| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To move an object, referred to as load, the sarcomeres in the muscle fibers of the skeletal muscle must shorten. The force generated by the contraction of the muscle (or shortening of the sarcomeres) is called muscle tension . However, muscle tension also is generated when the muscle is contracting against a load that does not move, resulting in two main types of skeletal muscle contractions: isotonic contractions and isometric contractions.
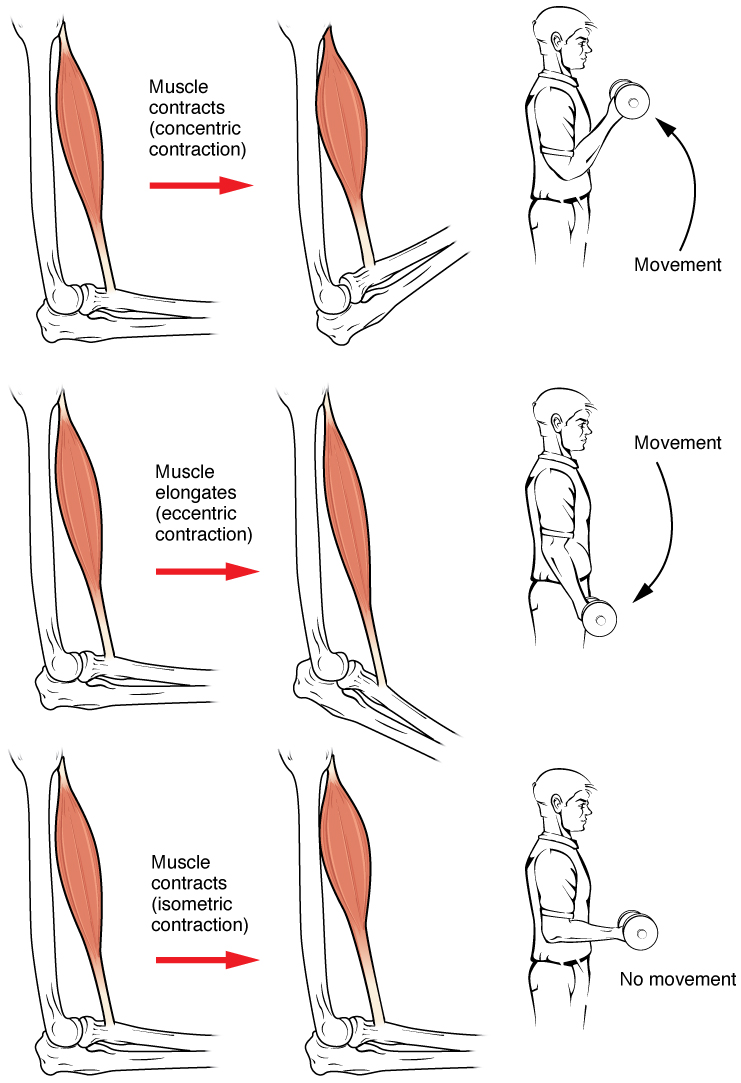
In isotonic contractions , where the tension in the muscle stays constant, a load is moved as the length of the muscle changes (shortens). There are two types of isotonic contractions: concentric and eccentric. A concentric contraction involves the muscle shortening to move a load. An example of this is the biceps brachii muscle contracting when a hand weight is brought upward with increasing muscle tension. As the biceps brachii contract, the angle of the elbow joint decreases as the forearm is brought toward the body. Here, the biceps brachii contracts as sarcomeres in its muscle fibers are shortening and cross-bridges form; the myosin heads pull the actin. An eccentric contraction occurs as the muscle tension diminishes and the muscle lengthens. In this case, the hand weight is lowered in a slow and controlled manner as the amount of cross-bridges being activated by nervous system stimulation decreases. In this case, as tension is released from the biceps brachii, the angle of the elbow joint increases. Eccentric contractions are also used for movement and balance of the body.
An isometric contraction occurs as the muscle produces tension without changing the angle of a skeletal joint. Isometric contractions involve sarcomere shortening and increasing muscle tension, but do not move a load, as the force produced cannot overcome the resistance provided by the load. For example, if one attempts to lift a hand weight that is too heavy, there will be sarcomere activation and shortening to a point, and ever-increasing muscle tension, but no change in the angle of the elbow joint. In everyday living, isometric contractions are active in maintaining posture and maintaining bone and joint stability. However, holding your head in an upright position occurs not because the muscles cannot move the head, but because the goal is to remain stationary and not produce movement. Most actions of the body are the result of a combination of isotonic and isometric contractions working together to produce a wide range of outcomes ( [link] ).
All of these muscle activities are under the exquisite control of the nervous system. Neural control regulates concentric, eccentric and isometric contractions, muscle fiber recruitment, and muscle tone. A crucial aspect of nervous system control of skeletal muscles is the role of motor units.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: support and movement' conversation and receive update notifications?