| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
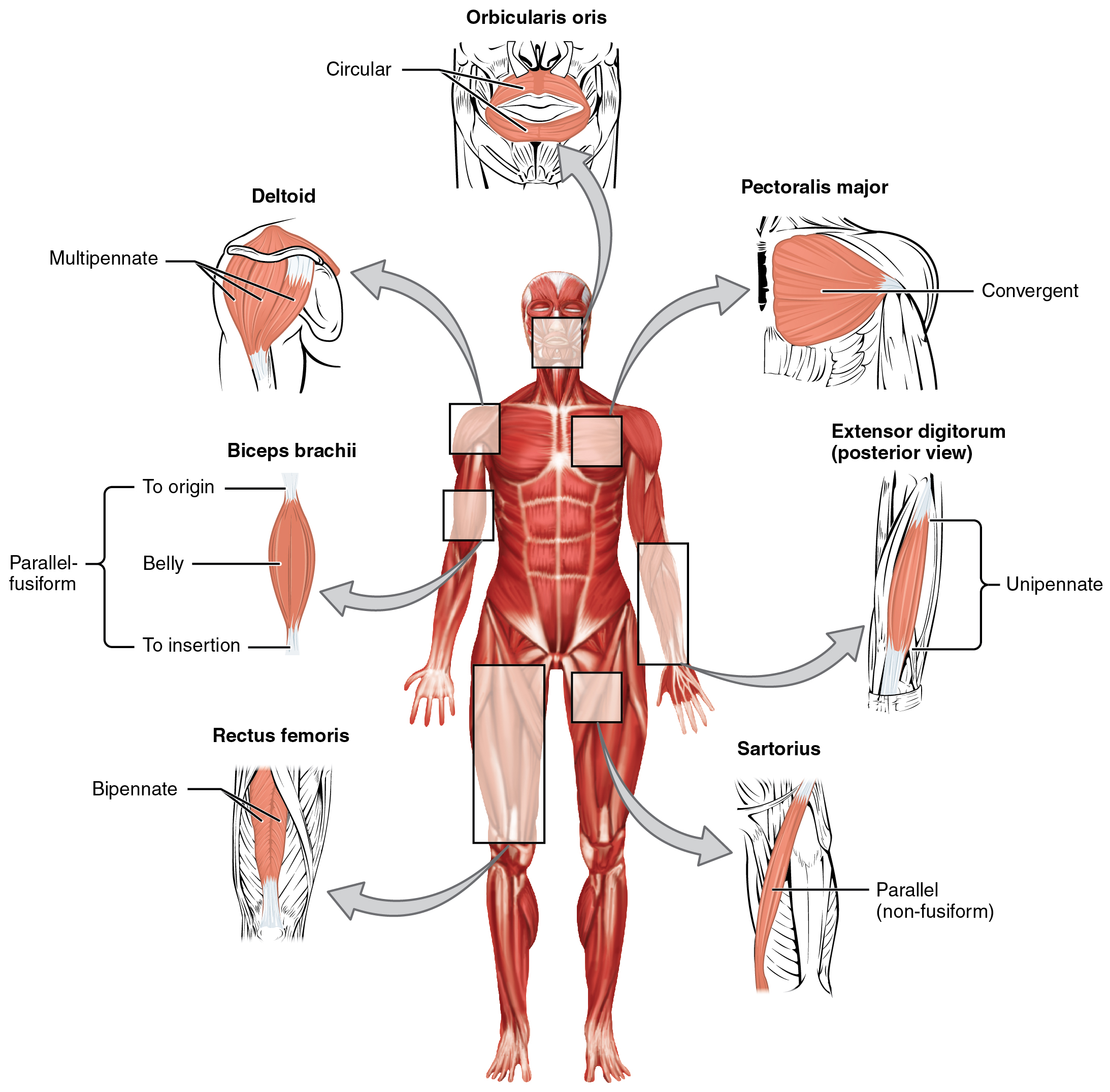

Circular muscles are also called sphincters (see [link] ). When they relax, the sphincters’ concentrically arranged bundles of muscle fibers increase the size of the opening, and when they contract, the size of the opening shrinks to the point of closure. The orbicularis oris muscle is a circular muscle that goes around the mouth. When it contracts, the oral opening becomes smaller, as when puckering the lips for whistling. Another example is the orbicularis oculi, one of which surrounds each eye. Consider, for example, the names of the two orbicularis muscles (orbicularis oris and oribicularis oculi), where part of the first name of both muscles is the same. The first part of orbicularis, orb (orb = “circular”), is a reference to a round or circular structure; it may also make one think of orbit, such as the moon’s path around the earth. The word oris (oris = “oral”) refers to the oral cavity, or the mouth. The word oculi (ocular = “eye”) refers to the eye.
