| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this module we examine how electromagnetic waves are classified into categories such as radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and so on, so that we can understand some of their similarities as well as some of their differences. We will also find that there are many connections with previously discussed topics, such as wavelength and resonance. A brief overview of the production and utilization of electromagnetic waves is found in [link] .
| Type of EM wave | Production | Applications | Life sciences aspect | Issues |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radio&TV | Accelerating charges | Communications Remote controls | MRI | Requires controls for band use |
| Microwaves | Accelerating charges&thermal agitation | Communications Ovens Radar | Deep heating | Cell phone use |
| Infrared | Thermal agitations&electronic transitions | Thermal imaging Heating | Absorbed by atmosphere | Greenhouse effect |
| Visible light | Thermal agitations&electronic transitions | All pervasive | Photosynthesis Human vision | |
| Ultraviolet | Thermal agitations&electronic transitions | Sterilization Cancer control | Vitamin D production | Ozone depletion Cancer causing |
| X-rays | Inner electronic transitions and fast collisions | Medical Security | Medical diagnosis Cancer therapy | Cancer causing |
| Gamma rays | Nuclear decay | Nuclear medicineSecurity | Medical diagnosis Cancer therapy | Cancer causing Radiation damage |
There are many types of waves, such as water waves and even earthquakes. Among the many shared attributes of waves are propagation speed, frequency, and wavelength. These are always related by the expression . This module concentrates on EM waves, but other modules contain examples of all of these characteristics for sound waves and submicroscopic particles.
As noted before, an electromagnetic wave has a frequency and a wavelength associated with it and travels at the speed of light, or . The relationship among these wave characteristics can be described by , where is the propagation speed of the wave, is the frequency, and is the wavelength. Here , so that for all electromagnetic waves,
Thus, for all electromagnetic waves, the greater the frequency, the smaller the wavelength.
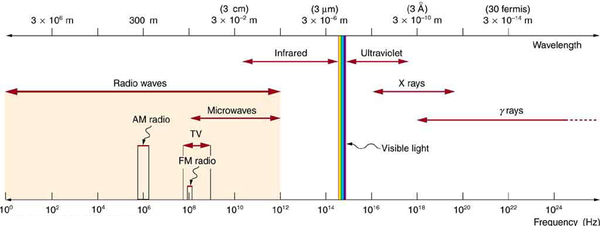
[link] shows how the various types of electromagnetic waves are categorized according to their wavelengths and frequencies—that is, it shows the electromagnetic spectrum. Many of the characteristics of the various types of electromagnetic waves are related to their frequencies and wavelengths, as we shall see.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General physics ii phy2202ca' conversation and receive update notifications?