| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Inside the cell, ligands bind to their internal receptors, allowing them to directly affect the cell’s DNA and protein-producing machinery. Using signal transduction pathways, receptors in the plasma membrane produce a variety of effects on the cell. The results of signaling pathways are extremely varied and depend on the type of cell involved as well as the external and internal conditions. A small sampling of responses is described below.
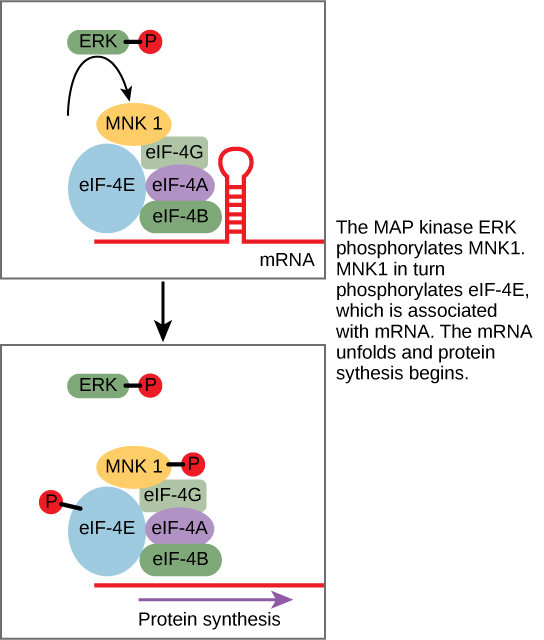
Some signal transduction pathways regulate the transcription of RNA. Others regulate the translation of proteins from mRNA. An example of a protein that regulates translation in the nucleus is the MAP kinase ERK. ERK is activated in a phosphorylation cascade when epidermal growth factor (EGF) binds the EGF receptor (see [link] ). Upon phosphorylation, ERK enters the nucleus and activates a protein kinase that, in turn, regulates protein translation ( [link] ).
The second kind of protein with which PKC can interact is a protein that acts as an inhibitor. An inhibitor is a molecule that binds to a protein and prevents it from functioning or reduces its function. In this case, the inhibitor is a protein called Iκ-B, which binds to the regulatory protein NF-κB. (The symbol κ represents the Greek letter kappa.) When Iκ-B is bound to NF-κB, the complex cannot enter the nucleus of the cell, but when Iκ-B is phosphorylated by PKC, it can no longer bind NF-κB, and NF-κB (a transcription factor) can enter the nucleus and initiate RNA transcription. In this case, the effect of phosphorylation is to inactivate an inhibitor and thereby activate the process of transcription.
The result of another signaling pathway affects muscle cells. The activation of β-adrenergic receptors in muscle cells by adrenaline leads to an increase in cyclic AMP (cAMP) inside the cell. Also known as epinephrine, adrenaline is a hormone (produced by the adrenal gland attached to the kidney) that readies the body for short-term emergencies. Cyclic AMP activates PKA (protein kinase A), which in turn phosphorylates two enzymes. The first enzyme promotes the degradation of glycogen by activating intermediate glycogen phosphorylase kinase (GPK) that in turn activates glycogen phosphorylase (GP) that catabolizes glycogen into glucose. (Recall that your body converts excess glucose to glycogen for short-term storage. When energy is needed, glycogen is quickly reconverted to glucose.) Phosphorylation of the second enzyme, glycogen synthase (GS), inhibits its ability to form glycogen from glucose. In this manner, a muscle cell obtains a ready pool of glucose by activating its formation via glycogen degradation and by inhibiting the use of glucose to form glycogen, thus preventing a futile cycle of glycogen degradation and synthesis. The glucose is then available for use by the muscle cell in response to a sudden surge of adrenaline—the “fight or flight” reflex.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ap biology - part 1: the cell' conversation and receive update notifications?