| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
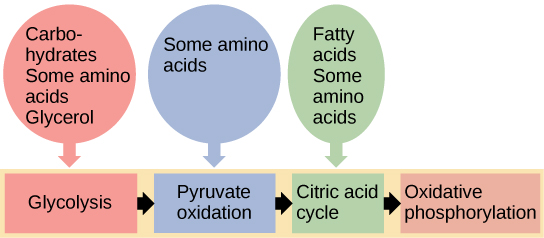
Triglycerides are a form of long-term energy storage in animals. Triglycerides are made of glycerol and three fatty acids. Animals can make most of the fatty acids they need. Triglycerides can be both made and broken down through parts of the glucose catabolism pathways. Glycerol can be phosphorylated to glycerol-3-phosphate, which continues through glycolysis. Fatty acids are catabolized in a process called beta-oxidation that takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria and converts their fatty acid chains into two carbon units of acetyl groups. The acetyl groups are picked up by CoA to form acetyl CoA that proceeds into the citric acid cycle.
An early form of photosynthesis developed that harnessed the sun’s energy using water as a source of hydrogen atoms, but this pathway did not produce free oxygen (anoxygenic photosynthesis). (Early photosynthesis did not produce free oxygen because it did not use water as the source of hydrogen ions; instead, it used materials like hydrogen sulfide and consequently produced sulfur). It is thought that glycolysis developed at this time and could take advantage of the simple sugars being produced, but these reactions were unable to fully extract the energy stored in the carbohydrates. The development of glycolysis probably predated the evolution of photosynthesis, as it was well suited to extract energy from materials spontaneously accumulating in the “primeval soup.” A later form of photosynthesis used water as a source of electrons and hydrogen, and generated free oxygen. Over time, the atmosphere became oxygenated, but not before the oxygen released oxidized metals in the ocean and created a “rust” layer in the sediment, permitting the dating of the rise of the first oxygenic photosynthesizers. Living things adapted to exploit this new atmosphere that allowed aerobic respiration as we know it to evolve. When the full process of oxygenic photosynthesis developed and the atmosphere became oxygenated, cells were finally able to use the oxygen expelled by photosynthesis to extract considerably more energy from the sugar molecules using the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
The breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids connect with the pathways of glucose catabolism. The simple sugars are galactose, fructose, glycogen, and pentose. These are catabolized during glycolysis. The amino acids from proteins connect with glucose catabolism through pyruvate, acetyl CoA, and components of the citric acid cycle. Cholesterol synthesis starts with acetyl groups, and the components of triglycerides come from glycerol-3-phosphate from glycolysis and acetyl groups produced in the mitochondria from pyruvate.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Ap biology - part 1: the cell' conversation and receive update notifications?