There are other muscles throughout the body named by their shape or location. The deltoid is a large, triangular-shaped muscle that covers the shoulder. It is so-named because the Greek letter delta looks like a triangle. The rectus abdomis (rector = “straight”) is the straight muscle in the anterior wall of the abdomen, while the rectus femoris is the straight muscle in the anterior compartment of the thigh.
When a muscle has a widespread expansion over a sizable area, but then the fascicles come to a single, common attachment point, the muscle is called convergent . The attachment point for a convergent muscle could be a tendon, an aponeurosis (a flat, broad tendon), or a raphe (a very slender tendon). The large muscle on the chest, the pectoralis major, is an example of a convergent muscle because it converges on the greater tubercle of the humerus via a tendon. The temporalis muscle of the cranium is another.
Pennate muscles (penna = “feathers”) blend into a tendon that runs through the central region of the muscle for its whole length, somewhat like the quill of a feather with the muscle arranged similar to the feathers. Due to this design, the muscle fibers in a pennate muscle can only pull at an angle, and as a result, contracting pennate muscles do not move their tendons very far. However, because a pennate muscle generally can hold more muscle fibers within it, it can produce relatively more tension for its size. There are three subtypes of pennate muscles.
In a unipennate muscle, the fascicles are located on one side of the tendon. The extensor digitorum of the forearm is an example of a unipennate muscle. A bipennate muscle has fascicles on both sides of the tendon. In some pennate muscles, the muscle fibers wrap around the tendon, sometimes forming individual fascicles in the process. This arrangement is referred to as multipennate . A common example is the deltoid muscle of the shoulder, which covers the shoulder but has a single tendon that inserts on the deltoid tuberosity of the humerus.
Because of fascicles, a portion of a multipennate muscle like the deltoid can be stimulated by the nervous system to change the direction of the pull. For example, when the deltoid muscle contracts, the arm abducts (moves away from midline in the sagittal plane), but when only the anterior fascicle is stimulated, the arm will abduct and flex (move anteriorly at the shoulder joint).
Skeletal muscles do not work by themselves. Muscles are arranged in pairs based on their functions. For muscles attached to the bones of the skeleton, the connection determines the force, speed, and range of movement. These characteristics depend on each other and can explain the general organization of the muscular and skeletal systems.
The skeleton and muscles act together to move the body. Have you ever used the back of a hammer to remove a nail from wood? The handle acts as a lever and the head of the hammer acts as a fulcrum, the fixed point that the force is applied to when you pull back or push down on the handle. The effort applied to this system is the pulling or pushing on the handle to remove the nail, which is the load, or “resistance” to the movement of the handle in the system. Our musculoskeletal system works in a similar manner, with bones being stiff levers and the articular endings of the bones—encased in synovial joints—acting as fulcrums. The load would be an object being lifted or any resistance to a movement (your head is a load when you are lifting it), and the effort, or applied force, comes from contracting skeletal muscle.
Skeletal muscles each have an origin and an insertion. The end of the muscle that attaches to the bone being pulled is called the muscle’s insertion and the end of the muscle attached to a fixed, or stabilized, bone is called the origin. The muscle primarily responsible for a movement is called the prime mover, and muscles that assist in this action are called synergists. A synergist that makes the insertion site more stable is called a fixator. Meanwhile, a muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. Several factors contribute to the force generated by a skeletal muscle. One is the arrangement of the fascicles in the skeletal muscle. Fascicles can be parallel, circular, convergent, pennate, fusiform, or triangular. Each arrangement has its own range of motion and ability to do work.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?