| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We only have to look as far as the nearest bathroom to find an example of an image formed by a mirror. Images in flat mirrors are the same size as the object and are located behind the mirror. Like lenses, mirrors can form a variety of images. For example, dental mirrors may produce a magnified image, just as makeup mirrors do. Security mirrors in shops, on the other hand, form images that are smaller than the object. We will use the law of reflection to understand how mirrors form images, and we will find that mirror images are analogous to those formed by lenses.
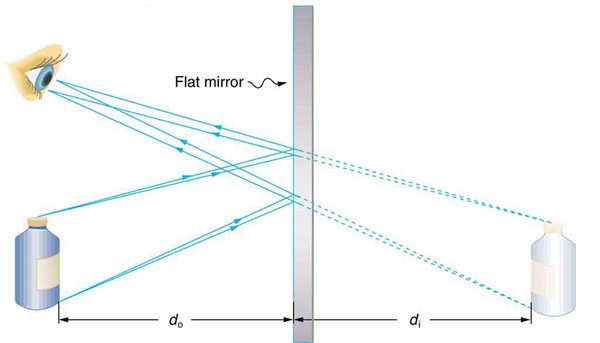
[link] helps illustrate how a flat mirror forms an image. Two rays are shown emerging from the same point, striking the mirror, and being reflected into the observer’s eye. The rays can diverge slightly, and both still get into the eye. If the rays are extrapolated backward, they seem to originate from a common point behind the mirror, locating the image. (The paths of the reflected rays into the eye are the same as if they had come directly from that point behind the mirror.) Using the law of reflection—the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence—we can see that the image and object are the same distance from the mirror. This is a virtual image, since it cannot be projected—the rays only appear to originate from a common point behind the mirror. Obviously, if you walk behind the mirror, you cannot see the image, since the rays do not go there. But in front of the mirror, the rays behave exactly as if they had come from behind the mirror, so that is where the image is situated.
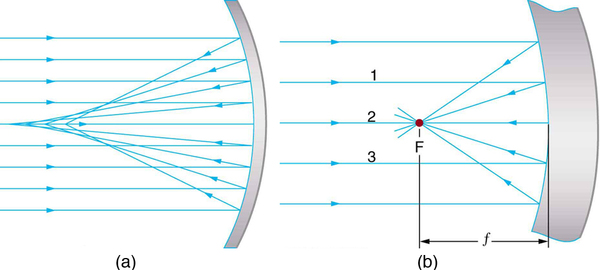
Now let us consider the focal length of a mirror—for example, the concave spherical mirrors in [link] . Rays of light that strike the surface follow the law of reflection. For a mirror that is large compared with its radius of curvature, as in [link] (a), we see that the reflected rays do not cross at the same point, and the mirror does not have a well-defined focal point. If the mirror had the shape of a parabola, the rays would all cross at a single point, and the mirror would have a well-defined focal point. But parabolic mirrors are much more expensive to make than spherical mirrors. The solution is to use a mirror that is small compared with its radius of curvature, as shown in [link] (b). (This is the mirror equivalent of the thin lens approximation.) To a very good approximation, this mirror has a well-defined focal point at F that is the focal distance from the center of the mirror. The focal length of a concave mirror is positive, since it is a converging mirror.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics subject knowledge enhancement course (ske)' conversation and receive update notifications?