| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Under what circumstances, if any, does a sample of solid AgCl completely dissolve in pure water?
when the amount of solid is so small that a saturated solution is not produced
Explain why the addition of NH 3 or HNO 3 to a saturated solution of Ag 2 CO 3 in contact with solid Ag 2 CO 3 increases the solubility of the solid.
Calculate the cadmium ion concentration, [Cd 2+ ], in a solution prepared by mixing 0.100 L of 0.0100 M Cd(NO 3 ) 2 with 1.150 L of 0.100 NH 3 ( aq ).
8 10 –5 M
Explain why addition of NH 3 or HNO 3 to a saturated solution of Cu(OH) 2 in contact with solid Cu(OH) 2 increases the solubility of the solid.
Sometimes equilibria for complex ions are described in terms of dissociation constants, K d . For the complex ion the dissociation reaction is:
and
Calculate the value of the formation constant, K f , for
5 10 23
Using the value of the formation constant for the complex ion calculate the dissociation constant.
Using the dissociation constant, K d = 7.8 10 –18 , calculate the equilibrium concentrations of Cd 2+ and CN – in a 0.250- M solution of
![This table has two main columns and three rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ) and Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header, “[ C d ( C N ) subscript 4 to the second power superscript negative sign ] [ C N superscript negative sign ] [ C d to the second power superscript positive sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of two rows and three columns. The first column contains the following: 0.250 and 0.250 minus x. The second column contains the following: 0 and 4 x. The third column contains the following: 0 and x.](/ocw/mirror/col11830_1.13_complete/m51131/CNX_Chem_15_02_ICETable3_img.jpg)
[Cd
2+ ] = 9.5
10
–5
M ; [CN
– ] = 3.8
10
–4
M
Using the dissociation constant, K d = 3.4 10 –15 , calculate the equilibrium concentrations of Zn 2+ and OH – in a 0.0465- M solution of
Using the dissociation constant, K d = 2.2 10 –34 , calculate the equilibrium concentrations of Co 3+ and NH 3 in a 0.500- M solution of
[Co 3+ ] = 3.0 10 –6 M ; [NH 3 ] = 1.8 10 –5 M
Using the dissociation constant, K d = 1 10 –44 , calculate the equilibrium concentrations of Fe 3+ and CN – in a 0.333 M solution of
Calculate the mass of potassium cyanide ion that must be added to 100 mL of solution to dissolve 2.0 10 –2 mol of silver cyanide, AgCN.
1.3 g
Calculate the minimum concentration of ammonia needed in 1.0 L of solution to dissolve 3.0 10 –3 mol of silver bromide.
A roll of 35-mm black and white photographic film contains about 0.27 g of unexposed AgBr before developing. What mass of Na 2 S 2 O 3 ·5H 2 O (sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate or hypo) in 1.0 L of developer is required to dissolve the AgBr as ( K f = 4.7 10 13 )?
0.79 g
We have seen an introductory definition of an acid: An acid is a compound that reacts with water and increases the amount of hydronium ion present. In the chapter on acids and bases, we saw two more definitions of acids: a compound that donates a proton (a hydrogen ion, H + ) to another compound is called a Brønsted-Lowry acid, and a Lewis acid is any species that can accept a pair of electrons. Explain why the introductory definition is a macroscopic definition, while the Brønsted-Lowry definition and the Lewis definition are microscopic definitions.
