| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
For this exercise, you will extend the system from Audio Effects: Using External Memory to generate a feedback-echo effect. You will then extend this echo effect to use the serial port on the DSP EVM. The serialinterface will receive data from a MATLAB GUI that allows the two system gains and the echo delay to be changed usingon-screen sliders.
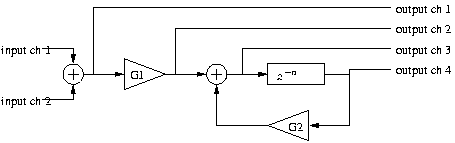
First, modify code from Audio Effects: Using External Memory to create the feedback-echo system shown in [link] . A one-tap feedback-echo is a simple audio effect that soundsremarkably good. You will use both channels of input by summing the two inputs so that either or both may be used asan input to the system. Also, send several test signals to the six-channel board's D/A converters:
You will also need to set both the input gain and the feedback gain to prevent overflow.
As you implement this code, ensure that the delay
n and the gain values
and
are stored in memory and can be easily changed
using the debugger. If you do this, it will be easier toextend your code to accept its parameters from MATLAB in
MATLAB Interface
Implementation .
To test your echo, connect a CD player or microphone to the input of the DSP EVM, and connect the output of the DSP EVMto a loudspeaker. Verify that an input signal echoes multiple times in the output and that the spacing betweenechoes matches the delay length you have chosen.
After studying the MATLAB interface outlined at the end of
Using the Serial Port with a MATLAB GUI , write MATLAB code
to send commands to the serial interface based on threesliders: two gain sliders (for
and
) and one delay slider (for
n ). Then
modify your code to accept those commands and change thevalues for
,
and
n . Make sure that
n can be set to values spanning the full range of 0 to
131,072, although it is not necessary that every number inthat range be represented.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Dsp laboratory with ti tms320c54x' conversation and receive update notifications?