| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
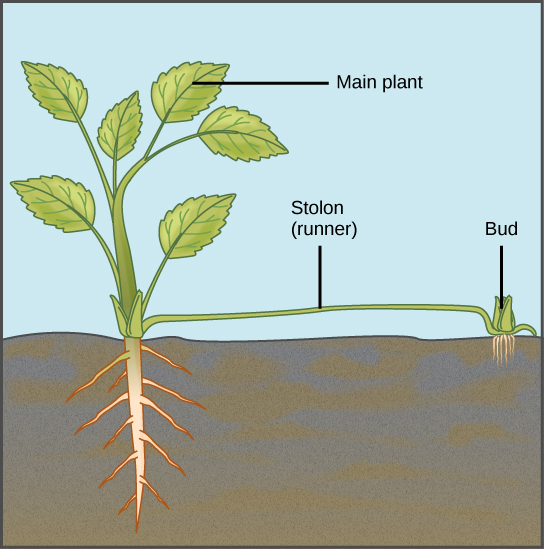
These methods are frequently employed to give rise to new, and sometimes novel, plants. They include grafting, cutting, layering, and micropropagation.
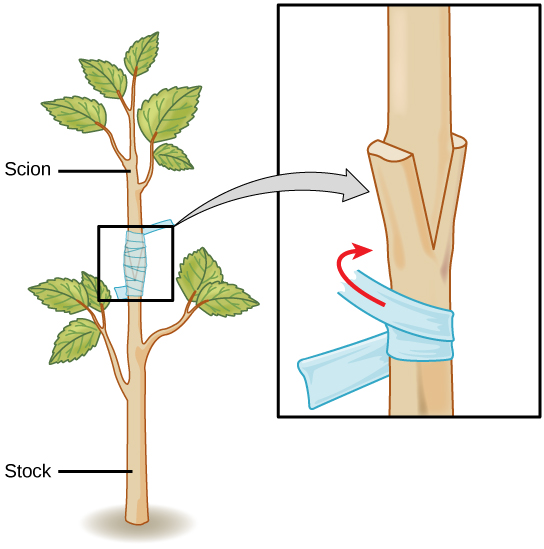
Grafting has long been used to produce novel varieties of roses, citrus species, and other plants. In grafting , two plant species are used; part of the stem of the desirable plant is grafted onto a rooted plant called the stock. The part that is grafted or attached is called the scion . Both are cut at an oblique angle (any angle other than a right angle), placed in close contact with each other, and are then held together [link] . Matching up these two surfaces as closely as possible is extremely important because these will be holding the plant together. The vascular systems of the two plants grow and fuse, forming a graft. After a period of time, the scion starts producing shoots, and eventually starts bearing flowers and fruits. Grafting is widely used in viticulture (grape growing) and the citrus industry. Scions capable of producing a particular fruit variety are grated onto root stock with specific resistance to disease.
Plants such as coleus and money plant are propagated through stem cuttings , where a portion of the stem containing nodes and internodes is placed in moist soil and allowed to root. In some species, stems can start producing a root even when placed only in water. For example, leaves of the African violet will root if kept in water undisturbed for several weeks.
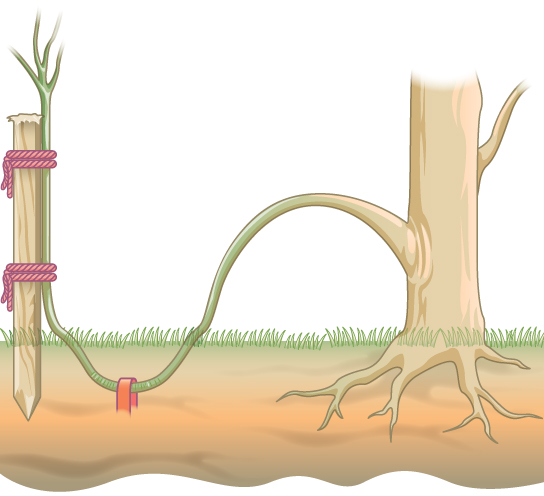
Layering is a method in which a stem attached to the plant is bent and covered with soil. Young stems that can be bent easily without any injury are preferred. Jasmine and bougainvillea (paper flower) can be propagated this way [link] . In some plants, a modified form of layering known as air layering is employed. A portion of the bark or outermost covering of the stem is removed and covered with moss, which is then taped. Some gardeners also apply rooting hormone. After some time, roots will appear, and this portion of the plant can be removed and transplanted into a separate pot.
Micropropagation (also called plant tissue culture) is a method of propagating a large number of plants from a single plant in a short time under laboratory conditions [link] . This method allows propagation of rare, endangered species that may be difficult to grow under natural conditions, are economically important, or are in demand as disease-free plants.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology 1308 bonus credit chapters--from openstax "biology"' conversation and receive update notifications?