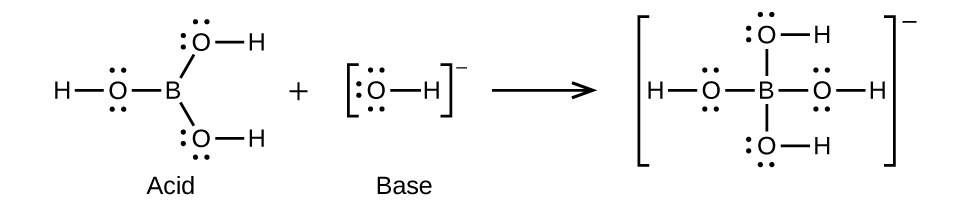
Write the Lewis structures of the reactants and product of each of the following equations, and identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base in each:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d) (use Al-Cl single bonds)
(e)
(a)
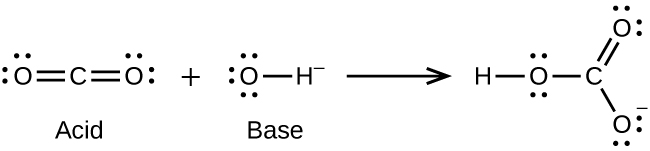 ;
;
(b)
 ;
;
(c)
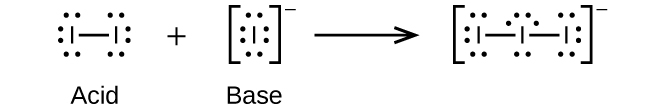 ;
;
(d)
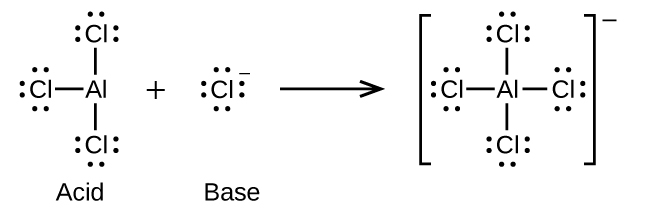 ;
;
(e)
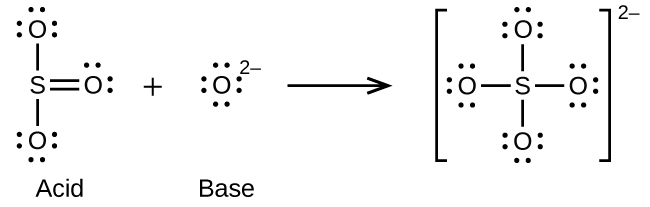
Write the Lewis structures of the reactants and product of each of the following equations, and identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base in each:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
Using Lewis structures, write balanced equations for the following reactions:
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(a)
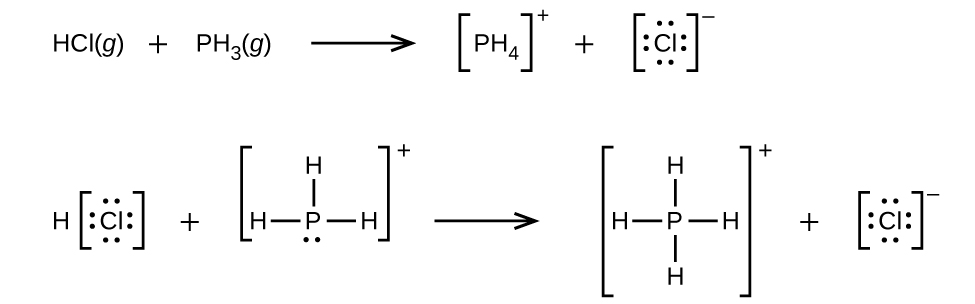 ;
;
(b)
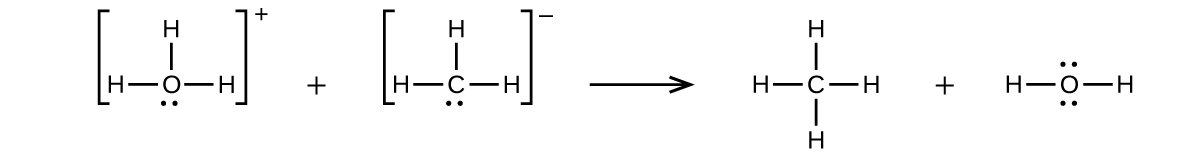 ;
;
(c)
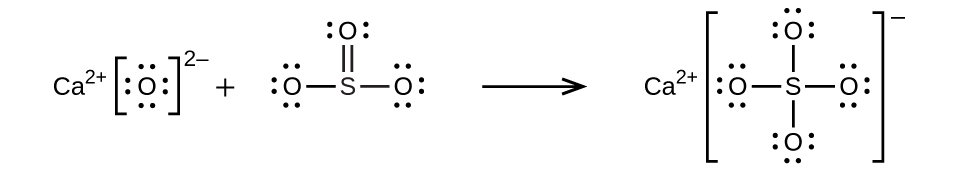 ;
;
(d)
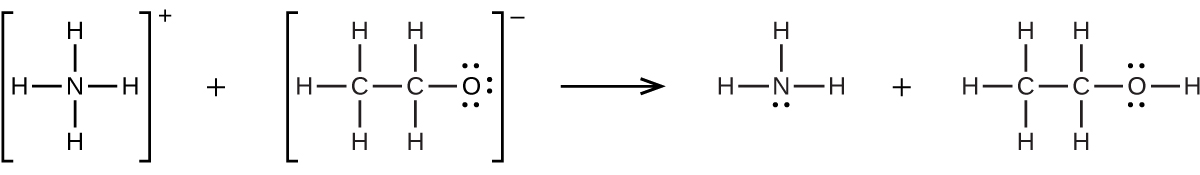
Calculate in a solution prepared by adding 0.0200 mol of NaCl to 0.250 L of a 0.100- M HgCl 2 solution.
In a titration of cyanide ion, 28.72 mL of 0.0100 M AgNO 3 is added before precipitation begins. [The reaction of Ag + with CN – goes to completion, producing the complex.] Precipitation of solid AgCN takes place when excess Ag + is added to the solution, above the amount needed to complete the formation of How many grams of NaCN were in the original sample?
0.0281 g
What are the concentrations of Ag + , CN – , and in a saturated solution of AgCN?
In dilute aqueous solution HF acts as a weak acid. However, pure liquid HF (boiling point = 19.5 °C) is a strong acid. In liquid HF, HNO 3 acts like a base and accepts protons. The acidity of liquid HF can be increased by adding one of several inorganic fluorides that are Lewis acids and accept F – ion (for example, BF 3 or SbF 5 ). Write balanced chemical equations for the reaction of pure HNO 3 with pure HF and of pure HF with BF 3 .
The simplest amino acid is glycine, H 2 NCH 2 CO 2 H. The common feature of amino acids is that they contain the functional groups: an amine group, –NH 2 , and a carboxylic acid group, –CO 2 H. An amino acid can function as either an acid or a base. For glycine, the acid strength of the carboxyl group is about the same as that of acetic acid, CH 3 CO 2 H, and the base strength of the amino group is slightly greater than that of ammonia, NH 3 .
(a) Write the Lewis structures of the ions that form when glycine is dissolved in 1 M HCl and in 1 M KOH.
(b) Write the Lewis structure of glycine when this amino acid is dissolved in water. (Hint: Consider the relative base strengths of the –NH 2 and groups.)
Boric acid, H 3 BO 3 , is not a Brønsted-Lowry acid but a Lewis acid.
(a) Write an equation for its reaction with water.
(b) Predict the shape of the anion thus formed.
(c) What is the hybridization on the boron consistent with the shape you have predicted?
(a) (b) The electronic and molecular shapes are the same—both tetrahedral. (c) The tetrahedral structure is consistent with sp 3 hybridization.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ut austin - principles of chemistry' conversation and receive update notifications?