| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
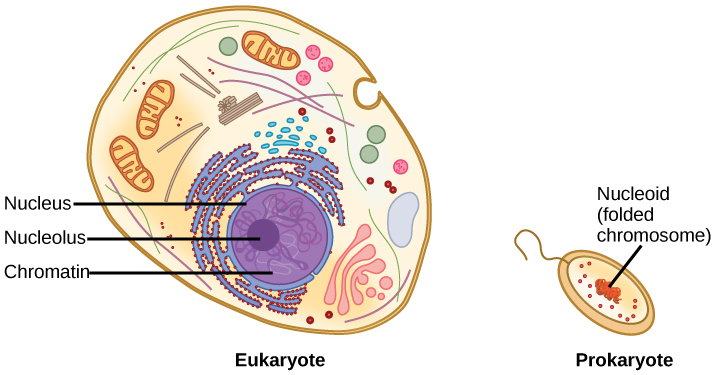
The size of the genome in one of the most well-studied prokaryotes, Escherichia coli, is 4.6 million base pairs, which would extend a distance of about 1.6 mm if stretched out. So how does this fit inside a small bacterial cell? The DNA is twisted beyond the double helix in what is known as supercoiling. Some proteins are known to be involved in the supercoiling; other proteins and enzymes help in maintaining the supercoiled structure.
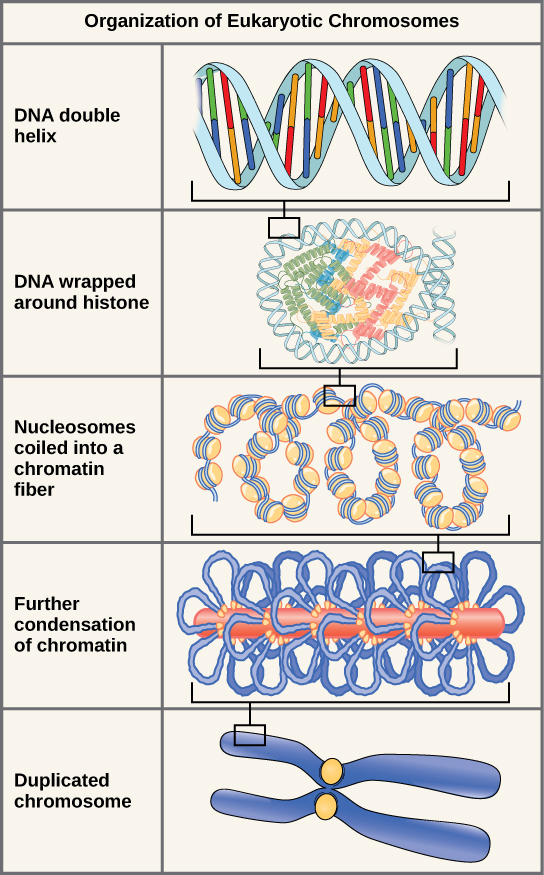
Eukaryotes, whose chromosomes each consist of a linear DNA molecule, employ a different type of packing strategy to fit their DNA inside the nucleus ( [link] ). At the most basic level, DNA is wrapped around proteins known as histones to form structures called nucleosomes. The DNA is wrapped tightly around the histone core. This nucleosome is linked to the next one by a short strand of DNA that is free of histones. This is also known as the “beads on a string” structure; the nucleosomes are the “beads” and the short lengths of DNA between them are the “string.” The nucleosomes, with their DNA coiled around them, stack compactly onto each other to form a 30-nm–wide fiber. This fiber is further coiled into a thicker and more compact structure. At the metaphase stage of mitosis, when the chromosomes are lined up in the center of the cell, the chromosomes are at their most compacted. They are approximately 700 nm in width, and are found in association with scaffold proteins.
In interphase, the phase of the cell cycle between mitoses at which the chromosomes are decondensed, eukaryotic chromosomes have two distinct regions that can be distinguished by staining. There is a tightly packaged region that stains darkly, and a less dense region. The darkly staining regions usually contain genes that are not active, and are found in the regions of the centromere and telomeres. The lightly staining regions usually contain genes that are active, with DNA packaged around nucleosomes but not further compacted.
Watch this animation of DNA packaging.
The model of the double-helix structure of DNA was proposed by Watson and Crick. The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands. Each strand is composed of nucleotides bonded together covalently between the phosphate group of one and the deoxyribose sugar of the next. From this backbone extend the bases. The bases of one strand bond to the bases of the second strand with hydrogen bonds. Adenine always bonds with thymine, and cytosine always bonds with guanine. The bonding causes the two strands to spiral around each other in a shape called a double helix. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a second nucleic acid found in cells. RNA is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides. It also differs from DNA in that it contains the sugar ribose, rather than deoxyribose, and the nucleotide uracil rather than thymine. Various RNA molecules function in the process of forming proteins from the genetic code in DNA.
Prokaryotes contain a single, double-stranded circular chromosome. Eukaryotes contain double-stranded linear DNA molecules packaged into chromosomes. The DNA helix is wrapped around proteins to form nucleosomes. The protein coils are further coiled, and during mitosis and meiosis, the chromosomes become even more greatly coiled to facilitate their movement. Chromosomes have two distinct regions which can be distinguished by staining, reflecting different degrees of packaging and determined by whether the DNA in a region is being expressed (euchromatin) or not (heterochromatin).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural history supplemental' conversation and receive update notifications?