| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Eukaryotic cells may contain anywhere from one to several thousand mitochondria, depending on the cell’s level of energy consumption. Each mitochondrion measures 1 to 10 micrometers in length and exists in the cell as a moving, fusing, and dividing oblong spheroid ( [link] ). However, mitochondria cannot survive outside the cell. As the atmosphere was oxygenated by photosynthesis, and as successful aerobic prokaryotes evolved, evidence suggests that an ancestral cell engulfed and kept alive a free-living, aerobic prokaryote. This gave the host cell the ability to use oxygen to release energy stored in nutrients. Several lines of evidence support that mitochondria are derived from this endosymbiotic event. Mitochondria are shaped like a specific group of bacteria and are surrounded by two membranes, which would result when one membrane-bound organism was engulfed by another membrane-bound organism. The mitochondrial inner membrane involves substantial infoldings or cristae that resemble the textured outer surface of certain bacteria.
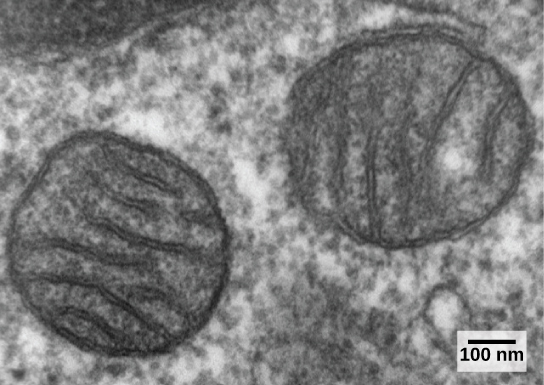
Mitochondria divide on their own by a process that resembles binary fission in prokaryotes. Mitochondria have their own circular DNA chromosome that carries genes similar to those expressed by bacteria. Mitochondria also have special ribosomes and transfer RNAs that resemble these components in prokaryotes. These features all support that mitochondria were once free-living prokaryotes.
Chloroplasts are one type of plastid , a group of related organelles in plant cells that are involved in the storage of starches, fats, proteins, and pigments. Chloroplasts contain the green pigment chlorophyll and play a role in photosynthesis. Genetic and morphological studies suggest that plastids evolved from the endosymbiosis of an ancestral cell that engulfed a photosynthetic cyanobacterium. Plastids are similar in size and shape to cyanobacteria and are enveloped by two or more membranes, corresponding to the inner and outer membranes of cyanobacteria. Like mitochondria, plastids also contain circular genomes and divide by a process reminiscent of prokaryotic cell division. The chloroplasts of red and green algae exhibit DNA sequences that are closely related to photosynthetic cyanobacteria, suggesting that red and green algae are direct descendants of this endosymbiotic event.
Mitochondria likely evolved before plastids because all eukaryotes have either functional mitochondria or mitochondria-like organelles. In contrast, plastids are only found in a subset of eukaryotes, such as terrestrial plants and algae. One hypothesis of the evolutionary steps leading to the first eukaryote is summarized in [link] .
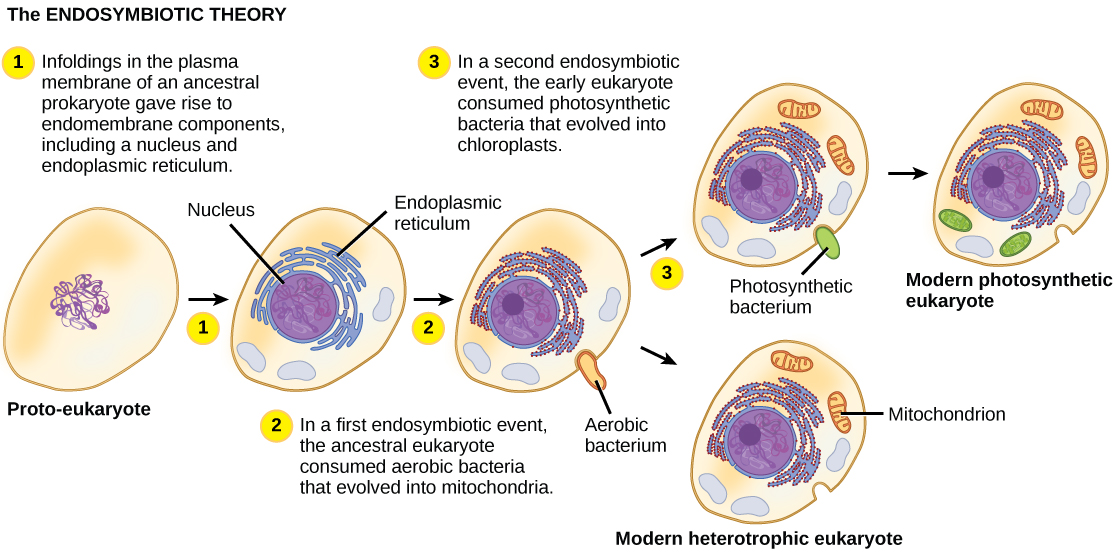
The exact steps leading to the first eukaryotic cell can only be hypothesized, and some controversy exists regarding which events actually took place and in what order. Spirochete bacteria have been hypothesized to have given rise to microtubules, and a flagellated prokaryote may have contributed the raw materials for eukaryotic flagella and cilia. Other scientists suggest that membrane proliferation and compartmentalization, not endosymbiotic events, led to the development of mitochondria and plastids. However, the vast majority of studies support the endosymbiotic hypothesis of eukaryotic evolution.
The early eukaryotes were unicellular like most protists are today, but as eukaryotes became more complex, the evolution of multicellularity allowed cells to remain small while still exhibiting specialized functions. The ancestors of today’s multicellular eukaryotes are thought to have evolved about 1.5 billion years ago.
The first eukaryotes evolved from ancestral prokaryotes by a process that involved membrane proliferation, the loss of a cell wall, the evolution of a cytoskeleton, and the acquisition and evolution of organelles. Nuclear eukaryotic genes appear to have had an origin in the Archaea, whereas the energy machinery of eukaryotic cells appears to be bacterial in origin. The mitochondria and plastids originated from endosymbiotic events when ancestral cells engulfed an aerobic bacterium (in the case of mitochondria) and a photosynthetic bacterium (in the case of chloroplasts). The evolution of mitochondria likely preceded the evolution of chloroplasts. There is evidence of secondary endosymbiotic events in which plastids appear to be the result of endosymbiosis after a previous endosymbiotic event.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural history supplemental' conversation and receive update notifications?