| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The continuity of life from one cell to another has its foundation in the reproduction of cells by way of the cell cycle. The cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events that describes the stages of a cell’s life from the division of a single parent cell to the production of two new daughter cells. The mechanisms involved in the cell cycle are highly regulated.
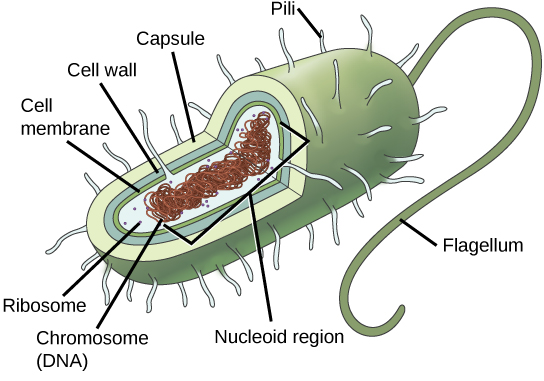
Before discussing the steps a cell must undertake to replicate, a deeper understanding of the structure and function of a cell’s genetic information is necessary. A cell’s DNA, packaged as a double-stranded DNA molecule, is called its genome . In prokaryotes, the genome is composed of a single, double-stranded DNA molecule in the form of a loop or circle ( [link] ). The region in the cell containing this genetic material is called a nucleoid. Some prokaryotes also have smaller loops of DNA called plasmids that are not essential for normal growth. Bacteria can exchange these plasmids with other bacteria, sometimes receiving beneficial new genes that the recipient can add to their chromosomal DNA. Antibiotic resistance is one trait that often spreads through a bacterial colony through plasmid exchange.
In eukaryotes, the genome consists of several double-stranded linear DNA molecules ( [link] ). Each species of eukaryotes has a characteristic number of chromosomes in the nuclei of its cells. Human body cells have 46 chromosomes, while human gametes (sperm or eggs) have 23 chromosomes each. A typical body cell, or somatic cell, contains two matched sets of chromosomes, a configuration known as diploid . The letter n is used to represent a single set of chromosomes; therefore, a diploid organism is designated 2 n . Human cells that contain one set of chromosomes are called gametes, or sex cells; these are eggs and sperm, and are designated 1n , or haploid .
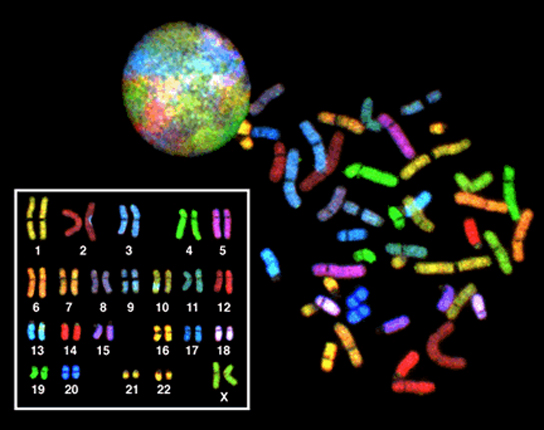
Matched pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism are called homologous (“same knowledge”) chromosomes . Homologous chromosomes are the same length and have specific nucleotide segments called genes in exactly the same location, or locus . Genes, the functional units of chromosomes, determine specific characteristics by coding for specific proteins. Traits are the variations of those characteristics. For example, hair color is a characteristic with traits that are blonde, brown, or black.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Cell biology' conversation and receive update notifications?