| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Let us consider various types of two-object collisions. These collisions are the easiest to analyze, and they illustrate many of the physical principles involved in collisions. The conservation of momentum principle is very useful here, and it can be used whenever the net external force on a system is zero.
We start with the elastic collision of two objects moving along the same line—a one-dimensional problem. An elastic collision is one that also conserves internal kinetic energy. Internal kinetic energy is the sum of the kinetic energies of the objects in the system. [link] illustrates an elastic collision in which internal kinetic energy and momentum are conserved.
Truly elastic collisions can only be achieved with subatomic particles, such as electrons striking nuclei. Macroscopic collisions can be very nearly, but not quite, elastic—some kinetic energy is always converted into other forms of energy such as heat transfer due to friction and sound. One macroscopic collision that is nearly elastic is that of two steel blocks on ice. Another nearly elastic collision is that between two carts with spring bumpers on an air track. Icy surfaces and air tracks are nearly frictionless, more readily allowing nearly elastic collisions on them.
An elastic collision is one that conserves internal kinetic energy.
Internal kinetic energy is the sum of the kinetic energies of the objects in the system.
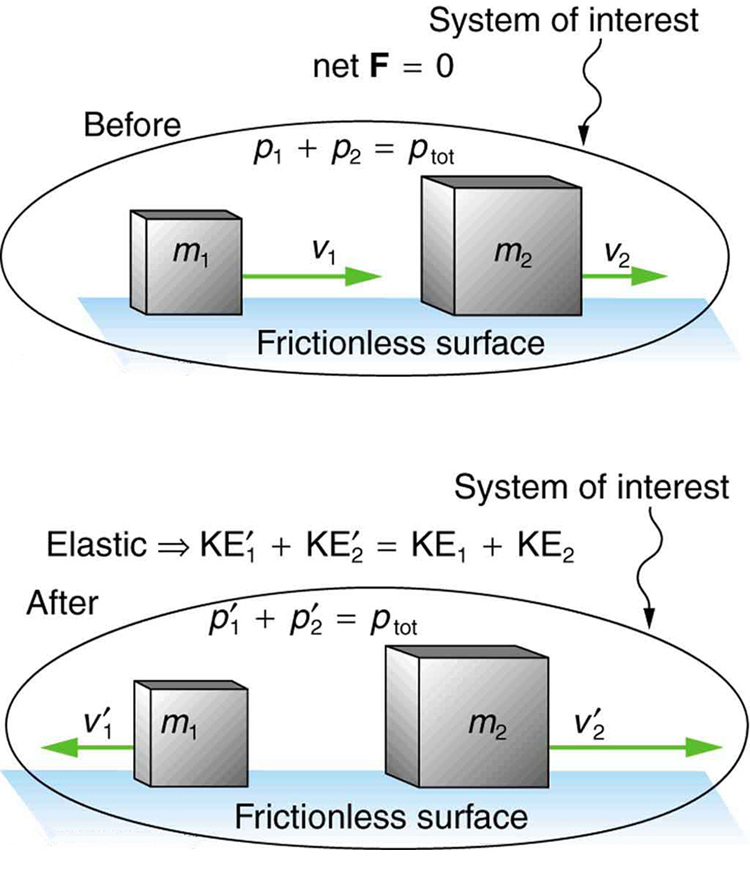
Now, to solve problems involving one-dimensional elastic collisions between two objects we can use the equations for conservation of momentum and conservation of internal kinetic energy. First, the equation for conservation of momentum for two objects in a one-dimensional collision is
or
where the primes (') indicate values after the collision. By definition, an elastic collision conserves internal kinetic energy, and so the sum of kinetic energies before the collision equals the sum after the collision. Thus,
expresses the equation for conservation of internal kinetic energy in a one-dimensional collision.
Calculate the velocities of two objects following an elastic collision, given that
Strategy and Concept
First, visualize what the initial conditions mean—a small object strikes a larger object that is initially at rest. This situation is slightly simpler than the situation shown in [link] where both objects are initially moving. We are asked to find two unknowns (the final velocities and ). To find two unknowns, we must use two independent equations. Because this collision is elastic, we can use the above two equations. Both can be simplified by the fact that object 2 is initially at rest, and thus . Once we simplify these equations, we combine them algebraically to solve for the unknowns.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to applied math and physics' conversation and receive update notifications?