| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Gametogenesis, the production of sperm and eggs, involves the process of meiosis. During meiosis, two nuclear divisions separate the paired chromosomes in the nucleus and then separate the chromatids that were made during an earlier stage of the cell’s life cycle. Meiosis and its associated cell divisions produces haploid cells with half of each pair of chromosomes normally found in diploid cells. The production of sperm is called spermatogenesis and the production of eggs is called oogenesis .
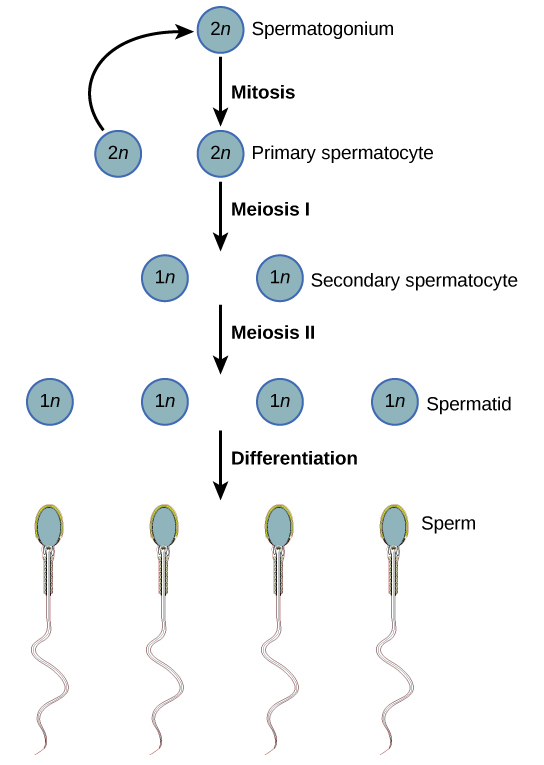
Spermatogenesis occurs in the wall of the seminiferous tubules, with the most primitive cells at the periphery of the tube and the most mature sperm at the lumen of the tube ( [link] ). Immediately under the capsule of the tubule are diploid, undifferentiated cells. These stem cells, each called a spermatogonium (pl. spermatogonia), go through mitosis to produce one cell that remains as a stem cell and a second cell called a primary spermatocyte that will undergo meiosis to produce sperm.
The diploid primary spermatocyte goes through meiosis I to produce two haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes. Each secondary spermatocyte divides after meiosis II to produce two cells called spermatids. The spermatids eventually reach the lumen of the tubule and grow a flagellum, becoming sperm cells. Four sperm result from each primary spermatocyte that goes through meiosis.
Visit this site to see the process of spermatogenesis.
Oogenesis occurs in the outermost layers of the ovaries. As with sperm production, oogenesis starts with a germ cell. In oogenesis, this germ cell is called an oogonium and forms during the embryological development of the individual. The oogonium undergoes mitosis to produce about one to two million oocytes by the time of birth.
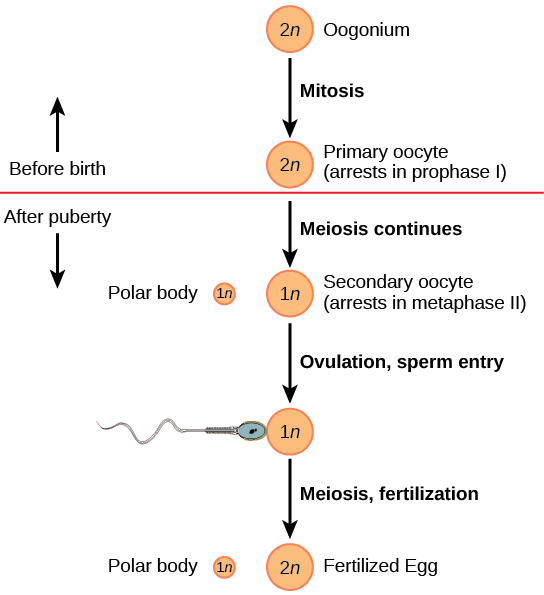
The primary oocytes begin meiosis before birth ( [link] ). However, the meiotic division is arrested in its progress in the first prophase stage. At the time of birth, all future eggs are in prophase I. This situation is in contrast with the male reproductive system in which sperm are produced continuously throughout the life of the individual. Starting at adolescence, anterior pituitary hormones cause the development of a few follicles in an ovary each month. This results in a primary oocyte finishing the first meiotic division. The cell divides unequally, with most of the cytoplasm and organelles going to one cell, called a secondary oocyte, and only one set of chromosomes and a small amount of cytoplasm going to the other cell. This second cell is called a polar body and usually dies. Cell division is again arrested, this time at metaphase II. At ovulation, this secondary oocyte is released and travels toward the uterus through the oviduct. If the secondary oocyte is fertilized, the cell continues through meiosis II, producing a second polar body and haploid egg, which fuses with the haploid sperm to form a fertilized egg (zygote) containing all 46 chromosomes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Concepts of biology_biol 101 dacc' conversation and receive update notifications?