| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Why is the index of refraction always greater than or equal to 1?
Does the fact that the light flash from lightning reaches you before its sound prove that the speed of light is extremely large or simply that it is greater than the speed of sound? Discuss how you could use this effect to get an estimate of the speed of light.
Will light change direction toward or away from the perpendicular when it goes from air to water? Water to glass? Glass to air?
Explain why an object in water always appears to be at a depth shallower than it actually is? Why do people sometimes sustain neck and spinal injuries when diving into unfamiliar ponds or waters?
Explain why a person’s legs appear very short when wading in a pool. Justify your explanation with a ray diagram showing the path of rays from the feet to the eye of an observer who is out of the water.
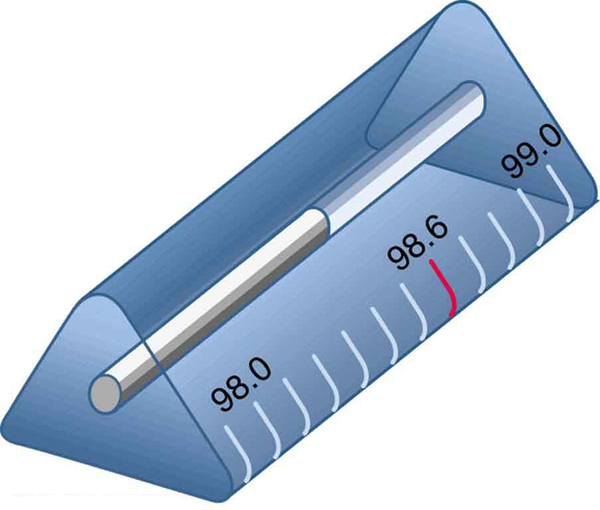
Why is the front surface of a thermometer curved as shown?
Suppose light were incident from air onto a material that had a negative index of refraction, say –1.3; where does the refracted light ray go?
What is the speed of light in water? In glycerine?
in water
in glycerine
What is the speed of light in air? In crown glass?
Calculate the index of refraction for a medium in which the speed of light is , and identify the most likely substance based on [link] .
, polystyrene
In what substance in [link] is the speed of light ?
There was a major collision of an asteroid with the Moon in medieval times. It was described by monks at Canterbury Cathedral in England as a red glow on and around the Moon. How long after the asteroid hit the Moon, which is away, would the light first arrive on Earth?
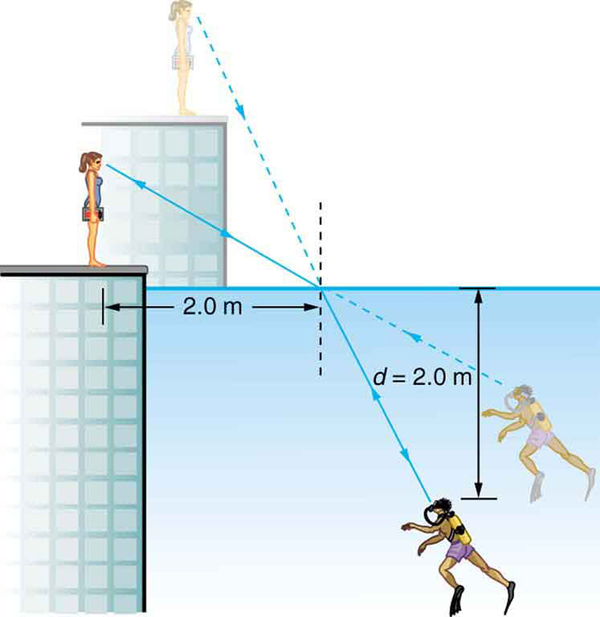
A scuba diver training in a pool looks at his instructor as shown in [link] . What angle does the ray from the instructor’s face make with the perpendicular to the water at the point where the ray enters? The angle between the ray in the water and the perpendicular to the water is .
Components of some computers communicate with each other through optical fibers having an index of refraction . What time in nanoseconds is required for a signal to travel 0.200 m through such a fiber?
(a) Using information in [link] , find the height of the instructor’s head above the water, noting that you will first have to calculate the angle of incidence. (b) Find the apparent depth of the diver’s head below water as seen by the instructor.
Suppose you have an unknown clear substance immersed in water, and you wish to identify it by finding its index of refraction. You arrange to have a beam of light enter it at an angle of , and you observe the angle of refraction to be . What is the index of refraction of the substance and its likely identity?
, fused quartz
On the Moon’s surface, lunar astronauts placed a corner reflector, off which a laser beam is periodically reflected. The distance to the Moon is calculated from the round-trip time. What percent correction is needed to account for the delay in time due to the slowing of light in Earth’s atmosphere? Assume the distance to the Moon is precisely , and Earth’s atmosphere (which varies in density with altitude) is equivalent to a layer 30.0 km thick with a constant index of refraction .
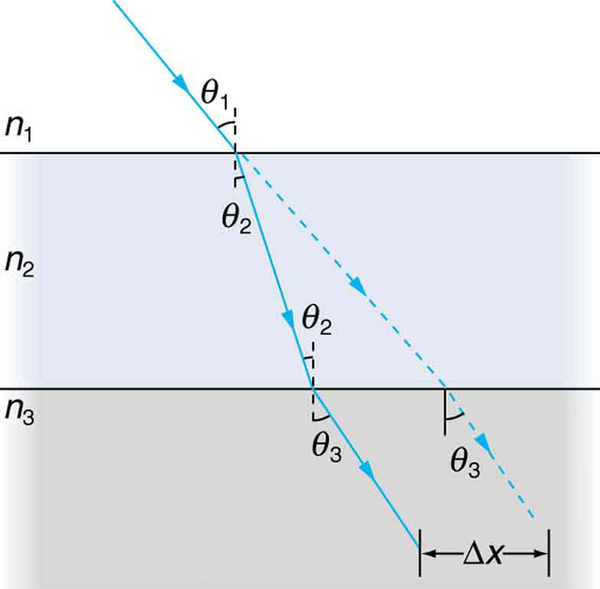
Suppose [link] represents a ray of light going from air through crown glass into water, such as going into a fish tank. Calculate the amount the ray is displaced by the glass ( ), given that the incident angle is and the glass is 1.00 cm thick.
[link] shows a ray of light passing from one medium into a second and then a third. Show that
is the same as it would be if the second medium were not present (provided total internal reflection does not occur).
Unreasonable Results
Suppose light travels from water to another substance, with an angle of incidence of and an angle of refraction of . (a) What is the index of refraction of the other substance? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which assumptions are unreasonable or inconsistent?
(a) 0.898
(b) Can’t have since this would imply a speed greater than .
(c) Refracted angle is too big relative to the angle of incidence.
Construct Your Own Problem
Consider sunlight entering the Earth’s atmosphere at sunrise and sunset—that is, at a incident angle. Taking the boundary between nearly empty space and the atmosphere to be sudden, calculate the angle of refraction for sunlight. This lengthens the time the Sun appears to be above the horizon, both at sunrise and sunset. Now construct a problem in which you determine the angle of refraction for different models of the atmosphere, such as various layers of varying density. Your instructor may wish to guide you on the level of complexity to consider and on how the index of refraction varies with air density.
Unreasonable Results
Light traveling from water to a gemstone strikes the surface at an angle of and has an angle of refraction of . (a) What is the speed of light in the gemstone? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which assumptions are unreasonable or inconsistent?
(a)
(b) Speed of light too slow, since index is much greater than that of diamond.
(c) Angle of refraction is unreasonable relative to the angle of incidence.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics subject knowledge enhancement course (ske)' conversation and receive update notifications?