| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Proteins have different shapes and molecular weights; some proteins are globular in shape whereas others are fibrous in nature. For example, hemoglobin is a globular protein, but collagen, found in our skin, is a fibrous protein. Protein shape is critical to its function. Changes in temperature, pH, and exposure to chemicals may lead to permanent changes in the shape of the protein, leading to a loss of function or denaturation (to be discussed in more detail later). All proteins are made up of different arrangements of the same 20 kinds of amino acids.
Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group (–NH 2 ), a carboxyl group (–COOH), and a hydrogen atom. Every amino acid also has another variable atom or group of atoms bonded to the central carbon atom known as the R group. The R group is the only difference in structure between the 20 amino acids; otherwise, the amino acids are identical ( [link] ).
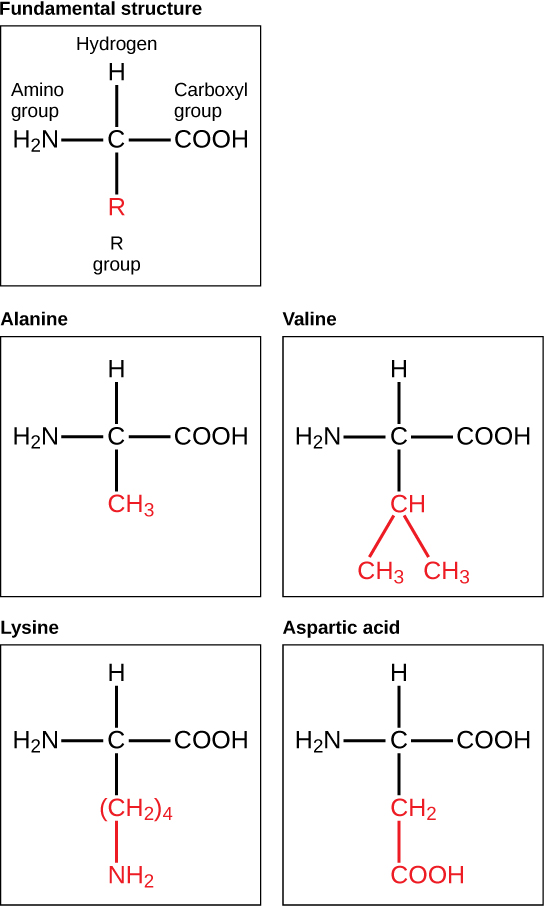
The chemical nature of the R group determines the chemical nature of the amino acid within its protein (that is, whether it is acidic, basic, polar, or nonpolar).
The sequence and number of amino acids ultimately determine a protein’s shape, size, and function. Each amino acid is attached to another amino acid by a covalent bond, known as a peptide bond, which is formed by a dehydration reaction. The carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of a second amino acid combine, releasing a water molecule. The resulting bond is the peptide bond.
The products formed by such a linkage are called polypeptides. While the terms polypeptide and protein are sometimes used interchangeably, a polypeptide is technically a polymer of amino acids, whereas the term protein is used for a polypeptide or polypeptides that have combined together, have a distinct shape, and have a unique function.
For example, scientists have determined that human cytochrome c contains 104 amino acids. For each cytochrome c molecule that has been sequenced to date from different organisms, 37 of these amino acids appear in the same position in each cytochrome c. This indicates that all of these organisms are descended from a common ancestor. On comparing the human and chimpanzee protein sequences, no sequence difference was found. When human and rhesus monkey sequences were compared, a single difference was found in one amino acid. In contrast, human-to-yeast comparisons show a difference in 44 amino acids, suggesting that humans and chimpanzees have a more recent common ancestor than humans and the rhesus monkey, or humans and yeast.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wbrown dacc life science' conversation and receive update notifications?