| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In land plants, a waxy, waterproof cover called a cuticle coats the aerial parts of the plant: leaves and stems. The cuticle also prevents intake of carbon dioxide needed for the synthesis of carbohydrates through photosynthesis. Stomata, or pores, that open and close to regulate traffic of gases and water vapor therefore appeared in plants as they moved into drier habitats.
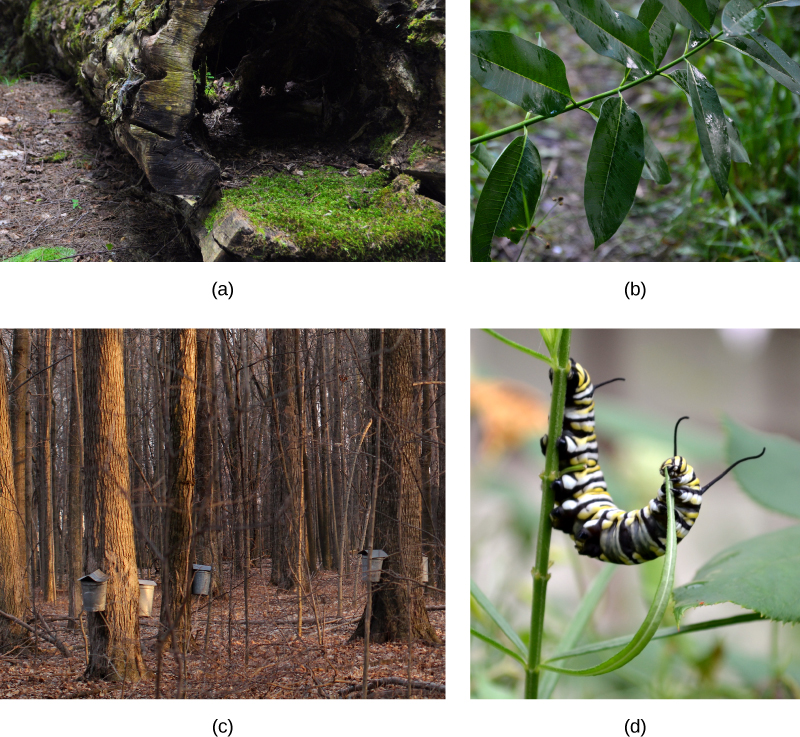
Plants cannot avoid predatory animals. Instead, they synthesize a large range of poisonous secondary metabolites: complex organic molecules such as alkaloids, whose noxious smells and unpleasant taste deter animals. These toxic compounds can cause severe diseases and even death.
Additionally, as plants coevolved with animals, sweet and nutritious metabolites were developed to lure animals into providing valuable assistance in dispersing pollen grains, fruit, or seeds. Plants have been coevolving with animal associates for hundreds of millions of years ( [link] ).

One of the most exciting recent developments in paleobotany is the use of analytical chemistry and molecular biology to study fossils. Preservation of molecular structures requires an environment free of oxygen, since oxidation and degradation of material through the activity of microorganisms depend on the presence of oxygen. One example of the use of analytical chemistry and molecular biology is in the identification of oleanane, a compound that deters pests and which, up to this point, appears to be unique to flowering plants. Oleanane was recovered from sediments dating from the Permian, much earlier than the current dates given for the appearance of the first flowering plants. Fossilized nucleic acids—DNA and RNA—yield the most information. Their sequences are analyzed and compared to those of living and related organisms. Through this analysis, evolutionary relationships can be built for plant lineages.
Some paleobotanists are skeptical of the conclusions drawn from the analysis of molecular fossils. For one, the chemical materials of interest degrade rapidly during initial isolation when exposed to air, as well as in further manipulations. There is always a high risk of contaminating the specimens with extraneous material, mostly from microorganisms. Nevertheless, as technology is refined, the analysis of DNA from fossilized plants will provide invaluable information on the evolution of plants and their adaptation to an ever-changing environment.

Land plants are classified into two major groups according to the absence or presence of vascular tissue, as detailed in [link] . Plants that lack vascular tissue formed of specialized cells for the transport of water and nutrients are referred to as nonvascular plants . The bryophytes, liverworts, mosses, and hornworts are seedless and nonvascular, and likely appeared early in land plant evolution. Vascular plants developed a network of cells that conduct water and solutes through the plant body. The first vascular plants appeared in the late Ordovician (461–444 million years ago) and were probably similar to lycophytes, which include club mosses (not to be confused with the mosses) and the pterophytes (ferns, horsetails, and whisk ferns). Lycophytes and pterophytes are referred to as seedless vascular plants. They do not produce seeds, which are embryos with their stored food reserves protected by a hard casing. The seed plants form the largest group of all existing plants and, hence, dominate the landscape. Seed plants include gymnosperms, most notably conifers, which produce “naked seeds,” and the most successful plants, the flowering plants, or angiosperms, which protect their seeds inside chambers at the center of a flower. The walls of these chambers later develop into fruits.
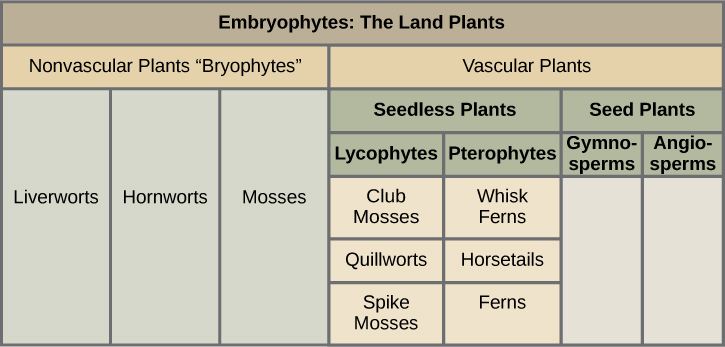
Land plants evolved traits that made it possible to colonize land and survive out of water. Adaptations to life on land include vascular tissues, roots, leaves, waxy cuticles, and a tough outer layer that protects the spores. Land plants include nonvascular plants and vascular plants. Vascular plants, which include seedless plants and plants with seeds, have apical meristems, and embryos with nutritional stores. All land plants share the following characteristics: alternation of generations, with the haploid plant called a gametophyte and the diploid plant called a sporophyte; formation of haploid spores in a sporangium; and formation of gametes in a gametangium.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University of georgia biology' conversation and receive update notifications?