| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
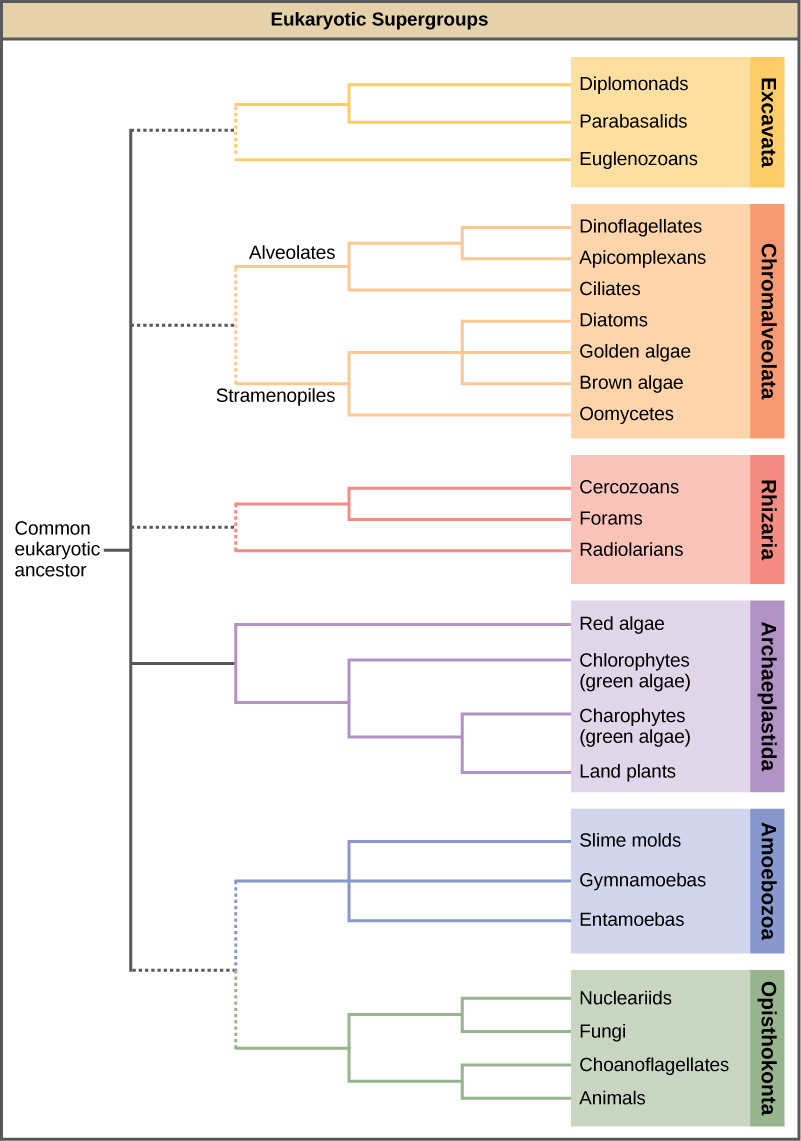
With the advent of DNA sequencing, the relationships among protist groups and between protist groups and other eukaryotes are beginning to become clearer. Many relationships that were based on morphological similarities are being replaced by new relationships based on genetic similarities. Protists that exhibit similar morphological features may have evolved analogous structures because of similar selective pressures—rather than because of recent common ancestry. This phenomenon is called convergent evolution. It is one reason why protist classification is so challenging. The emerging classification scheme groups the entire domain Eukaryota into six “supergroups” that contain all of the protists as well as animals, plants, and fungi ( [link] ); these include the Excavata , Chromalveolata , Rhizaria , Archaeplastida , Amoebozoa , and Opisthokonta . The supergroups are believed to be monophyletic; all organisms within each supergroup are believed to have evolved from a single common ancestor, and thus all members are most closely related to each other than to organisms outside that group. There is still evidence lacking for the monophyly of some groups.
Many protists are pathogenic parasites that must infect other organisms to survive and propagate. Protist parasites include the causative agents of malaria, African sleeping sickness, and waterborne gastroenteritis in humans. Other protist pathogens prey on plants, effecting massive destruction of food crops.
Members of the genus Plasmodium must infect a mosquito and a vertebrate to complete their life cycle. In vertebrates, the parasite develops in liver cells and goes on to infect red blood cells, bursting from and destroying the blood cells with each asexual replication cycle ( [link] ). Of the four Plasmodium species known to infect humans, P . falciparum accounts for 50 percent of all malaria cases and is the primary cause of disease-related fatalities in tropical regions of the world. In 2010, it was estimated that malaria caused between 0.5 and 1 million deaths, mostly in African children. During the course of malaria, P . falciparum can infect and destroy more than one-half of a human’s circulating blood cells, leading to severe anemia. In response to waste products released as the parasites burst from infected blood cells, the host immune system mounts a massive inflammatory response with delirium-inducing fever episodes, as parasites destroy red blood cells, spilling parasite waste into the blood stream. P . falciparum is transmitted to humans by the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae . Techniques to kill, sterilize, or avoid exposure to this highly aggressive mosquito species are crucial to malaria control.
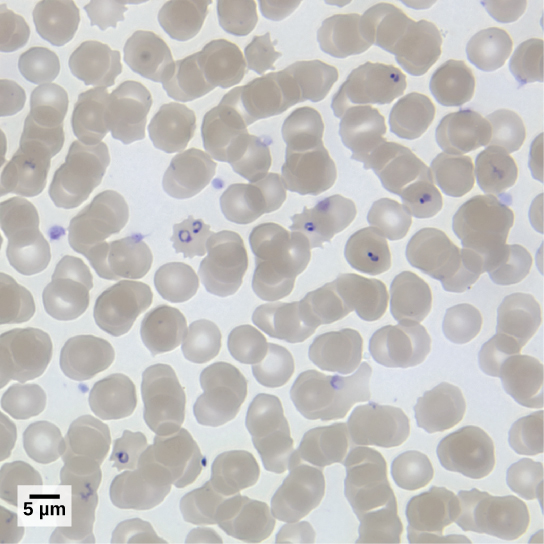
This movie depicts the pathogenesis of Plasmodium falciparum , the causative agent of malaria.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University of georgia biology' conversation and receive update notifications?