allele is sorted would be equally likely to contain either a Y or a y allele. Thus, there are four equally likely gametes that can be formed when the RrYy heterozygote is self-crossed, as follows: RY , rY , Ry , and ry . Arranging these gametes along the top and left of a 4 × 4 Punnett square ( [link] ) gives us 16 equally likely genotypic combinations. From these genotypes, we find a phenotypic ratio of 9 round–yellow:3 round–green:3 wrinkled–yellow:1 wrinkled–green ( [link] ). These are the offspring ratios we would expect, assuming we performed the crosses with a large enough sample size.
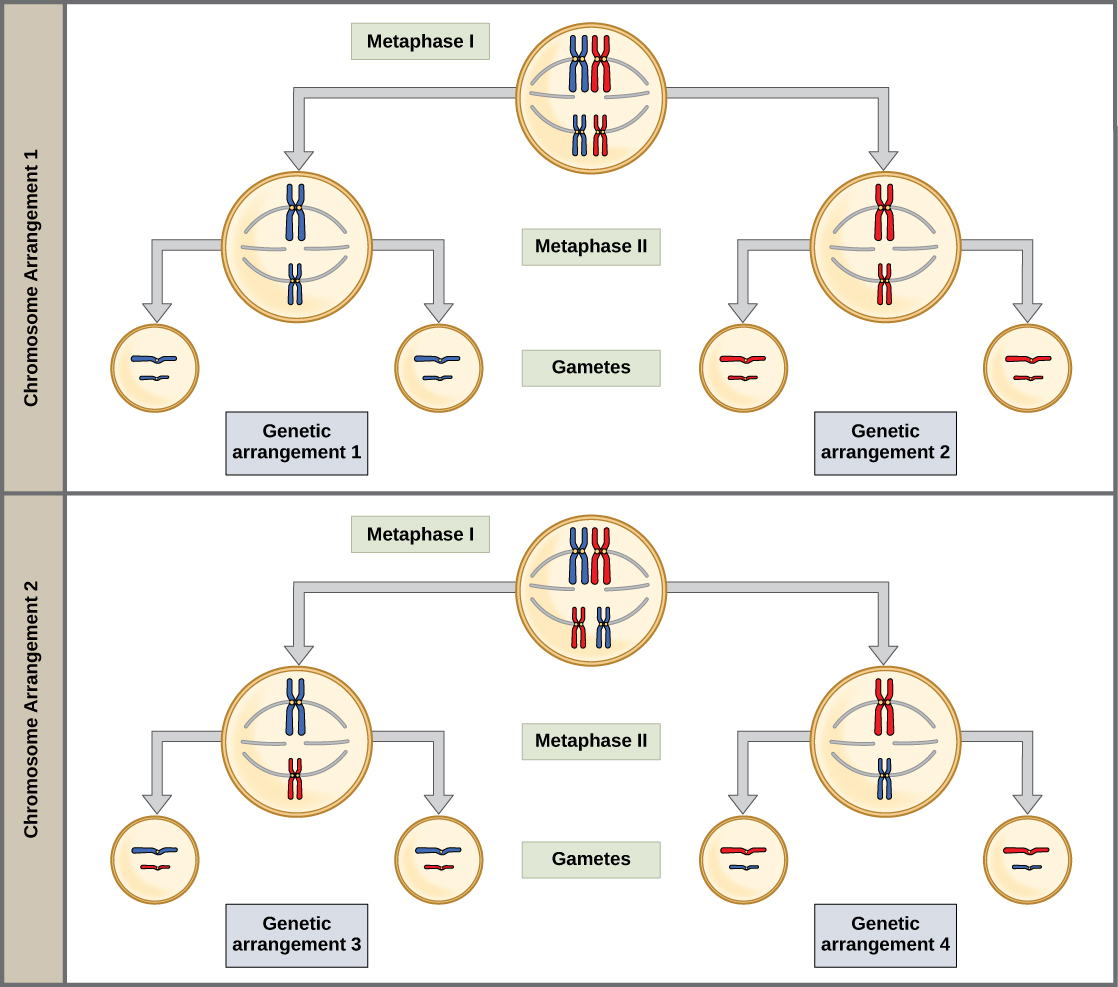
The physical basis for the law of independent assortment also lies in meiosis I, in which the different homologous pairs line up in random orientations. Each gamete can contain any combination of paternal and maternal chromosomes (and therefore the genes on them) because the orientation of tetrads on the metaphase plane is random ( [link] ).
When true-breeding, or homozygous, individuals that differ for a certain trait are crossed, all of the offspring will be heterozygous for that trait. If the traits are inherited as dominant and recessive, the F 1 offspring will all exhibit the same phenotype as the parent homozygous for the dominant trait. If these heterozygous offspring are self-crossed, the resulting F 2 offspring will be equally likely to inherit gametes carrying the dominant or recessive trait, giving rise to offspring of which one quarter are homozygous dominant, half are heterozygous, and one quarter are homozygous recessive. Because homozygous dominant and heterozygous individuals are phenotypically identical, the observed traits in the F 2 offspring will exhibit a ratio of three dominant to one recessive.
Mendel postulated that genes (characteristics) are inherited as pairs of alleles (traits) that behave in a dominant and recessive pattern. Alleles segregate into gametes such that each gamete is equally likely to receive either one of the two alleles present in a diploid individual. In addition, genes are assorted into gametes independently of one another. That is, in general, alleles are not more likely to segregate into a gamete with a particular allele of another gene.
[link] In pea plants, round peas ( R ) are dominant to wrinkled peas ( r ). You do a test cross between a pea plant with wrinkled peas (genotype rr ) and a plant of unknown genotype that has round peas. You end up with three plants, all which have round peas. From this data, can you tell if the parent plant is homozygous dominant or heterozygous?
[link] You cannot be sure if the plant is homozygous or heterozygous as the data set is too small: by random chance, all three plants might have acquired only the dominant gene even if the recessive one is present.
[link] In pea plants, purple flowers ( P ) are dominant to white ( p ), and yellow peas ( Y ) are dominant to green ( y ). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for a cross between PpYY and ppYy pea plants? How many squares would you need to complete a Punnett square analysis of this cross?
[link] The possible genotypes are PpYY , PpYy , ppYY , and ppYy . The former two genotypes would result in plants with purple flowers and yellow peas, while the latter two genotypes would result in plants with white flowers with yellow peas, for a 1:1 ratio of each phenotype. You only need a 2 × 2 Punnett square (four squares total) to do this analysis because two of the alleles are homozygous.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology for slcc biol 1010' conversation and receive update notifications?