| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
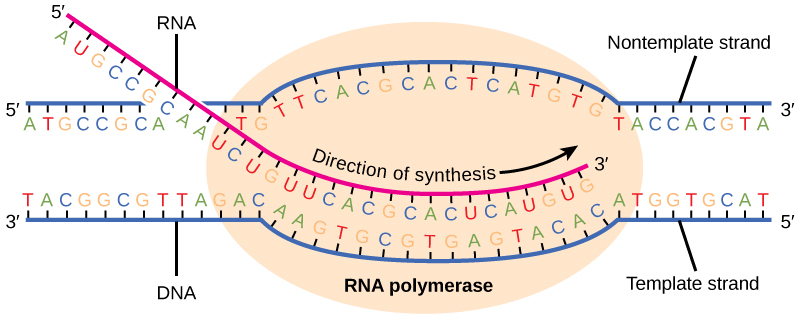
Once a gene is transcribed, the prokaryotic polymerase needs to be instructed to dissociate from the DNA template and liberate the newly made mRNA. Depending on the gene being transcribed, there are two kinds of termination signals, but both involve repeated nucleotide sequences in the DNA template that result in RNA polymerase stalling, leaving the DNA template, and freeing the mRNA transcript.
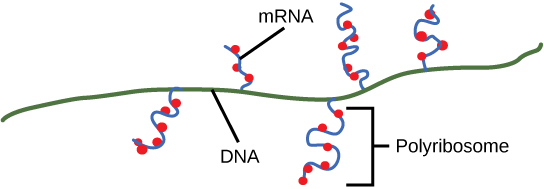
On termination, the process of transcription is complete. In a prokaryotic cell, by the time termination occurs, the transcript would already have been used to partially synthesize numerous copies of the encoded protein because these processes can occur concurrently using multiple ribosomes (polyribosomes) ( [link] ). In contrast, the presence of a nucleus in eukaryotic cells precludes simultaneous transcription and translation.
The newly transcribed eukaryotic mRNAs must undergo several processing steps before they can be transferred from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and translated into a protein. The additional steps involved in eukaryotic mRNA maturation create a molecule that is much more stable than a prokaryotic mRNA. For example, eukaryotic mRNAs last for several hours, whereas the typical prokaryotic mRNA lasts no more than five seconds.
The mRNA transcript is first coated in RNA-stabilizing proteins to prevent it from degrading while it is processed and exported out of the nucleus. This occurs while the pre-mRNA still is being synthesized by adding a special nucleotide “cap” to the 5' end of the growing transcript. In addition to preventing degradation, factors involved in protein synthesis recognize the cap to help initiate translation by ribosomes.
Once elongation is complete, an enzyme then adds a string of approximately 200 adenine residues to the 3' end, called the poly-A tail. This modification further protects the pre-mRNA from degradation and signals to cellular factors that the transcript needs to be exported to the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic genes are composed of protein-coding sequences called exons ( ex- on signifies that they are ex pressed) and int ervening sequences called introns ( int- ron denotes their int ervening role). Introns are removed from the pre-mRNA during processing. Intron sequences in mRNA do not encode functional proteins. It is essential that all of a pre-mRNA’s introns be completely and precisely removed before protein synthesis so that the exons join together to code for the correct amino acids. If the process errs by even a single nucleotide, the sequence of the rejoined exons would be shifted, and the resulting protein would be nonfunctional. The process of removing introns and reconnecting exons is called splicing ( [link] ). Introns are removed and degraded while the pre-mRNA is still in the nucleus.
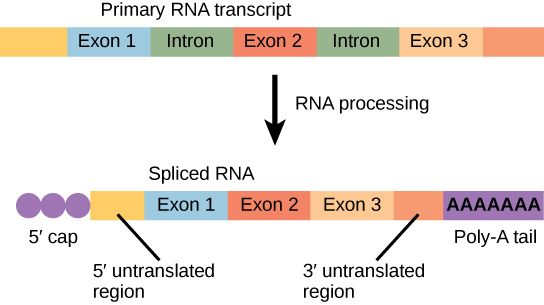
In prokaryotes, mRNA synthesis is initiated at a promoter sequence on the DNA template. Elongation synthesizes new mRNA. Termination liberates the mRNA and occurs by mechanisms that stall the RNA polymerase and cause it to fall off the DNA template. Newly transcribed eukaryotic mRNAs are modified with a cap and a poly-A tail. These structures protect the mature mRNA from degradation and help export it from the nucleus. Eukaryotic mRNAs also undergo splicing, in which introns are removed and exons are reconnected with single-nucleotide accuracy. Only finished mRNAs are exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural history supplemental' conversation and receive update notifications?