| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
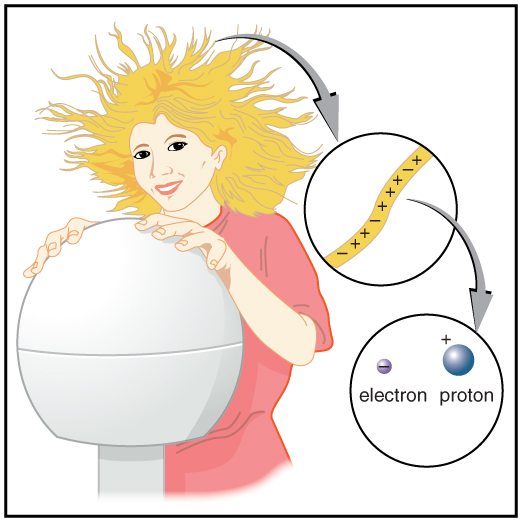
[link] shows a person touching a Van de Graaff generator and receiving excess positive charge. The expanded view of a hair shows the existence of both types of charges but an excess of positive. The repulsion of these positive like charges causes the strands of hair to repel other strands of hair and to stand up. The further blowup shows an artist’s conception of an electron and a proton perhaps found in an atom in a strand of hair.
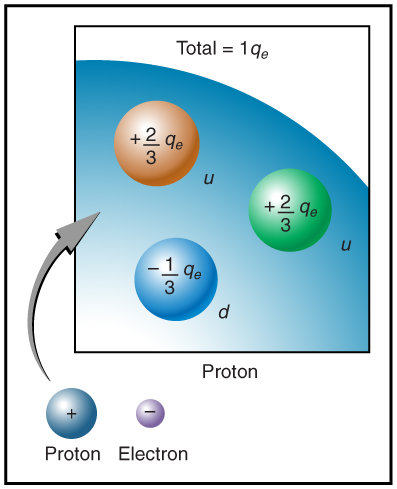
The electron seems to have no substructure; in contrast, when the substructure of protons is explored by scattering extremely energetic electrons from them, it appears that there are point-like particles inside the proton. These sub-particles, named quarks, have never been directly observed, but they are believed to carry fractional charges as seen in [link] . Charges on electrons and protons and all other directly observable particles are unitary, but these quark substructures carry charges of either or . There are continuing attempts to observe fractional charge directly and to learn of the properties of quarks, which are perhaps the ultimate substructure of matter.
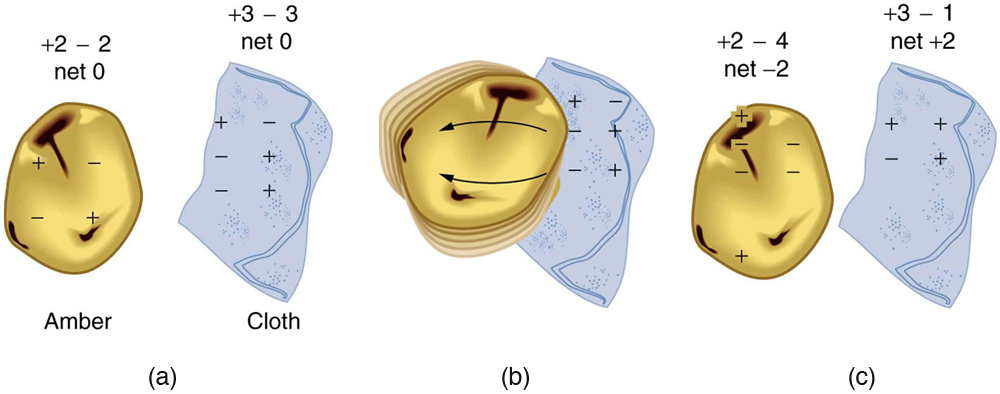
Charges in atoms and molecules can be separated—for example, by rubbing materials together. Some atoms and molecules have a greater affinity for electrons than others and will become negatively charged by close contact in rubbing, leaving the other material positively charged. (See [link] .) Positive charge can similarly be induced by rubbing. Methods other than rubbing can also separate charges. Batteries, for example, use combinations of substances that interact in such a way as to separate charges. Chemical interactions may transfer negative charge from one substance to the other, making one battery terminal negative and leaving the first one positive.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introductory physics - for kpu phys 1100 (2015 edition)' conversation and receive update notifications?