| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
331
814
61,118
10,000
Find the difference between 88,526 and 26,412.
62,114
In each of these problems, each bottom digit is less than the corresponding top digit. This may not always be the case. We will examine the case where the bottom digit is greater than the corresponding top digit in the next section.
We do not have a name for . We need to rename 84 in order to continue. We'll do so as follows:
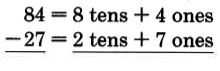
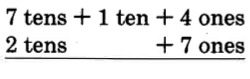
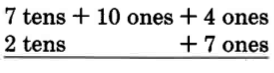
Our new name for 84 is 7 tens + 14 ones.
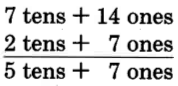
Notice that we converted 8 tens to 7 tens + 1 ten, and then we converted the 1 ten to 10 ones. We then had 14 ones and were able to perform the subtraction.
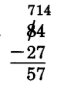
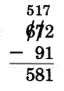
Perform the following subtractions. Show the expanded form for the first three problems.
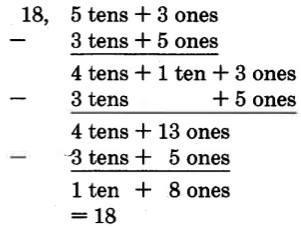
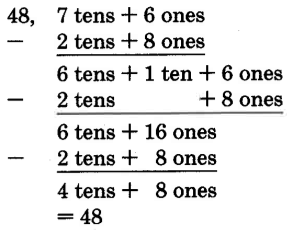
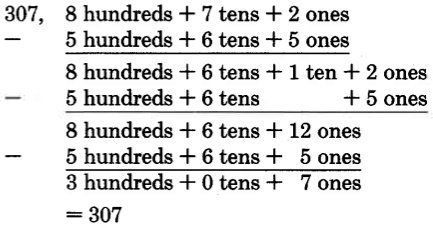
85
709
3,104
Perform the Subtractions. Borrowing more than once if necessary


After borrowing, we have

Perform the following subtractions.
168
55,640
1,189
It often happens in a subtraction problem that we have to borrow from one or more zeros. This occurs in problems such as
We'll examine each case.
Consider the problem
Since we do not have a name for , we must borrow from 0.
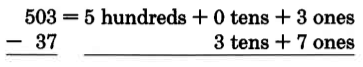
Since there are no tens to borrow, we must borrow 1 hundred. One hundred = 10 tens.

We can now borrow 1 ten from 10 tens (leaving 9 tens). One ten = 10 ones and 10 ones + 3 ones = 13 ones.
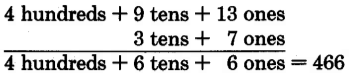
Now we can suggest the following method for borrowing from a single zero.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Contemporary math applications' conversation and receive update notifications?