| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Which of the following statements about bone tissue is false?
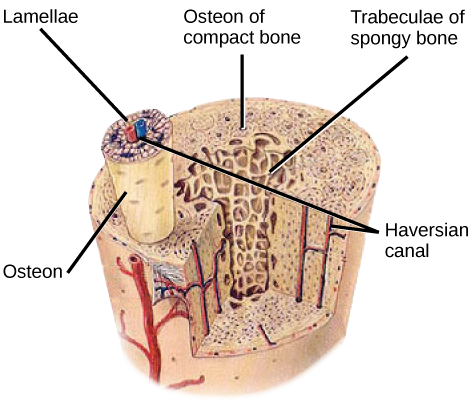
Whereas compact bone tissue forms the outer layer of all bones, spongy bone or cancellous bone forms the inner layer of all bones. Spongy bone tissue does not contain osteons that constitute compact bone tissue. Instead, it consists of trabeculae , which are lamellae that are arranged as rods or plates. Red bone marrow is found between the trabuculae. Blood vessels within this tissue deliver nutrients to osteocytes and remove waste. The red bone marrow of the femur and the interior of other large bones, such as the ileum, forms blood cells.
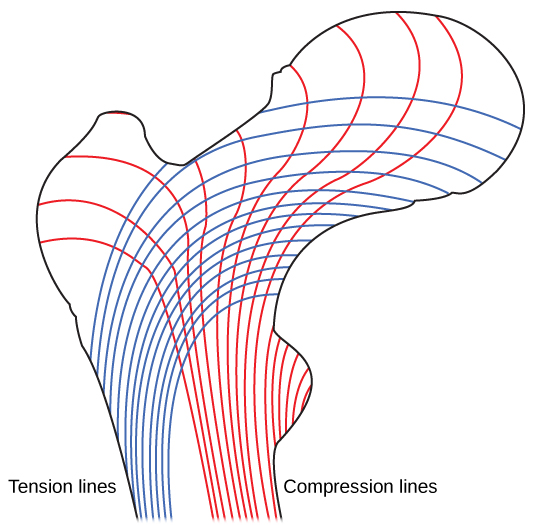
Spongy bone reduces the density of bone and allows the ends of long bones to compress as the result of stresses applied to the bone. Spongy bone is prominent in areas of bones that are not heavily stressed or where stresses arrive from many directions. The epiphyses of bones, such as the neck of the femur, are subject to stress from many directions. Imagine laying a heavy framed picture flat on the floor. You could hold up one side of the picture with a toothpick if the toothpick was perpendicular to the floor and the picture. Now drill a hole and stick the toothpick into the wall to hang up the picture. In this case, the function of the toothpick is to transmit the downward pressure of the picture to the wall. The force on the picture is straight down to the floor, but the force on the toothpick is both the picture wire pulling down and the bottom of the hole in the wall pushing up. The toothpick will break off right at the wall.
The neck of the femur is horizontal like the toothpick in the wall. The weight of the body pushes it down near the joint, but the vertical diaphysis of the femur pushes it up at the other end. The neck of the femur must be strong enough to transfer the downward force of the body weight horizontally to the vertical shaft of the femur ( [link] ).
View micrographs of musculoskeletal tissues as you review the anatomy.
Bone consists of four types of cells: osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes, and osteoprogenitor cells. Osteoblasts are bone cells that are responsible for bone formation. Osteoblasts synthesize and secrete the organic part and inorganic part of the extracellular matrix of bone tissue, and collagen fibers. Osteoblasts become trapped in these secretions and differentiate into less active osteocytes. Osteoclasts are large bone cells with up to 50 nuclei. They remove bone structure by releasing lysosomal enzymes and acids that dissolve the bony matrix. These minerals, released from bones into the blood, help regulate calcium concentrations in body fluids. Bone may also be resorbed for remodeling, if the applied stresses have changed. Osteocytes are mature bone cells and are the main cells in bony connective tissue; these cells cannot divide. Osteocytes maintain normal bone structure by recycling the mineral salts in the bony matrix. Osteoprogenitor cells are squamous stem cells that divide to produce daughter cells that differentiate into osteoblasts. Osteoprogenitor cells are important in the repair of fractures.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bmcc 103 - concepts of biology' conversation and receive update notifications?